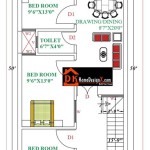
Tiny House Building Plans are detailed instructions and specifications that guide the construction of small, often mobile homes. These plans typically include architectural drawings, material lists, and construction details, providing a roadmap for individuals to design and build their own tiny houses. From compact cabins to cozy RVs, tiny houses offer an alternative lifestyle that emphasizes sustainability, affordability, and flexibility.
Building a tiny house from scratch can be challenging, but with a well-designed plan, the process becomes more manageable. Tiny House Building Plans provide a crucial foundation for successful construction, ensuring that the project meets building codes, is structurally sound, and aligns with the owner’s specific needs and vision. Whether you’re a seasoned builder or a first-time homeowner, these plans empower individuals to create custom-tailored living spaces that maximize space and minimize environmental impact.
Tiny House Building Plans serve as a comprehensive guide for constructing compact and often mobile homes. These plans typically encompass architectural drawings, material lists, and construction details, providing a roadmap for individuals to design and build their own tiny houses.
- Detailed Architectural Drawings
- Comprehensive Material Lists
- Step-by-Step Construction Details
- Building Code Compliance
- Structural Integrity Assurance
- Customized Design Options
- Space Optimization Techniques
- Sustainability Considerations
- Cost-Effective Solutions
- Foundation and Utility Integration
By incorporating these elements, Tiny House Building Plans empower individuals to create custom-tailored living spaces that maximize space, minimize environmental impact, and align with their specific needs and vision.
Detailed Architectural Drawings
Detailed architectural drawings are a crucial component of Tiny House Building Plans, providing a visual representation of the structure’s design and layout. These drawings typically include floor plans, elevations, sections, and details, which together provide a comprehensive understanding of the tiny house’s design intent and construction requirements.
Floor plans depict the arrangement of rooms, hallways, and other spaces within the tiny house, showing the placement of walls, windows, doors, and fixtures. Elevations illustrate the exterior appearance of the house from different sides, showcasing the roofline, siding materials, and architectural features. Sections provide vertical slices through the house, revealing the interior layout, ceiling heights, and structural elements such as framing and insulation.
Detailed architectural drawings also include specifications for materials, finishes, and construction methods. These specifications ensure that the tiny house is built to code and meets the owner’s desired level of quality and durability. By providing clear and comprehensive visual instructions, detailed architectural drawings enable builders to accurately construct the tiny house, minimizing errors and ensuring a successful outcome.
Overall, detailed architectural drawings are essential for ensuring that the tiny house is built according to plan and meets the owner’s specific requirements. These drawings serve as a roadmap for the construction process, providing a visual guide that facilitates efficient and accurate construction.
Comprehensive Material Lists
Comprehensive material lists are an integral part of Tiny House Building Plans, providing a detailed inventory of all the materials required to construct the tiny house. These lists typically include the quantity, size, and specifications for each material, ensuring that builders have a clear understanding of the materials needed and can accurately estimate the cost of construction.
Material lists are organized by category, such as framing materials, roofing materials, siding materials, insulation materials, and interior finishes. For each category, the list specifies the type of material, its dimensions, and the quantity required. For example, the framing materials list might include items such as studs, joists, and plywood, along with their respective lengths and quantities.
In addition to basic materials, comprehensive material lists also include items such as hardware, fasteners, sealants, and adhesives. These items are essential for assembling the tiny house and ensuring its structural integrity and durability. The list also includes specifications for windows, doors, appliances, and fixtures, providing a complete picture of all the materials needed to finish the tiny house.
By providing a comprehensive inventory of all the materials required, material lists help builders stay organized and avoid costly delays or errors during the construction process. These lists also enable builders to accurately estimate the cost of construction and make informed decisions about material selection.
Overall, comprehensive material lists are essential for ensuring that builders have all the necessary materials on hand to construct the tiny house efficiently and cost-effectively.
Step-by-Step Construction Details
Step-by-step construction details are a critical component of Tiny House Building Plans, providing builders with clear and concise instructions on how to assemble the tiny house. These details typically include written instructions, diagrams, and photographs, guiding builders through each stage of the construction process, from laying the foundation to installing the finishing touches.
The construction details are organized in a logical sequence, starting with the preparation of the building site and foundation. They then progress through the framing, roofing, siding, insulation, and interior finishing stages. Each step is explained in detail, with clear instructions on how to properly install materials, connect components, and ensure structural integrity.
The instructions are supplemented with diagrams and photographs, which provide visual aids that help builders understand the construction process and avoid errors. The diagrams illustrate the placement and assembly of structural components, while the photographs show real-world examples of completed work. This combination of written instructions and visual aids ensures that builders have a clear understanding of how to construct the tiny house safely and efficiently.
In addition to providing general construction details, Tiny House Building Plans often include specific instructions for unique features or design elements. For example, if the tiny house has a loft or sleeping alcove, the plans will include detailed instructions on how to frame and construct these features. Similarly, if the tiny house incorporates sustainable or energy-efficient elements, such as solar panels or rainwater harvesting systems, the plans will provide specific instructions on how to install and integrate these systems.
Overall, step-by-step construction details are essential for ensuring that the tiny house is built correctly and safely. These details provide builders with a clear roadmap for the construction process, minimizing errors and ensuring a successful outcome.
Building Code Compliance
Tiny House Building Plans must adhere to applicable building codes to ensure the safety and habitability of the structure. Building codes are regulations established by local governments to ensure that buildings meet minimum standards for structural integrity, fire safety, and energy efficiency. By complying with building codes, tiny house builders can obtain permits and inspections, which are often required for insurance and legal occupancy.
- Structural Safety
Building codes specify requirements for the structural design of tiny houses, including the size and spacing of framing members, the strength of materials used, and the overall stability of the structure. These requirements are in place to ensure that tiny houses can withstand wind, snow, and other environmental loads.
- Fire Safety
Building codes also include fire safety regulations, such as the use of fire-resistant materials, the installation of smoke detectors and fire extinguishers, and the provision of adequate exits. These regulations are essential for protecting the occupants of tiny houses in the event of a fire.
- Energy Efficiency
Building codes increasingly include energy efficiency requirements, such as insulation standards, window glazing requirements, and the use of energy-efficient appliances and lighting. These requirements are designed to reduce the environmental impact of tiny houses and lower energy costs for occupants.
- Accessibility
Building codes also include accessibility requirements, such as the provision of ramps and grab bars, to ensure that tiny houses are accessible to people with disabilities. These requirements are essential for creating inclusive and equitable housing options.
By incorporating building code compliance into Tiny House Building Plans, builders can ensure that their structures are safe, habitable, and meet the requirements of local authorities. This ensures that tiny houses are not only aesthetically pleasing but also structurally sound and environmentally responsible.
Structural Integrity Assurance
Structural integrity assurance is a critical aspect of Tiny House Building Plans, ensuring that the structure is able to withstand various loads and forces without collapsing or failing. By incorporating structural integrity measures into the plans, builders can create tiny houses that are safe and habitable for their occupants.
- Load Calculations
Tiny House Building Plans must account for various loads that the structure will experience, including dead loads (the weight of the structure itself), live loads (the weight of occupants and their belongings), wind loads, and snow loads. Structural engineers perform load calculations to determine the forces that the tiny house will be subjected to and design the structure accordingly.
- Material Selection
The choice of materials used in the construction of a tiny house has a significant impact on its structural integrity. Tiny House Building Plans specify the appropriate materials for the framing, roofing, siding, and other structural components, ensuring that the tiny house is built to withstand the intended loads.
- Proper Construction Techniques
Proper construction techniques are essential for ensuring the structural integrity of a tiny house. Tiny House Building Plans provide detailed instructions on how to properly frame, join, and assemble the various components of the structure. These instructions help builders avoid common construction errors that could compromise the structural integrity of the tiny house.
- Engineering Certification
In some cases, Tiny House Building Plans may include engineering certification. This certification verifies that the plans have been reviewed and approved by a licensed structural engineer, ensuring that the design meets applicable building codes and standards. Engineering certification can provide additional assurance of the structural integrity of the tiny house.
By incorporating structural integrity measures into Tiny House Building Plans, builders can create tiny houses that are safe, durable, and able to withstand the rigors of daily use and environmental conditions. This ensures that tiny house occupants can enjoy their homes with peace of mind, knowing that their structures are built to last.
Customized Design Options
Tiny House Building Plans offer a wide range of customized design options, allowing builders to create tiny houses that are tailored to their specific needs and preferences. These options empower individuals to design tiny houses that reflect their unique style, maximize space utilization, and accommodate their desired amenities and features.
One of the key benefits of customized design options is the ability to optimize space utilization. Tiny houses are inherently space-constrained, so it is essential to make the most of every square foot. Customized design options allow builders to incorporate creative storage solutions, multi-functional furniture, and innovative layouts to maximize space and create a comfortable and functional living environment.
In addition to space optimization, customized design options enable builders to incorporate personal style and preferences into their tiny houses. From the exterior siding and roofing materials to the interior finishes and fixtures, builders can choose from a wide range of options to create a tiny house that reflects their unique aesthetic sensibilities. This level of customization ensures that the tiny house feels like a true home, rather than a generic or cookie-cutter design.
Furthermore, customized design options allow builders to accommodate specific amenities and features that meet their individual needs. For example, builders can incorporate energy-efficient appliances, solar panels, or rainwater harvesting systems to create a sustainable and eco-conscious tiny house. Similarly, builders can design tiny houses with accessible features, such as ramps, grab bars, and wider doorways, to ensure accessibility for individuals with disabilities.
Overall, customized design options are a defining characteristic of Tiny House Building Plans. These options empower builders to create tiny houses that are not only practical and functional but also reflect their unique style, maximize space utilization, and accommodate their desired amenities and features.
Space Optimization Techniques
Space optimization is a crucial aspect of Tiny House Building Plans, as every square foot of space must be utilized efficiently to create a comfortable and functional living environment. Tiny House Building Plans incorporate a range of innovative space optimization techniques to maximize space and create the illusion of a larger space.
One common space optimization technique is the use of multi-functional furniture. For example, a sofa can be designed with built-in storage compartments, eliminating the need for a separate storage unit. Similarly, a bed can be designed with drawers or shelves underneath, providing additional storage space without taking up extra floor space.
Another space optimization technique is the use of vertical space. Tiny House Building Plans often incorporate loft spaces, sleeping alcoves, and built-in shelves to maximize vertical space utilization. Loft spaces can be used for sleeping, storage, or as a cozy reading nook, while sleeping alcoves provide a private and space-efficient sleeping area. Built-in shelves can be used to store books, dcor, and other items, freeing up valuable floor space.
In addition to multi-functional furniture and vertical space utilization, Tiny House Building Plans also incorporate clever storage solutions to maximize space. These solutions include under-bed storage drawers, hidden compartments in walls, and pull-out pantries. By incorporating these innovative storage solutions, Tiny House Building Plans ensure that every inch of space is utilized efficiently, creating a comfortable and functional living environment.
Overall, space optimization techniques are essential for creating comfortable and functional tiny houses. By incorporating multi-functional furniture, maximizing vertical space, and implementing clever storage solutions, Tiny House Building Plans empower builders to create tiny houses that feel spacious and inviting, despite their compact size.
Sustainability Considerations
Sustainability is a key consideration in Tiny House Building Plans, as tiny houses are often designed to minimize their environmental impact and promote a more sustainable lifestyle. Tiny House Building Plans incorporate a range of sustainable features and materials to reduce energy consumption, conserve resources, and protect the environment.
- Energy Efficiency
Tiny House Building Plans prioritize energy efficiency to reduce energy consumption and lower utility costs. This is achieved through the use of insulated walls, roofs, and windows, as well as energy-efficient appliances and lighting. Some Tiny House Building Plans also incorporate renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines, to generate electricity and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
- Water Conservation
Water conservation is another important aspect of sustainability in Tiny House Building Plans. These plans often incorporate water-saving fixtures and appliances, such as low-flow toilets and faucets, to reduce water usage. Rainwater harvesting systems can also be incorporated to collect and store rainwater for non-potable uses, such as watering plants or flushing toilets.
- Material Selection
The choice of materials used in Tiny House Building Plans has a significant impact on the sustainability of the structure. Tiny House Building Plans often specify the use of sustainable materials, such as recycled or reclaimed wood, bamboo, and cork. These materials have a lower environmental impact than traditional building materials and can help reduce the carbon footprint of the tiny house.
- Waste Reduction
Tiny House Building Plans also promote waste reduction by encouraging the use of durable and long-lasting materials. By choosing high-quality materials and incorporating proper construction techniques, Tiny House Building Plans aim to minimize waste and extend the lifespan of the tiny house, reducing its overall environmental impact.
Overall, sustainability considerations are an integral part of Tiny House Building Plans. By incorporating sustainable features and materials, tiny houses can minimize their environmental impact, promote a more sustainable lifestyle, and contribute to a greener future.
Cost-Effective Solutions
Cost-effectiveness is a primary consideration in Tiny House Building Plans, as tiny houses are often built on a budget. Tiny House Building Plans incorporate a range of cost-effective solutions to reduce construction costs and make tiny houses more affordable.
- Smart Design
Tiny House Building Plans prioritize smart design to maximize space and minimize material usage. By optimizing the layout and incorporating multi-functional spaces, Tiny House Building Plans reduce the need for additional rooms or structures, lowering construction costs.
- Material Selection
Tiny House Building Plans carefully consider material selection to balance cost and quality. These plans often specify the use of affordable and durable materials, such as recycled or reclaimed wood, corrugated metal, and vinyl siding. By choosing cost-effective materials without sacrificing structural integrity, Tiny House Building Plans help reduce construction costs.
- Simple Construction Techniques
Tiny House Building Plans favor simple construction techniques to reduce labor costs and make construction more accessible to do-it-yourself builders. These plans avoid complex architectural features and intricate details, which can increase construction time and costs.
- Energy Efficiency
Investing in energy efficiency measures can save money in the long run by reducing energy bills. Tiny House Building Plans incorporate energy-efficient features, such as insulated walls and roofs, energy-efficient appliances, and natural lighting, to minimize energy consumption and lower utility costs.
Overall, cost-effective solutions are an essential aspect of Tiny House Building Plans. By incorporating smart design, selecting affordable materials, employing simple construction techniques, and prioritizing energy efficiency, Tiny House Building Plans empower individuals to build tiny houses that are not only affordable but also comfortable, functional, and sustainable.
Foundation and Utility Integration
Foundation and utility integration is a crucial aspect of Tiny House Building Plans, ensuring that the tiny house is structurally sound, safe, and connected to essential services. Tiny House Building Plans provide detailed instructions on how to properly install the foundation and integrate utilities, ensuring that the tiny house can withstand environmental conditions and provide a comfortable and functional living space.
The foundation of a tiny house is responsible for transferring the weight of the structure to the ground and preventing the tiny house from sinking or shifting. Tiny House Building Plans specify the type of foundation that is appropriate for the soil conditions and climate of the building site. Common foundation types for tiny houses include concrete slabs, piers, and screw piles.
Once the foundation is installed, the next step is to integrate utilities into the tiny house. This includes connecting the tiny house to water, sewer, and electrical services. Tiny House Building Plans provide detailed instructions on how to properly connect these utilities, ensuring that the tiny house has access to clean water, can dispose of wastewater, and has a reliable source of electricity.
In addition to basic utilities, Tiny House Building Plans may also include instructions on how to integrate renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines. By incorporating renewable energy sources, tiny house owners can reduce their reliance on fossil fuels and create a more sustainable living environment.
Overall, foundation and utility integration are essential aspects of Tiny House Building Plans. By providing detailed instructions on how to properly install the foundation and integrate utilities, Tiny House Building Plans ensure that tiny houses are safe, habitable, and connected to essential services.








![The Top 8 Tiny House Floor Plans [2020 Choosing Guide] Tiny Living Life](https://i2.wp.com/inylivinglife.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/pad-tiny.jpg)

Related Posts