The House Plan, a widely utilized approach in the architectural and construction industries, delineates the design and layout of a building. It serves as a blueprint, providing a comprehensive representation of the structure’s dimensions, materials, and functional spaces. The plan encompasses detailed drawings, specifications, and calculations that guide the construction process, ensuring the efficient and accurate realization of the desired design.
In practice, architects and builders rely on The House Plan to communicate their vision and specifications clearly. For instance, a residential house plan might include designated areas for bedrooms, bathrooms, a kitchen, and living room, along with detailed information on wall heights, window placement, and material selections. This comprehensive documentation streamlines the construction process, reducing errors and facilitating collaboration among architects, contractors, and clients.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the intricacies of The House Plan, exploring its purpose, components, and the various uses it serves in the architectural and construction fields.
The House Plan serves as a comprehensive guide for the design and construction of a building, encompassing various important elements:
- Floor plans
- Elevations
- Sections
- Details
- Specifications
- Materials list
- Construction schedule
- Cost estimates
- Building codes
- Sustainability features
These elements work together to provide a clear and detailed representation of the building’s design and construction requirements.
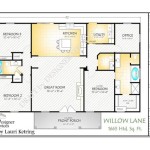
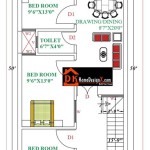
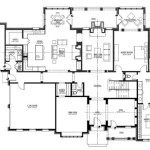
Floor plans
Floor plans are an essential component of The House Plan, providing a detailed representation of each level of the building. They include the layout of rooms, walls, doors, windows, and other architectural features, as viewed from above.
- Overall layout: Floor plans show the spatial relationships between different rooms and areas, allowing for an understanding of the building’s overall functionality and flow.
- Room dimensions: Floor plans include precise measurements of each room, ensuring that furniture, fixtures, and other elements can be planned and placed appropriately.
- Circulation patterns: Floor plans indicate the movement of people through the building, taking into account factors such as traffic flow, accessibility, and safety.
- Structural elements: Floor plans also identify structural elements such as columns, beams, and walls, providing information about the building’s load-bearing capacity and overall stability.
Floor plans are crucial for architects, builders, and clients alike, as they provide a clear understanding of the building’s design and layout. They enable stakeholders to visualize the space, make informed decisions, and ensure that the building meets its intended purpose and adheres to building codes and regulations.
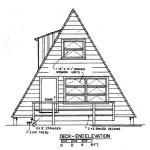
Elevations
Elevations are another critical component of The House Plan, providing a detailed representation of the building’s exterior walls as viewed from different sides. They are typically drawn to scale and include the following information:
- Exterior dimensions: Elevations show the height and width of the building, as well as the overall shape and proportions.
- Window and door placement: Elevations indicate the location, size, and style of windows and doors, providing insight into the building’s natural lighting and ventilation.
- Architectural features: Elevations capture the architectural details of the building’s exterior, such as cornices, moldings, and decorative elements.
- Materials and finishes: Elevations specify the materials and finishes used on the exterior walls, including siding, brick, stone, or stucco.
Elevations are essential for visualizing the building’s external appearance and ensuring that it aligns with the desired architectural style and aesthetic.
In addition to their aesthetic value, elevations play a crucial role in the construction process. They provide builders with precise measurements and details for framing, window and door installation, and exterior finishes. By carefully following the elevations, builders can ensure that the building’s exterior is constructed accurately and according to the architect’s design intent.
Furthermore, elevations are often used in conjunction with floor plans to create three-dimensional models of the building. These models allow architects and clients to visualize the building from different perspectives and assess its overall design and functionality.
Overall, elevations are an indispensable part of The House Plan, providing detailed information about the building’s exterior appearance, construction requirements, and overall architectural style.
Sections
Sections are a type of technical drawing used in The House Plan to illustrate the vertical elements of a building. They are typically drawn to scale and provide a detailed representation of the building’s interior structure, spatial relationships, and materiality.
Sections are essential for understanding the three-dimensional aspects of a building’s design. They allow architects and builders to visualize the building’s interior layout, the relationship between different levels and spaces, and the structural elements that support the building.
Sections are also crucial for construction purposes. They provide builders with precise measurements and details for framing, wall construction, and the installation of mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems. By carefully following the sections, builders can ensure that the building’s interior is constructed accurately and according to the architect’s design intent.
In addition to their practical value, sections can also be used to showcase the architectural features and interior design of a building. They can be rendered with realistic materials and textures to create visually appealing representations of the building’s interior spaces.
Overall, sections are an indispensable part of The House Plan, providing detailed information about the building’s interior structure, spatial relationships, and materiality. They are essential for both design and construction purposes, and they can also be used to create visually appealing representations of the building’s interior spaces.
Details
Details are an essential component of The House Plan, providing precise instructions and specifications for the construction and finishing of the building. They include:
- Material specifications: Details specify the types and grades of materials to be used for various elements of the building, such as concrete,, and drywall. They also include information about the finishes and coatings to be applied, such as paint, stain, and tile.
- Construction methods: Details provide step-by-step instructions for how to construct different elements of the building, such as framing, roofing, and siding. They include diagrams, sketches, and written descriptions to ensure that the building is constructed according to the architect’s design intent.
- Trim and millwork: Details specify the design and dimensions of trim and millwork elements, such as baseboards, crown molding, and window casings. They also include information about the materials and finishes to be used.
- Hardware: Details specify the types and locations of hardware, such as doorknobs, hinges, and locks. They also include information about the finishes and materials to be used.
Details are essential for ensuring that the building is constructed accurately and according to the architect’s design intent. They provide builders with precise instructions and specifications for every aspect of the construction process, from the foundation to the finishing touches.
Specifications
Specifications are a critical component of The House Plan, providing detailed and comprehensive instructions for the construction and finishing of the building. They complement the drawings and provide essential information that is not easily conveyed through graphical representations alone.
- Materials and finishes: Specifications include a detailed list of all materials and finishes to be used in the construction of the building. This includes everything from the type of concrete used in the foundation to the paint color on the walls. Specifications ensure that all materials and finishes are of the correct quality and that they are installed according to the architect’s design intent.
- Equipment and appliances: Specifications also include a list of all equipment and appliances to be installed in the building. This includes items such as HVAC systems, plumbing fixtures, and kitchen appliances. Specifications provide detailed information about the performance and efficiency of each piece of equipment, ensuring that the building meets the desired standards for comfort and functionality.
- Construction methods: In addition to materials and finishes, specifications also provide instructions on how to construct the building. This includes information on framing techniques, roofing methods, and siding installation. Specifications ensure that the building is constructed in a safe and durable manner, in accordance with building codes and regulations.
- Sustainability features: For buildings that incorporate sustainable design features, specifications provide detailed information on the materials and systems used to achieve sustainability goals. This includes information on energy-efficient appliances, renewable energy systems, and water-saving fixtures. Specifications ensure that the building meets the desired standards for sustainability and environmental performance.
Overall, specifications are an essential part of The House Plan, providing detailed and comprehensive instructions for the construction and finishing of the building. They ensure that the building is constructed in a safe, durable, and sustainable manner, in accordance with the architect’s design intent and building codes and regulations.
Materials list
The materials list is a comprehensive inventory of all the materials required to construct the building. It includes the following information:
- Material type: The materials list identifies the type of each material used in the construction of the building. This includes everything from the concrete used in the foundation to the paint used on the walls.
- Quantity: The materials list specifies the quantity of each material required. This information is essential for ordering and budgeting purposes.
- Dimensions: The materials list includes the dimensions of each material. This information is necessary for cutting and assembling the materials on site.
- Supplier: The materials list may also include the supplier of each material. This information can be helpful for sourcing and purchasing the materials.
The materials list is an essential part of The House Plan. It provides a detailed and comprehensive account of all the materials required to construct the building. This information is essential for accurate ordering and budgeting, as well as for ensuring that the building is constructed according to the architect’s design intent.
The materials list is typically organized by type of material. For example, there may be a section for concrete, a section for lumber, and a section for hardware. This organization makes it easy to find the information you need quickly and easily.
The materials list is also cross-referenced with the drawings and specifications. This ensures that all of the materials listed in the materials list are actually used in the construction of the building. The cross-referencing also makes it easy to find the details of a particular material, such as the size, shape, and finish.
The materials list is an essential tool for contractors and builders. It provides them with the information they need to order and purchase the materials necessary to construct the building. The materials list also helps contractors to track the progress of the construction project and to identify any potential delays or problems.
The materials list is also a valuable resource for architects and engineers. It provides them with a detailed and comprehensive account of all the materials used in the construction of the building. This information can be helpful for designing future buildings and for evaluating the performance of existing buildings.
The materials list is a complex and detailed document. However, it is an essential part of The House Plan. It provides a comprehensive inventory of all the materials required to construct the building. This information is essential for accurate ordering and budgeting, as well as for ensuring that the building is constructed according to the architect’s design intent.
Construction schedule
The construction schedule is a detailed plan that outlines the sequence of activities and tasks required to complete the construction of a building. It is an essential part of The House Plan, as it provides a roadmap for the construction process and helps to ensure that the project is completed on time and within budget.
The construction schedule is typically developed by the contractor in collaboration with the architect and other members of the project team. It takes into account a variety of factors, including the size and complexity of the project, the availability of materials and labor, and the weather conditions. The schedule is typically broken down into smaller tasks, each with its own start and end date. This allows the contractor to track the progress of the project and identify any potential delays or problems.
The construction schedule is a valuable tool for both the contractor and the client. It allows the contractor to plan and coordinate the construction process efficiently, and it provides the client with a clear understanding of the expected timeline for the project. The schedule can also be used to track the progress of the project and to identify any potential delays or problems.
In addition to its practical value, the construction schedule can also be used as a legal document. In the event of a dispute between the contractor and the client, the schedule can be used to determine whether the contractor has met their contractual obligations.
The construction schedule typically includes the following information:
- A list of all the tasks that need to be completed
- The start and end date for each task
- The resources that will be required for each task
- The dependencies between tasks
- The overall timeline for the project
The construction schedule is a living document that is updated regularly as the project progresses. This ensures that the schedule remains accurate and reflects the latest information available.
The construction schedule is a critical tool for managing the construction process. It helps to:
- Plan and coordinate the work of multiple contractors and subcontractors
- Identify and mitigate potential delays and problems
- Track the progress of the project and ensure that it is completed on time and within budget
- Communicate the project timeline to the client and other stakeholders
A well-managed construction schedule can help to ensure that the construction process is efficient and successful.
In addition to the information listed above, the construction schedule may also include the following:
- A list of milestones
- A risk assessment
- A contingency plan
Milestones are important events in the construction process, such as the completion of the foundation, the framing of the walls, and the installation of the roof. A risk assessment identifies potential risks to the project and outlines strategies for mitigating those risks. A contingency plan outlines the steps that will be taken in the event of a delay or problem.
The construction schedule is a complex and detailed document. However, it is an essential tool for managing the construction process and ensuring that the project is completed on time and within budget.
Cost estimates
Cost estimates are an essential part of The House Plan, as they provide a detailed breakdown of the expected costs associated with the construction of a building. This information is critical for both the client and the contractor, as it allows them to make informed decisions about the project and to ensure that the project is completed within budget.
Cost estimates are typically developed by the contractor in collaboration with the architect and other members of the project team. They take into account a variety of factors, including the size and complexity of the project, the cost of materials and labor, and the local building codes and regulations. The cost estimate is typically broken down into smaller categories, such as materials, labor, and overhead costs. This allows the contractor to track the costs of the project and identify any potential areas for savings.
The cost estimate is a valuable tool for both the client and the contractor. It allows the client to understand the expected costs of the project and to make informed decisions about the design and construction of the building. The cost estimate also allows the contractor to plan and budget for the project, and to identify any potential areas for savings.
In addition to its practical value, the cost estimate can also be used as a legal document. In the event of a dispute between the contractor and the client, the cost estimate can be used to determine whether the contractor has met their contractual obligations.
The cost estimate typically includes the following information:
- A detailed breakdown of the costs of materials, labor, and overhead
- A contingency fund to cover unexpected costs
- A timeline for the project, including the estimated start and end dates
- A list of assumptions and exclusions
The cost estimate is a living document that is updated regularly as the project progresses. This ensures that the cost estimate remains accurate and reflects the latest information available.
The cost estimate is a critical tool for managing the construction process. It helps to:
- Plan and budget for the project
- Identify and mitigate potential cost overruns
- Track the progress of the project and ensure that it is completed within budget
- Communicate the project costs to the client and other stakeholders
A well-managed cost estimate can help to ensure that the construction process is efficient and successful.
In addition to the information listed above, the cost estimate may also include the following:
- A life-cycle cost analysis
- A value engineering study
A life-cycle cost analysis takes into account the total cost of owning and operating a building over its lifetime. A value engineering study identifies ways to reduce the cost of a building without sacrificing quality or functionality.
The cost estimate is a complex and detailed document. However, it is an essential tool for managing the construction process and ensuring that the project is completed within budget.
Paragraph after details:
Cost estimates are an essential part of The House Plan, as they provide a detailed breakdown of the expected costs associated with the construction of a building. This information is critical for both the client and the contractor, as it allows them to make informed decisions about the project and to ensure that the project is completed within budget.
Cost estimates are typically developed by the contractor in collaboration with the architect and other members of the project team. They take into account a variety of factors, including the size and complexity of the project, the cost of materials and labor, and the local building codes and regulations. The cost estimate is typically broken down into smaller categories, such as materials, labor, and overhead costs. This allows the contractor to track the costs of the project and identify any potential areas for savings.
Building codes
Building codes are a set of regulations that govern the design, construction, and alteration of buildings. They are in place to ensure that buildings are safe, habitable, and energy-efficient. Building codes are typically developed by local governments and may vary from one jurisdiction to another. However, there are some national and international building codes that are widely adopted.
The International Building Code (IBC) is a model building code that is used by many municipalities in the United States. The IBC sets minimum requirements for the design and construction of buildings, including structural requirements, fire safety requirements, and accessibility requirements. The IBC is updated every three years to ensure that it reflects the latest advances in building technology and safety.
The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) develops a number of codes and standards related to fire safety. The NFPA 101 Life Safety Code is a model code that sets minimum requirements for the design and construction of buildings to protect occupants from fire. The NFPA 101 Life Safety Code is used by many municipalities in the United States and is also referenced by the IBC.
The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) develops standards for the design and construction of HVAC systems. The ASHRAE 90.1 Energy Standard for Buildings Except Low-Rise Residential Buildings is a model code that sets minimum requirements for the energy efficiency of buildings. The ASHRAE 90.1 Energy Standard for Buildings Except Low-Rise Residential Buildings is used by many municipalities in the United States and is also referenced by the IBC.
Building codes are an essential part of The House Plan. They ensure that buildings are safe, habitable, and energy-efficient. Building codes are developed by experts in the fields of architecture, engineering, and fire safety. They are based on the latest research and best practices.
Sustainability features
Energy efficiency
Sustainability features are becoming increasingly important in The House Plan as people become more aware of the environmental impact of buildings. Energy efficiency is one of the most important sustainability features, as it can help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and save money on energy bills. There are a number of ways to improve the energy efficiency of a building, including:
- Insulating the building envelope to reduce heat loss and gain
- Installing energy-efficient windows and doors
- Using energy-efficient appliances and lighting
- Installing a solar energy system
- Using passive solar design principles to heat and cool the building naturally
Water conservation
Water conservation is another important sustainability feature, as it can help to reduce water consumption and protect water resources. There are a number of ways to conserve water in a building, including:
- Installing low-flow toilets and faucets
- Using water-efficient landscaping
- Collecting rainwater for irrigation
- Recycling greywater for non-potable uses
Material selection
The materials used in the construction of a building can also have a significant impact on its sustainability. Sustainable materials are those that are produced in an environmentally friendly way and that have a low environmental impact. There are a number of sustainable materials that can be used in The House Plan, including:
- Recycled materials
- Renewable materials
- Low-VOC materials
- Locally sourced materials
Indoor environmental quality
The indoor environmental quality (IEQ) of a building refers to the quality of the air and other environmental factors inside the building. Good IEQ can help to improve the health and well-being of occupants. There are a number of ways to improve the IEQ of a building, including:
- Providing adequate ventilation
- Controlling moisture levels
- Using low-VOC materials
- Providing access to daylight
Sustainability features can add value to a building by reducing operating costs, improving occupant health and well-being, and reducing the environmental impact of the building. When considering sustainability features for The House Plan, it is important to weigh the initial cost of the features against the long-term benefits.









Related Posts