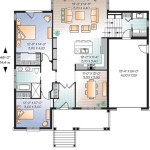
Architectural house plans are detailed blueprints that outline the design and construction of a house. They serve as a comprehensive guide for architects, builders, and homeowners, providing precise instructions on every aspect of the building’s structure, layout, and systems. For instance, in the construction of a residential home, architectural house plans would specify the number of rooms, their dimensions and locations within the house, as well as the placement of windows, doors, and other fixtures.
These plans are not mere sketches; they adhere to strict building codes and standards, ensuring that the finished structure is safe, functional, and aesthetically pleasing. By following the guidelines laid out in architectural house plans, builders can construct homes that meet the specific needs and preferences of homeowners while adhering to all applicable regulations.
Moving forward, this article will delve into the various components of architectural house plans, exploring their significance and providing insights into how they contribute to the successful realization of dream homes.
Architectural house plans serve as crucial blueprints for constructing homes, and they comprise several important components that contribute to their effectiveness. Here are eight key points to consider:
- Floor plans
- Elevations
- Sections
- Details
- Specifications
- Codes and standards
- Sustainability
- Client requirements
These elements work together to provide a comprehensive guide for architects, builders, and homeowners, enabling them to visualize, construct, and inhabit spaces that meet their specific needs and aspirations.
Floor plans
Floor plans are detailed drawings that depict the layout of a house from above, showing the arrangement of rooms, walls, doors, and windows. They provide a comprehensive overview of the house’s interior space and are essential for visualizing the flow and functionality of the home.
- Room layout: Floor plans indicate the size, shape, and location of each room within the house. This allows architects and homeowners to plan the placement of furniture, fixtures, and other elements to maximize space utilization and create a cohesive design.
- Circulation: Floor plans show the pathways and connections between different rooms, ensuring smooth and efficient movement throughout the house. They help determine the placement of hallways, staircases, and other transitional spaces to facilitate easy access to all areas of the home.
- Structural elements: Floor plans include the location of load-bearing walls, beams, and columns, which are crucial for the structural integrity of the house. This information guides builders in selecting appropriate materials and construction methods to ensure the stability and safety of the structure.
- Utilities and systems: Floor plans also indicate the placement of utilities such as plumbing, electrical, and HVAC systems. This helps contractors plan the installation and maintenance of these systems, ensuring that they are accessible and functional.
Overall, floor plans are indispensable tools for architects, builders, and homeowners, providing a clear understanding of the spatial organization and functionality of a house at the planning stage.
Elevations
Elevations are two-dimensional drawings that depict the exterior walls of a house from different sides, typically the front, back, and sides. They show the height, width, and proportions of the house, as well as the placement of windows, doors, and other architectural features. Elevations are crucial for visualizing the external appearance of the house and ensuring its aesthetic appeal.
Facade design: Elevations allow architects and homeowners to design the facade of the house, which is its outward-facing appearance. They can experiment with different combinations of materials, colors, and textures to create a visually pleasing exterior that complements the surrounding environment and reflects the desired architectural style.
Window and door placement: Elevations indicate the size, shape, and location of windows and doors on each side of the house. This is important for controlling natural light, ventilation, and views, as well as for maintaining the overall balance and symmetry of the facade.
Roof design: Elevations show the type and pitch of the roof, which can significantly impact the overall appearance and functionality of the house. Architects can use elevations to explore different roof designs, such as gable, hip, or flat roofs, and determine their compatibility with the architectural style and surrounding environment.
Furthermore, elevations are essential for obtaining building permits and ensuring compliance with local building codes and regulations. They provide a clear representation of the house’s external dimensions and features, allowing authorities to assess its adherence to zoning requirements and safety standards.
Sections
Sections are two-dimensional drawings that depict a vertical slice through a house, revealing the interiorelements from the ground up. They provide detailed information about the house’s height, the thickness of walls and floors, and the relationship between different levels and spaces.
Structural components: Sections show the location and dimensions of structural elements such as foundations, walls, beams, and columns. This information is crucial for ensuring the structural integrity and stability of the house, as it allows architects and engineers to calculate the load-bearing capacity and design the house to withstand various forces.
Interior layout: Sections reveal the vertical relationship between different levels and spaces within the house. They show the height of ceilings, the location of stairs, and the placement of openings such as windows and doors on different floors. This helps architects and homeowners visualize the flow of space and the overall volume of the house.
Building systems: Sections also indicate the location and routing of building systems, including plumbing, electrical, and HVAC systems. This information is essential for planning the installation and maintenance of these systems, ensuring that they are accessible and functional throughout the house.
Overall, sections are essential for understanding the three-dimensional structure and organization of a house. They provide valuable insights into the house’s structural integrity, interior layout, and building systems, guiding architects, builders, and homeowners in creating safe, functional, and aesthetically pleasing living spaces.
Details
Details are precise drawings that provide specific information about individual components and elements of a house. They complement the general drawings by zooming in on particular aspects, ensuring that every aspect of the house is carefully considered and executed during construction.
- Construction details: These details provide specific instructions on how to construct different elements of the house, such as wall framing, roof framing, and floor systems. They include dimensions, material specifications, and assembly methods, ensuring that builders have a clear understanding of how to put the house together.
- Millwork details: Millwork refers to the custom-made wooden components of a house, such as cabinets, moldings, and built-in furniture. Details for millwork specify the design, dimensions, and materials used, ensuring that these elements are crafted to the exact specifications of the architect and homeowner.
- Hardware details: Hardware details provide information about the types and placement of hardware used throughout the house, including doorknobs, hinges, and window latches. These details ensure that the hardware matches the overall design aesthetic and functions smoothly.
- Fixture details: Fixture details specify the types and locations of fixtures, such as sinks, faucets, toilets, and light fixtures. These details ensure that the fixtures are compatible with the plumbing and electrical systems and that they meet the specific needs and preferences of the homeowner.
Overall, details play a crucial role in ensuring that every aspect of the house is carefully planned and executed. They provide precise instructions for builders, ensuring that the finished house meets the design intent and the expectations of the homeowner.
Specifications
Material specifications
Material specifications outline the types and quality of materials to be used in the construction of the house. These specifications cover a wide range of elements, including structural materials such as lumber, concrete, and steel, as well as finish materials such as flooring, countertops, and paint. By clearly defining the materials to be used, specifications ensure that the house meets the desired levels of durability, performance, and aesthetic appeal.
Product specifications
Product specifications provide detailed information about specific products and equipment to be installed in the house. These specifications include the make, model, and performance characteristics of products such as windows, doors, appliances, and lighting fixtures. By specifying specific products, architects and homeowners can ensure that the house is equipped with high-quality, reliable components that meet their specific needs and preferences.
Construction methods
Construction methods specifications outline the specific techniques and procedures to be followed during the construction process. These specifications cover aspects such as framing techniques, roofing methods, and insulation installation. By clearly defining the construction methods to be used, specifications help ensure that the house is built in a safe, efficient, and code-compliant manner.
Sustainability specifications
Sustainability specifications address the environmental impact of the house’s construction and operation. These specifications may include measures to reduce energy consumption, conserve water, and minimize waste. By incorporating sustainability specifications, architects and homeowners can create houses that are not only comfortable and functional but also environmentally responsible.
Codes and standards
Architectural house plans must adhere to a variety of codes and standards to ensure the safety, functionality, and habitability of the building. These codes and standards are established by government agencies and professional organizations to regulate the design and construction of buildings.
- Building codes: Building codes are the minimum requirements for the design and construction of buildings. They cover a wide range of topics, including structural integrity, fire safety, energy efficiency, and accessibility. Building codes are typically enforced by local governments, and they help to ensure that buildings are safe and habitable.
- Zoning codes: Zoning codes regulate the use of land and the types of buildings that can be constructed in specific areas. These codes are typically established by local governments, and they help to ensure that land is used in a compatible and orderly manner.
- Energy codes: Energy codes are designed to reduce the energy consumption of buildings. These codes specify minimum levels of energy efficiency for building envelopes, HVAC systems, and other building components. Energy codes are typically established by state or federal governments, and they help to reduce the environmental impact of buildings.
- Accessibility codes: Accessibility codes ensure that buildings are accessible to people with disabilities. These codes specify minimum requirements for ramps, elevators, doorways, and other building features. Accessibility codes are typically established by state or federal governments, and they help to ensure that people with disabilities have equal access to buildings.
Architects and builders must be familiar with the codes and standards that apply to their projects. By following these codes and standards, they can help to ensure that their buildings are safe, functional, and habitable.
Sustainability
Energy efficiency
Sustainable architectural house plans prioritize energy efficiency to reduce the environmental impact of the building and lower energy costs for the occupants. This can be achieved through various strategies, such as:
- Insulation: Adequate insulation in walls, ceilings, and floors minimizes heat loss and gain, reducing the need for heating and cooling.
- Energy-efficient windows and doors: Windows and doors with high thermal resistance and low air leakage can significantly reduce energy loss.
- Passive solar design: Orienting the house to take advantage of natural sunlight can reduce the need for artificial lighting and heating.
- Energy-efficient appliances and lighting: Choosing appliances and lighting fixtures with high energy efficiency ratings can further reduce energy consumption.
- Renewable energy sources: Incorporating renewable energy sources such as solar panels or geothermal heating can generate clean energy and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
Water conservation
Sustainable architectural house plans also focus on water conservation to minimize the environmental impact and reduce water bills. This can be achieved through:
- Low-flow fixtures: Installing low-flow faucets, showerheads, and toilets can significantly reduce water usage.
- Rainwater harvesting: Collecting and storing rainwater for non-potable uses, such as irrigation or flushing toilets, can reduce strain on municipal water supplies.
- Drought-tolerant landscaping: Choosing plants that are native to the local climate and require less water can reduce outdoor water usage.
- Greywater reuse: Diverting wastewater from sinks and showers for non-potable uses, such as watering plants, can further conserve water.
Material selection
The choice of building materials can also contribute to the sustainability of a house. Sustainable materials are those that are sourced responsibly, have a low environmental impact, and promote occupant health. Here are some considerations for sustainable material selection:
- Recycled and renewable materials: Using recycled materials, such as reclaimed wood or recycled steel, reduces the demand for new resources.
- Low-VOC materials: Choosing materials with low volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions can improve indoor air quality.
- Durable and low-maintenance materials: Selecting durable materials that require less maintenance and replacement can reduce the long-term environmental impact of the building.
- Locally sourced materials: Using materials that are sourced locally reduces transportation-related emissions and supports the local economy.
Site planning
The way a house is positioned on its site can also impact its sustainability. Careful site planning can take advantage of natural resources and reduce the environmental impact:
- Orientation: Orienting the house to maximize natural light and ventilation can reduce energy consumption for lighting and cooling.
- Landscaping: Planting trees and vegetation around the house can provide shade, reduce heat absorption, and improve air quality.
- Stormwater management: Implementing measures such as rain gardens or permeable pavements can help manage stormwater runoff and reduce the risk of flooding.
- Site preservation: Minimizing the disturbance of the natural site during construction can preserve ecosystems and protect biodiversity.
Client requirements
Functional requirements
Client requirements for architectural house plans often start with functional requirements. These requirements outline the specific needs and preferences of the occupants in terms of how they want to use the space. Functional requirements may include the number of bedrooms and bathrooms, the size and layout of different rooms, the desired flow of traffic, and any special features or amenities. The architect will work closely with the client to understand their functional requirements and translate them into a design that meets their needs.
Aesthetic requirements
In addition to functional requirements, clients may also have aesthetic requirements for their house plans. These requirements may relate to the overall architectural style of the house, the exterior finishes, the interior design, and the landscaping. The architect will work with the client to develop a design that meets their aesthetic preferences while also considering the functional requirements and the constraints of the site.
Budgetary requirements
Budgetary requirements are another important consideration for architectural house plans. The client will need to provide the architect with a budget for the project, and the architect will design the house accordingly. The budget will impact the size of the house, the materials used, and the level of finishes. The architect will work with the client to develop a design that meets their budgetary requirements while also meeting their functional and aesthetic needs.
Site-specific requirements
The specific characteristics of the building site will also impact the design of the house. The architect will need to consider the size and shape of the lot, the topography, the orientation to the sun, and any existing vegetation or structures. The architect will work with the client to develop a design that takes advantage of the site’s features and minimizes its constraints.
Once the architect has a clear understanding of the client’s requirements, they will begin to develop a design for the house. The design process will typically involve several iterations, as the architect works with the client to refine the design and ensure that it meets their needs and preferences.










Related Posts