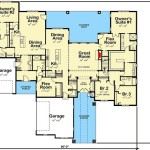
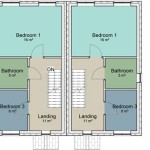
A house electrical plan is a detailed blueprint that outlines the electrical system of a residential building. It serves as a comprehensive guide for electricians during the installation, maintenance, and repair of electrical components. The plan provides a visual representation of the electrical layout, including the location of outlets, switches, lighting fixtures, and the distribution of electrical circuits throughout the house.
Electrical plans are essential for ensuring the safety and efficiency of a home’s electrical system. They help prevent electrical hazards, such as overloaded circuits, improper wiring, and faulty connections. By providing a clear and accurate representation of the electrical system, electrical plans enable electricians to work more efficiently and accurately, minimizing the risk of errors and ensuring the proper functioning of the electrical infrastructure.
In the following sections, we will delve into the details of house electrical plans, discussing their components, the importance of following electrical codes, and the benefits of having a comprehensive electrical plan in place.
A comprehensive electrical plan is essential for the safety and functionality of any house. Here are 10 important points to consider:
- Outlets and switches placement
- Lighting fixture locations
- Circuit distribution
- Electrical panel details
- Conduit and wiring routes
- Grounding and bonding
- Code compliance
- Future expansion
- Energy efficiency
- Safety features
By incorporating these elements into your electrical plan, you can ensure a safe, efficient, and up-to-date electrical system for your home.
Outlets and switches placement
The placement of outlets and switches in a house is crucial for both convenience and safety. Outlets should be placed in accessible locations where they can be easily reached without the use of extension cords. Switches should be placed at entrances to rooms and at the top and bottom of stairs.
The number of outlets and switches required in a room depends on the size of the room and its intended use. Kitchens and bathrooms typically require more outlets than other rooms, due to the presence of appliances and other electrical devices. Bedrooms and living rooms typically require a mix of outlets and switches, to accommodate lighting, electronics, and other devices.
When placing outlets and switches, it is important to consider the furniture layout and traffic flow in the room. Outlets and switches should be placed in locations where they will not be blocked by furniture or appliances. They should also be placed in locations where they will not pose a tripping hazard.
In addition to convenience and safety, the placement of outlets and switches can also affect the aesthetics of a room. Outlets and switches that are placed in inconspicuous locations can help to create a more streamlined and modern look. Outlets and switches that are placed in more visible locations can be used to add a decorative touch to a room.
By carefully considering the placement of outlets and switches, you can ensure that your home is both safe and convenient to use.
Lighting fixture locations
The placement of lighting fixtures is an important part of any house electrical plan. Lighting can affect the mood, atmosphere, and functionality of a space. When planning the location of lighting fixtures, there are several factors to consider:
- Task lighting: Task lighting is used to provide focused light for specific activities, such as reading, cooking, or working. Task lighting fixtures should be placed close to the area where the light is needed and should be adjustable to direct the light where it is most effective.
- Ambient lighting: Ambient lighting is used to provide general illumination to a space. Ambient lighting fixtures should be placed evenly throughout a room and should provide a soft, diffused light. Ambient lighting can be provided by ceiling lights, wall sconces, or table lamps.
- Accent lighting: Accent lighting is used to highlight specific features of a room, such as a painting, a piece of furniture, or an architectural detail. Accent lighting fixtures should be placed strategically to create a dramatic effect and to draw attention to the desired feature.
- Natural light: Natural light is the best source of light for any space. When planning the location of lighting fixtures, it is important to take advantage of natural light as much as possible. Place windows and skylights in areas where they will provide the most natural light and use artificial lighting to supplement natural light when necessary.
By considering these factors, you can create a lighting plan that will provide the right amount of light for your needs and that will create a comfortable and inviting atmosphere in your home.
Circuit distribution
Circuit distribution is an important part of any house electrical plan. It refers to the way in which electrical circuits are distributed throughout the house. Proper circuit distribution ensures that each circuit is properly sized and protected, and that the electrical load is evenly distributed across all circuits.
- Number of circuits: The number of circuits required in a house depends on the size of the house and the number of electrical devices that will be used. A typical house will have between 10 and 20 circuits. Each circuit should be dedicated to a specific area of the house, such as the kitchen, living room, or bedrooms.
- Circuit amperage: The amperage of a circuit is the maximum amount of current that can flow through the circuit. Circuits are typically rated for 15 amps or 20 amps. The amperage of a circuit should be based on the type of electrical devices that will be used on the circuit. For example, a circuit that will be used to power a refrigerator should be rated for 20 amps.
- Circuit protection: Each circuit should be protected by a circuit breaker or fuse. Circuit breakers and fuses are designed to trip or blow when the current on the circuit exceeds a safe level. This helps to prevent electrical fires and other hazards.
- Grounding: All electrical circuits should be properly grounded. Grounding provides a path for electrical current to flow back to the electrical panel in the event of a fault. This helps to protect people and property from electrical shock.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your house electrical plan is safe and efficient.
Electrical panel details
The electrical panel is the central point of distribution for electricity in a house. It contains circuit breakers or fuses that protect the electrical circuits from overloads and short circuits. The electrical panel also contains the main breaker or fuse, which disconnects all power to the house.
- Location:
The electrical panel should be located in a central and accessible location, such as a basement, garage, or utility room. It should be easy to reach and operate in case of an emergency. - Size:
The size of the electrical panel is determined by the number of circuits in the house. A typical house will have a 100-amp or 200-amp electrical panel. The size of the electrical panel should be adequate to handle the electrical load of the house. - Circuit breakers or fuses:
Circuit breakers or fuses are used to protect the electrical circuits from overloads and short circuits. Circuit breakers can be reset, while fuses must be replaced when they blow. It is important to use the correct size circuit breaker or fuse for each circuit. - Main breaker or fuse:
The main breaker or fuse is the largest circuit breaker or fuse in the electrical panel. It disconnects all power to the house. The main breaker or fuse should be turned off before working on any electrical circuits.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your electrical panel is safe and efficient.
Conduit and wiring routes
Conduit and wiring routes are an important part of any house electrical plan. Conduit is a metal or plastic pipe that protects electrical wires from damage. Wiring routes are the paths that the electrical wires take from the electrical panel to the outlets, switches, and other electrical devices in the house.
- Conduit types:
There are two main types of conduit: rigid conduit and flexible conduit. Rigid conduit is made of metal and is more durable than flexible conduit. Flexible conduit is made of plastic and is easier to install than rigid conduit. The type of conduit that is used for a particular application will depend on the location and the type of electrical wires that are being used. - Conduit installation:
Conduit is typically installed in walls, ceilings, and floors. It can also be installed outside of the house, but it must be protected from the elements. When installing conduit, it is important to use the proper fittings and to secure the conduit to the structure of the house. - Wiring routes:
Wiring routes should be planned carefully to avoid damage to the wires. Wires should be run in a straight line, as much as possible, and they should be secured to the structure of the house. Wires should not be run through walls or ceilings that are likely to be damaged, such as walls that are subject to moisture or that are likely to be punctured by nails or screws. - Wire types:
There are many different types of electrical wires that can be used in a house. The type of wire that is used for a particular application will depend on the amperage of the circuit and the length of the run. It is important to use the correct type of wire for each application, as using the wrong type of wire can create a fire hazard.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure that the conduit and wiring routes in your house are safe and efficient.
Grounding and bonding
Grounding and bonding are essential parts of any house electrical plan. Grounding provides a path for electrical current to flow back to the electrical panel in the event of a fault. This helps to protect people and property from electrical shock. Bonding connects all of the metal parts of an electrical system together, including the electrical panel, the electrical outlets, and the electrical appliances. This helps to ensure that all of the metal parts are at the same electrical potential, which reduces the risk of electrical shock.
- Grounding electrode system:
The grounding electrode system is the part of the electrical system that provides the path for electrical current to flow back to the electrical panel. The grounding electrode system typically consists of a metal rod or pipe that is driven into the ground. The grounding electrode system should be installed in accordance with the local electrical code. - Grounding conductors:
Grounding conductors are the wires that connect the electrical panel to the grounding electrode system. Grounding conductors should be made of bare copper or aluminum and should be sized in accordance with the local electrical code. - Bonding conductors:
Bonding conductors are the wires that connect the metal parts of an electrical system together. Bonding conductors should be made of bare copper or aluminum and should be sized in accordance with the local electrical code. - Equipment grounding:
Equipment grounding is the process of connecting the metal parts of an electrical appliance to the grounding electrode system. Equipment grounding helps to protect people from electrical shock by providing a path for electrical current to flow back to the electrical panel in the event of a fault.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your house electrical plan is safe and efficient.
Code compliance
Code compliance is an important part of any house electrical plan. Electrical codes are regulations that are designed to ensure the safety of electrical installations. By following electrical codes, you can help to prevent electrical fires, shocks, and other hazards.
There are many different electrical codes that apply to house electrical plans. These codes include the National Electrical Code (NEC), the International Electrical Code (IEC), and the local electrical code. The NEC is a set of minimum requirements for the safe installation of electrical equipment in the United States. The IEC is a set of international standards for the safe installation of electrical equipment. The local electrical code is a set of regulations that are specific to the local area. It is important to follow the local electrical code, as it may contain additional requirements that are not included in the NEC or the IEC.
When designing a house electrical plan, it is important to work with a qualified electrician who is familiar with the applicable electrical codes. A qualified electrician can help you to design a safe and code-compliant electrical plan.
There are many benefits to following electrical codes. By following electrical codes, you can help to ensure the safety of your family and home. You can also help to avoid costly repairs and insurance claims. In some cases, following electrical codes may even be required by law.
By following these guidelines, you can help to ensure that your house electrical plan is safe and code-compliant.
Future expansion
When designing a house electrical plan, it is important to consider future expansion. This means planning for the possibility of adding additional electrical circuits or devices in the future. By planning for future expansion, you can avoid the need to make costly changes to your electrical system later on.
- Adding additional circuits
One way to plan for future expansion is to add additional circuits to your electrical panel. This will give you the flexibility to add additional outlets, switches, or other electrical devices in the future without having to rewire your entire house. It is a good idea to add at least one or two extra circuits to your electrical panel, even if you do not have any immediate plans to use them.
- Installing conduit
Another way to plan for future expansion is to install conduit in your walls and ceilings. Conduit is a metal or plastic pipe that protects electrical wires from damage. By installing conduit, you can easily add additional electrical wires in the future without having to tear open your walls and ceilings.
- Using modular wiring systems
Modular wiring systems are another good way to plan for future expansion. Modular wiring systems use pre-fabricated components that can be easily added or removed. This makes it easy to add additional outlets, switches, or other electrical devices in the future.
- Leaving space in your electrical panel
When installing your electrical panel, be sure to leave some space for future expansion. This will give you the flexibility to add additional circuit breakers or fuses in the future without having to replace your entire electrical panel.
By following these tips, you can plan for future expansion and avoid the need to make costly changes to your electrical system later on.
Energy efficiency
Energy efficiency is an important consideration for any house electrical plan. By designing your electrical system to be energy efficient, you can save money on your energy bills and help to reduce your environmental impact.
There are many different ways to improve the energy efficiency of your house electrical plan. Some of the most effective methods include:
- Using energy-efficient appliances:
Energy-efficient appliances use less energy to operate than traditional appliances. Look for appliances that have the Energy Star label. Energy Star is a government program that certifies appliances that meet certain energy efficiency standards. - Installing LED lighting:
LED lighting is much more energy efficient than traditional incandescent lighting. LED bulbs use up to 90% less energy than incandescent bulbs and they last much longer. - Using smart thermostats:
Smart thermostats can help you to save energy by automatically adjusting the temperature in your home based on your schedule and preferences. Smart thermostats can also be controlled remotely, so you can adjust the temperature in your home even when you’re away. - Installing solar panels:
Solar panels can generate electricity from the sun, which can help to reduce your reliance on the grid. Solar panels can be installed on the roof of your home or on a ground-mounted system.
By incorporating these energy-efficient measures into your house electrical plan, you can save money on your energy bills and help to reduce your environmental impact.
In addition to the energy-efficient measures listed above, there are many other small changes you can make to your daily routine to save energy. For example, you can unplug electronics when you’re not using them, turn off lights when you leave a room, and adjust your thermostat by a few degrees.
By making a few small changes to your house electrical plan and your daily routine, you can make a big impact on your energy consumption.
Safety features
Safety should be a top priority when designing a house electrical plan. By incorporating safety features into your plan, you can help to protect your family and your home from electrical hazards.
- Ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs)
GFCIs are designed to protect people from electrical shock. They work by monitoring the flow of electricity in a circuit and tripping if there is a sudden increase in current. GFCIs are required in all wet or damp locations, such as bathrooms, kitchens, and outdoor areas.
- Arc fault circuit interrupters (AFCIs)
AFCIs are designed to protect against electrical fires. They work by detecting dangerous electrical arcs and tripping the circuit if an arc is detected. AFCIs are required in all bedrooms in new homes. They are also recommended for use in other areas of the home, such as living rooms and dining rooms.
- Surge protectors
Surge protectors are designed to protect electronic devices from damage caused by power surges. Power surges can occur when there is a sudden increase in voltage, such as when lightning strikes or when a large appliance is turned on. Surge protectors are available in a variety of shapes and sizes, and they can be plugged into any standard electrical outlet.
- Smoke and carbon monoxide detectors
Smoke and carbon monoxide detectors are essential for protecting your family from fire and carbon monoxide poisoning. Smoke detectors should be installed in every bedroom and on every level of your home. Carbon monoxide detectors should be installed in every bedroom and in any other area where there is a potential for carbon monoxide to accumulate, such as near a fireplace or wood stove.
By incorporating these safety features into your house electrical plan, you can help to protect your family and your home from electrical hazards.










Related Posts