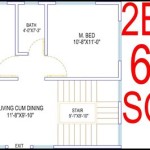
Tiny House On Wheels Plans serve as blueprints for constructing compact, portable dwellings mounted on a trailer base. These plans provide detailed instructions and specifications, enabling individuals or builders to create their own customized tiny houses that can be towed effortlessly.
Tiny houses on wheels have gained popularity due to their affordability, mobility, and eco-friendly nature. They offer a unique lifestyle solution for those seeking downsizing, travel, or sustainable living options. For instance, a couple seeking to minimize their environmental impact might opt for a tiny house on wheels with energy-efficient appliances and a solar panel system for independent power generation.
In the following sections, we will delve into the various aspects of Tiny House On Wheels Plans, covering design considerations, construction techniques, and the legal implications of building and owning one.
When considering Tiny House On Wheels Plans, several key points merit attention:
- Space optimization
- Layout efficiency
- Weight distribution
- Materials selection
- Trailer specifications
- Towing capacity
- Legal regulations
- Construction techniques
- Cost considerations
By carefully addressing these aspects, individuals can create functional and aesthetically pleasing tiny houses on wheels that meet their specific needs and aspirations.
Space optimization
Space optimization is paramount in Tiny House On Wheels Plans, as every square foot must be utilized efficiently to create a functional and comfortable living space. Clever design strategies and innovative storage solutions are essential to maximize space without compromising livability.
One effective technique is to incorporate multi-purpose furniture. For instance, a couch can double as a guest bed, while ottomans can serve as storage containers. Additionally, utilizing vertical space through the installation of shelves, cabinets, and lofts can significantly increase storage capacity.
Another crucial aspect is the strategic placement of windows and doors. Well-positioned windows not only provide natural light and ventilation but also create the illusion of a larger space. Doors should be designed to minimize wasted space, such as sliding doors or pocket doors.
Furthermore, careful planning of the kitchen and bathroom areas is essential. Compact appliances, such as a two-burner stove and a mini-fridge, can save valuable space. In the bathroom, a composting toilet or a wet bath (a combined shower and toilet) can optimize space utilization.
By implementing these space-saving techniques, individuals can create tiny houses on wheels that are both functional and comfortable, despite their compact size.
Layout efficiency
Layout efficiency in Tiny House On Wheels Plans is crucial to create a functional and comfortable living space within a limited footprint. Careful consideration of the placement and size of each room, as well as the flow of traffic, is essential to maximize space utilization and livability.
One important aspect of layout efficiency is the use of open floor plans. By minimizing the number of walls and partitions, tiny houses can feel more spacious and airy. Multi-purpose spaces, such as a living room that doubles as a dining area, can also help to save space and create a more flexible living environment.
Another key factor to consider is the placement of windows and doors. Natural light can make a tiny house feel larger and more inviting, so it is important to incorporate windows into the design wherever possible. Doors should be positioned to minimize wasted space, and sliding doors or pocket doors can be used to save even more room.
Finally, it is important to think carefully about the placement of furniture and appliances. Bulky furniture can quickly overwhelm a small space, so it is best to choose pieces that are compact and multifunctional. Appliances should be chosen based on their size and energy efficiency to minimize space consumption and utility costs.
By carefully considering layout efficiency, individuals can create tiny houses on wheels that are both functional and comfortable, despite their compact size.
Weight distribution
Weight distribution is a critical aspect of Tiny House On Wheels Plans, as it affects the safety and stability of the structure while being towed. Proper weight distribution ensures that the weight is evenly distributed across the trailer’s axles, preventing the tiny house from becoming top-heavy or unbalanced.
To achieve optimal weight distribution, it is important to carefully consider the placement of heavy items, such as appliances, furniture, and water tanks. Heavier items should be placed near the center of the trailer, directly above the axles. This helps to keep the center of gravity low and reduces the risk of swaying or tipping.
Another important factor to consider is the overall height of the tiny house. A taller tiny house will have a higher center of gravity, which can make it more susceptible to wind gusts and other external forces. Therefore, it is important to keep the height of the tiny house as low as possible while still maintaining adequate headroom.
Finally, it is important to ensure that the trailer itself is properly rated for the weight of the tiny house. Overloading the trailer can put undue stress on the frame and axles, leading to premature wear and tear or even structural failure.
Materials selection
Materials selection plays a vital role in Tiny House On Wheels Plans, as the choice of materials can significantly impact the weight, durability, cost, and overall performance of the structure. Careful consideration of the available options and their suitability for the intended use is essential.
For the exterior walls, popular materials include:
- Wood: Wood is a traditional choice for tiny houses on wheels, offering a classic and natural look. It is relatively easy to work with and can be painted or stained to match any desired aesthetic. However, wood requires regular maintenance to protect it from moisture and decay.
- Metal: Metal siding, such as aluminum or steel, is a durable and low-maintenance option. It is resistant to rot and pests, and can withstand harsh weather conditions. Metal siding is also relatively lightweight, which can be beneficial for weight distribution.
- Composite materials: Composite materials, such as fiber cement or vinyl, offer a combination of durability and low maintenance. They are resistant to moisture, rot, and pests, and come in a variety of colors and textures to suit different tastes.
Trailer specifications
Trailer specifications are a crucial aspect of Tiny House On Wheels Plans, as the trailer serves as the foundation and support structure for the tiny house. The choice of trailer will depend on the size, weight, and design of the tiny house, as well as the intended use and towing capabilities.
One of the most important considerations is the trailer’s weight capacity. The trailer must be able to safely support the weight of the tiny house, including all of its contents and occupants. Overloading the trailer can put undue stress on the frame and axles, leading to premature wear and tear or even structural failure.
Another important consideration is the trailer’s size. The trailer must be long enough and wide enough to accommodate the tiny house, and it must also have a high enough clearance to allow for headroom and proper drainage. Additionally, the trailer’s width must be compatible with the towing vehicle, and it should not exceed the maximum width allowed for road travel in the intended areas of use.
The type of trailer used for a tiny house on wheels will also depend on the intended use and towing capabilities. For example, a bumper-pull trailer is a good option for smaller tiny houses that can be towed by a standard pickup truck. However, a gooseneck trailer or a fifth-wheel trailer may be necessary for larger tiny houses or for towing with a heavy-duty truck.
Towing capacity
Towing capacity refers to the maximum weight that a vehicle is safely able to tow. It is determined by a number of factors, including the vehicle’s engine power, transmission, frame strength, and suspension system. When selecting a towing vehicle for a tiny house on wheels, it is crucial to ensure that the vehicle has sufficient towing capacity to safely handle the weight of the tiny house, including all of its contents and occupants.
To determine the towing capacity of a particular vehicle, refer to the owner’s manual or consult with the vehicle manufacturer. It is important to note that the towing capacity may vary depending on the specific configuration of the vehicle, such as the type of engine, transmission, and drive system. Additionally, factors such as altitude, road conditions, and wind speed can also affect the towing capacity.
If the towing capacity of the vehicle is exceeded, it can put undue stress on the vehicle’s engine, transmission, and brakes, leading to premature wear and tear or even catastrophic failure. It can also compromise the stability and handling of the vehicle, increasing the risk of an accident.
Therefore, it is essential to carefully consider the towing capacity of the vehicle when planning to tow a tiny house on wheels. If the towing capacity is insufficient, it may be necessary to upgrade to a more powerful vehicle or consider reducing the weight of the tiny house.
Legal regulations
When building and owning a tiny house on wheels, it is essential to be aware of the legal regulations that apply in your area. These regulations may vary depending on the jurisdiction, but they typically cover aspects such as:
- Building codes
Tiny houses on wheels must comply with applicable building codes, which may include requirements for structural integrity, safety features, and energy efficiency. It is important to consult with local building officials to ensure that your tiny house meets all of the necessary requirements.
- Zoning laws
Zoning laws regulate the use of land and property in specific areas. In some cases, tiny houses on wheels may be prohibited or restricted in certain zoning districts. It is important to check with local zoning authorities to determine if there are any restrictions on tiny houses in your area.
- Vehicle registration and insurance
Tiny houses on wheels are typically classified as recreational vehicles (RVs) and must be registered and insured accordingly. The registration and insurance requirements may vary depending on the jurisdiction, so it is important to check with your local department of motor vehicles.
- Parking and occupancy
There may be restrictions on where you can park and occupy your tiny house on wheels. Some jurisdictions may have designated RV parks or campgrounds where tiny houses are allowed, while others may prohibit overnight parking on public property. It is important to be aware of the local regulations regarding parking and occupancy.
By understanding and complying with the legal regulations that apply to tiny houses on wheels, you can avoid potential problems and ensure that your tiny house is safe and legal to occupy.
Construction techniques
The construction techniques used in Tiny House On Wheels Plans must ensure the structural integrity and durability of the tiny house while also adhering to weight restrictions. Here are some commonly used construction techniques:
Framing
The frame of a tiny house on wheels typically consists of a combination of wood and metal framing. Wood framing is lightweight and easy to work with, while metal framing is stronger and more durable. The frame is designed to distribute the weight of the tiny house evenly and to withstand the stresses of towing and travel.
Sheathing
The exterior walls and roof of a tiny house on wheels are typically sheathed with a layer of plywood or OSB (oriented strand board). Sheathing provides a solid base for the exterior siding and helps to protect the frame from the elements.
Insulation
Insulation is crucial for maintaining a comfortable temperature inside the tiny house, especially in extreme weather conditions. Common insulation materials used in tiny houses on wheels include fiberglass, spray foam, and cellulose. Insulation helps to reduce heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer, improving energy efficiency and comfort.
Siding
The exterior siding of a tiny house on wheels can be made from a variety of materials, including wood, metal, vinyl, and composite materials. Siding protects the exterior of the tiny house from the elements and gives it a finished look.
Roofing
The roof of a tiny house on wheels is typically constructed with a layer of plywood or OSB, covered with a waterproof membrane and topped with roofing shingles or metal roofing. The roof must be strong enough to withstand wind and snow loads and to protect the interior of the tiny house from the elements.
Cost considerations
Cost is a significant factor to consider when planning a Tiny House On Wheels project. The overall cost will vary depending on a number of factors, including the size and complexity of the tiny house, the materials used, and the level of DIY involvement.
Materials
The cost of materials will vary depending on the type and quality of materials used. For example, using higher-quality materials, such as sustainably sourced wood or energy-efficient appliances, will increase the overall cost. It is important to carefully consider the materials used and to compare prices from different suppliers.
Labor
If you are not planning to build the tiny house yourself, you will need to factor in the cost of labor. The cost of labor will vary depending on the complexity of the project and the location. It is important to get quotes from multiple contractors before making a decision.
Permits and fees
Depending on your location, you may need to obtain building permits and pay associated fees. The cost of permits and fees will vary depending on the jurisdiction. It is important to check with your local building department to determine the specific requirements and costs.
Other costs
In addition to the major costs mentioned above, there are a number of other costs to consider, such as:
- Appliances
- Furniture
- Utilities
- Insurance
- Maintenance
It is important to factor in these costs when budgeting for your Tiny House On Wheels project.










Related Posts