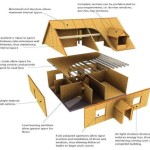
Multi Family House Plans are architectural drawings that outline the design and layout of a building intended to house multiple families or units under one roof. These plans typically include specifications for the number of units, the size and configuration of each unit, and the shared common areas within the building.
Multi Family House Plans are essential for developers and architects designing apartment buildings, townhouses, and other residential structures that accommodate multiple families. They ensure that the building meets building codes, provides adequate living space for tenants, and optimizes the use of available land or space.
In the following sections, we will explore the key elements to consider when creating Multi Family House Plans, discuss the different types of multi family housing designs, and provide tips for designing efficient and livable multi family homes.
When designing Multi Family House Plans, there are several important points to consider:
- Number of units
- Unit size and configuration
- Shared common areas
- Building codes
- Tenant needs
- Land use optimization
- Energy efficiency
- Accessibility
By carefully considering these factors, architects and developers can create Multi Family House Plans that meet the needs of tenants, comply with regulations, and make efficient use of space and resources.
Number of units
The number of units in a multi family house plan is a crucial factor to consider, as it impacts the overall size, design, and cost of the building. The number of units can range from two to several dozen, depending on the type of multi family housing being built and the available land or space.
- Small multi family buildings typically have two to four units, and are often designed as duplexes, triplexes, or fourplexes. These buildings are often suitable for small families or individuals seeking affordable housing options.
- Medium multi family buildings typically have five to ten units, and may be designed as townhouses, garden apartments, or small apartment buildings. These buildings offer a good balance between privacy and shared amenities, and are popular with families and young professionals.
- Large multi family buildings typically have more than ten units, and may be designed as high-rise apartments, luxury condominiums, or mixed-use developments. These buildings offer a wider range of amenities and unit types, and are often located in urban areas with high demand for housing.
- Mixed-use developments combine residential units with commercial or retail space on the ground floor. These developments offer convenience and walkability for residents, and can help to revitalize urban neighborhoods.
When determining the number of units for a multi family house plan, developers and architects must consider factors such as market demand, land availability, and zoning regulations. They must also ensure that the building design provides adequate living space and privacy for tenants, while also optimizing the use of available space and resources.
Unit size and configuration
The size and configuration of units in a multi family house plan are critical factors that impact the livability, marketability, and overall success of the development. When designing unit layouts, architects and developers must consider a range of factors, including:
- Tenant needs: The size and configuration of units should meet the needs of the target tenant base. For example, a building designed for families may require larger units with more bedrooms and bathrooms, while a building designed for young professionals may require smaller, more efficient units.
- Market demand: Developers must research the local market to determine the types and sizes of units that are in high demand. This information can be used to inform the design of the building and ensure that the units are appealing to potential tenants.
- Building codes: Local building codes may impose minimum requirements for unit size and configuration. These codes are designed to ensure that units are habitable and meet certain safety standards.
- Land use optimization: The size and configuration of units can impact the overall efficiency of the building design. Architects must carefully plan the layout of units to maximize the use of available space and minimize wasted areas.
In addition to these factors, architects and developers must also consider the following when designing unit layouts:
- Privacy: Units should be designed to provide tenants with a sense of privacy, even in close proximity to other units. This can be achieved through the use of soundproofing materials, separate entrances, and thoughtful placement of windows and balconies.
- Natural light: Units should be designed to maximize natural light, which can improve tenant well-being and reduce energy costs. This can be achieved through the use of large windows, skylights, and open floor plans.
- Storage space: Units should include adequate storage space to meet the needs of tenants. This can be achieved through the use of closets, built-in shelves, and other storage solutions.
- Accessibility: Units should be designed to be accessible to all tenants, including those with disabilities. This can be achieved through the use of ramps, elevators, and accessible features in bathrooms and kitchens.
By carefully considering all of these factors, architects and developers can create Multi Family House Plans that offer tenants comfortable, livable, and marketable units.
Shared common areas
Shared common areas in multi family house plans are spaces that are accessible to all tenants in the building. These areas can include lobbies, hallways, elevators, stairwells, laundry facilities, and outdoor amenities such as courtyards, patios, and swimming pools. Shared common areas play an important role in creating a sense of community and providing tenants with a variety of spaces to socialize, relax, and pursue their interests.
When designing shared common areas, architects and developers must consider a range of factors, including:
- Tenant needs: The design of shared common areas should meet the needs of the target tenant base. For example, a building designed for families may require larger common areas with more amenities, while a building designed for young professionals may require smaller, more efficient common areas.
- Building size and type: The size and type of building will impact the design of shared common areas. Larger buildings will typically have more extensive common areas, while smaller buildings may have more limited common areas.
- Budget: The budget for the building will impact the design and finishes of shared common areas. Architects and developers must carefully plan the use of materials and finishes to create common areas that are both attractive and cost-effective.
- Building codes: Local building codes may impose minimum requirements for the size and accessibility of shared common areas. These codes are designed to ensure that common areas are safe and accessible to all tenants.
In addition to these factors, architects and developers must also consider the following when designing shared common areas:
- Flexibility: Shared common areas should be designed to be flexible and adaptable to meet the changing needs of tenants. For example, a common area could be designed to serve as a gathering space, a study area, or a fitness center.
- Durability: Shared common areas should be designed to be durable and easy to maintain. This is especially important for areas that receive a lot of foot traffic, such as lobbies and hallways.
- Aesthetics: Shared common areas should be designed to be aesthetically pleasing and inviting. This can be achieved through the use of attractive materials, finishes, and lighting.
- Security: Shared common areas should be designed to be secure and well-lit. This can help to deter crime and create a sense of safety for tenants.
By carefully considering all of these factors, architects and developers can create Multi Family House Plans that offer tenants attractive, functional, and inviting shared common areas.
Building codes
Building codes are regulations that govern the design, construction, and maintenance of buildings. These codes are in place to ensure that buildings are safe, habitable, and accessible to all users. Multi family house plans must comply with all applicable building codes, which may vary depending on the jurisdiction in which the building is located.
Building codes typically address a wide range of issues, including:
- Structural safety: Building codes ensure that buildings are structurally sound and can withstand the forces of nature, such as earthquakes and high winds.
- Fire safety: Building codes require the use of fire-resistant materials and systems to help prevent the spread of fire in buildings.
- Health and sanitation: Building codes ensure that buildings have adequate ventilation, natural light, and sanitation facilities to protect the health of occupants.
- Accessibility: Building codes require that buildings are accessible to people with disabilities, including those who use wheelchairs or have other mobility impairments.
- Energy efficiency: Building codes may include requirements for energy-efficient features, such as insulation and high-efficiency appliances, to reduce energy consumption and costs.
Architects and developers must be familiar with the building codes that apply to their jurisdiction in order to design and construct multi family house plans that meet all applicable requirements. Failure to comply with building codes can result in delays, fines, or even the inability to obtain a building permit.
In addition to the general building codes that apply to all buildings, there may be specific codes that apply to multi family housing. These codes may address issues such as the number of units per building, the size and configuration of units, and the provision of shared common areas. Architects and developers must be aware of all applicable codes in order to design and construct multi family house plans that meet all requirements.
Building codes are essential for ensuring the safety, habitability, and accessibility of multi family housing. By complying with all applicable building codes, architects and developers can create multi family house plans that meet the needs of tenants and provide a safe and healthy living environment.
Tenant needs
Tenant needs are a critical factor to consider when designing Multi Family House Plans. After all, the ultimate goal of any multi family housing development is to create a space that is safe, comfortable, and appealing to tenants. By understanding and addressing the needs of tenants, architects and developers can create multi family house plans that are more likely to be successful.
One of the most important tenant needs is privacy. Tenants want to feel like they have their own private space, even if they are living in close proximity to other units. This can be achieved through the use of soundproofing materials, separate entrances, and thoughtful placement of windows and balconies.
Another important tenant need is natural light. Natural light can improve mood, boost productivity, and reduce energy costs. Architects and developers should design multi family house plans that maximize natural light in all units. This can be achieved through the use of large windows, skylights, and open floor plans.
Tenant needs also include access to shared common areas. Shared common areas provide tenants with a space to socialize, relax, and pursue their interests. These areas can include lobbies, hallways, elevators, stairwells, laundry facilities, and outdoor amenities such as courtyards, patios, and swimming pools. When designing shared common areas, architects and developers should consider the needs of the target tenant base. For example, a building designed for families may require larger common areas with more amenities, while a building designed for young professionals may require smaller, more efficient common areas.
Finally, tenants need to feel safe and secure in their homes. This can be achieved through the use of security features such as door locks, security cameras, and controlled access to the building. Architects and developers should also consider the placement of units and common areas to minimize opportunities for crime.
By understanding and addressing the needs of tenants, architects and developers can create Multi Family House Plans that are more likely to be successful. These plans will create a safe, comfortable, and appealing living environment for tenants, which will lead to higher occupancy rates and lower turnover costs.
Land use optimization
Land use optimization is an important factor to consider when designing Multi Family House Plans. The goal of land use optimization is to make the most efficient use of the available land or space while meeting the needs of the tenants. This can be achieved through careful planning and design, as well as the use of innovative building techniques.
- Vertical space utilization: One way to optimize land use is to utilize vertical space. This can be achieved through the use of multiple stories, which allows for more units to be built on a smaller footprint. Vertical space utilization can also be achieved through the use of mezzanines and lofts, which can create additional living space without increasing the overall footprint of the building.
- Compact unit design: Another way to optimize land use is to design compact units. This can be achieved through the use of efficient floor plans and space-saving features. For example, units can be designed with open floor plans, which eliminate the need for hallways and other wasted space. Units can also be designed with built-in storage, which reduces the need for separate furniture and frees up floor space.
- Shared common areas: Shared common areas can also be used to optimize land use. By providing shared amenities such as laundry facilities, fitness centers, and courtyards, architects and developers can reduce the need for these amenities in individual units. This can free up space in units for more living space or storage.
- Mixed-use developments: Mixed-use developments are another way to optimize land use. These developments combine residential units with commercial or retail space on the ground floor. This can help to revitalize urban neighborhoods and reduce the need for car travel.
By carefully considering land use optimization, architects and developers can create Multi Family House Plans that make the most efficient use of available land or space. This can lead to lower construction costs, higher occupancy rates, and a more sustainable development.
Energy efficiency
Energy efficiency is an important consideration for Multi Family House Plans. By incorporating energy-efficient features into the design of multi family buildings, architects and developers can reduce energy consumption and costs for tenants, while also reducing the environmental impact of the building. There are a number of different energy-efficient features that can be incorporated into Multi Family House Plans, including:
Insulation: Insulation is one of the most important energy-efficient features that can be incorporated into a multi family building. Insulation helps to keep the building warm in the winter and cool in the summer, which can reduce the need for heating and cooling. Insulation can be installed in the walls, ceilings, and floors of a building.
Windows and doors: Windows and doors are another important source of energy loss in a building. By installing energy-efficient windows and doors, architects and developers can reduce the amount of heat that is lost through these openings. Energy-efficient windows and doors are typically made with double or triple glazing, and they may also have a low-emissivity (Low-E) coating, which helps to reflect heat back into the building.
Appliances: The appliances that are used in a multi family building can also have a significant impact on energy consumption. By installing energy-efficient appliances, architects and developers can reduce the amount of energy that is used by tenants. Energy-efficient appliances are typically rated by their Energy Star rating, which indicates how much energy the appliance uses compared to other similar appliances.
Lighting: Lighting is another area where energy savings can be made. By installing energy-efficient lighting fixtures, architects and developers can reduce the amount of energy that is used for lighting. Energy-efficient lighting fixtures typically use LED or CFL bulbs, which are more energy-efficient than traditional incandescent bulbs.
Renewable energy sources: Renewable energy sources can also be used to reduce the energy consumption of a multi family building. Solar panels can be installed on the roof of the building to generate electricity, and wind turbines can be installed on the property to generate wind power. Renewable energy sources can help to reduce the building’s reliance on fossil fuels, which can lead to lower energy costs and a reduced environmental impact.
By incorporating energy-efficient features into the design of Multi Family House Plans, architects and developers can create buildings that are more comfortable, affordable, and sustainable for tenants.
Accessibility
Accessibility is an important consideration for Multi Family House Plans. Multi family buildings should be designed to be accessible to all people, regardless of their age, disability, or other factors. This means that buildings should be designed to provide equal access to all units, common areas, and amenities.
There are a number of different accessibility features that can be incorporated into Multi Family House Plans. These features include:
- Ramps: Ramps provide access to buildings and common areas for people who use wheelchairs or other mobility devices. Ramps should be designed with a gentle slope and a non-slip surface.
- Elevators: Elevators provide access to upper floors for people who cannot use stairs. Elevators should be large enough to accommodate wheelchairs and other mobility devices.
- Accessible entrances: Accessible entrances are designed to be easy to enter and exit for people with disabilities. Accessible entrances should be level with the ground and have wide doorways.
- Accessible units: Accessible units are designed to be accessible to people with disabilities. Accessible units may include features such as wider doorways, roll-in showers, and lever-operated faucets.
- Service animals: Multi family buildings should be designed to accommodate service animals. This means that buildings should allow tenants to have service animals in their units and in common areas.
By incorporating accessibility features into the design of Multi Family House Plans, architects and developers can create buildings that are more inclusive and welcoming to all people.
In addition to the specific accessibility features listed above, there are a number of other design considerations that can be made to improve accessibility. These considerations include:
- Universal design: Universal design is a design approach that seeks to create spaces that are accessible to all people, regardless of their age, disability, or other factors. Universal design principles can be applied to all aspects of building design, from the layout of the building to the selection of materials and finishes.
- Wayfinding: Wayfinding is the process of helping people to find their way around a building. Good wayfinding can help to improve accessibility for people with cognitive disabilities or visual impairments. Wayfinding can be improved through the use of clear signage, maps, and other wayfinding tools.
- Training: Building staff should be trained on how to assist people with disabilities. This training can help to ensure that all tenants have a positive experience in the building.
By considering accessibility in all aspects of design, architects and developers can create Multi Family House Plans that are inclusive and welcoming to all people.










Related Posts