Slanted Roof House Plans: Design Ideas and Practical Benefits
Slanted roofs, also known as pitched roofs, represent a classic architectural element found across diverse geographical regions and design styles. Their enduring popularity stems from a combination of aesthetic appeal and practical functionality. When considering house plans, understanding the nuances of slanted roof designs is crucial for making informed decisions about both the visual character and performance of a residential structure. This article explores various design ideas associated with slanted roofs, outlines the practical benefits they offer, and highlights key considerations for successful implementation.
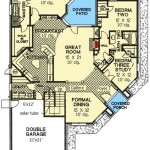
Furthermore, the prevalence of digital resources such as PDF documents containing slanted roof house plans facilitates the accessibility of design information for prospective homeowners and building professionals. These resources often incorporate detailed specifications, schematics, and visual renderings, providing a comprehensive understanding of the project before construction begins.
Aesthetic Variety and Design Considerations
Slanted roofs are far from a monolithic design element; instead, they offer a wide spectrum of aesthetic possibilities. The pitch, or angle, of the roof is a primary determinant of its visual impact. Steeper pitches are often associated with traditional styles like Victorian or Gothic Revival, contributing to a sense of grandeur and formality. Shallower pitches, on the other hand, tend to be more prevalent in contemporary or minimalist designs, promoting a sleek and understated aesthetic. The choice of roofing material also plays a significant role in defining the overall look of the structure. Asphalt shingles, clay tiles, metal roofing, and wood shakes each impart a distinct texture and color palette, impacting the perceived style of the house. Considerations such as color matching with the siding and trim further contribute to a cohesive design.
Beyond the fundamental pitch and material selection, several design variations exist within the realm of slanted roofs. Gable roofs, characterized by two sloping sides that meet at a ridge, are a common and versatile choice. Hip roofs, featuring slopes on all four sides, offer enhanced stability and a more symmetrical appearance. Mansard roofs, with their double-sloped design, provide additional attic space and a unique aesthetic. Gambrel roofs, similar to mansard roofs but with a more pronounced curve, are often associated with barn-style architecture. The selection of a specific roof type is contingent upon factors such as the desired aesthetic, the structural requirements of the building, and budgetary constraints.
Additionally, the integration of elements such as dormers, skylights, and roof windows can enhance the functionality and visual appeal of a slanted roof. Dormers, which project vertically from the roof plane, provide additional headroom and natural light to attic spaces. Skylights and roof windows allow sunlight to penetrate the interior spaces, reducing the reliance on artificial lighting. These elements must be carefully integrated into the overall design to ensure proper weatherproofing and structural integrity.
Architects and designers often use digital modeling software to visualize different slanted roof designs and assess their impact on the building's overall appearance. This allows for experimentation with various pitches, materials, and design elements before finalizing the house plans. Detailed PDF documents containing these plans typically include elevations, sections, and material specifications, providing a comprehensive guide for the construction process.
Practical Benefits of Slanted Roofs
Beyond their aesthetic contributions, slanted roofs offer a range of practical benefits that contribute to the overall performance and longevity of a building. One of the most significant advantages is their ability to effectively shed water and snow. The sloped surface allows precipitation to drain away quickly, minimizing the risk of water damage to the roof structure and interior spaces. This is particularly important in regions with high rainfall or snowfall. The angle of the slope, combined with the choice of roofing material, directly affects the efficiency of water and snow removal.
Slanted roofs also play a role in regulating the temperature of a building. During the summer months, the roof can act as a barrier to solar heat gain, reducing the need for air conditioning. The attic space beneath the roof can provide additional insulation, further minimizing heat transfer. Proper ventilation within the attic is crucial for preventing moisture buildup and maintaining a comfortable indoor environment. Conversely, during the winter months, a well-insulated slanted roof can help to retain heat, reducing energy consumption for heating purposes. The effectiveness of the roof in regulating temperature is dependent upon factors such as the insulation level, the ventilation system, and the reflective properties of the roofing material.
Another practical benefit of slanted roofs is their potential for creating additional living space. The attic space beneath the roof can be converted into bedrooms, offices, or recreational areas. This can significantly increase the usable square footage of a house without expanding the footprint of the building. The availability of sufficient headroom is a key consideration when converting attic space. Dormers can be added to increase headroom and provide natural light, making the space more livable. The structural integrity of the roof must also be assessed to ensure that it can support the additional weight of living space.
Furthermore, slanted roofs can contribute to the structural stability of a building. The angled surfaces distribute weight more evenly than flat roofs, reducing stress on the walls and foundation. This is particularly important in areas prone to earthquakes or high winds. The design of the roof must be carefully engineered to withstand the anticipated loads. Building codes often specify minimum requirements for roof pitch, roofing material, and structural support to ensure safety and durability. PDF documents containing slanted roof house plans typically include detailed structural calculations and specifications to ensure compliance with these codes.
Key Considerations for Implementation
The successful implementation of slanted roof house plans requires careful consideration of several key factors. One of the most important is the selection of appropriate roofing materials. The choice of material should be based on factors such as climate, budget, aesthetic preferences, and durability requirements. Asphalt shingles are a cost-effective and widely available option, while clay tiles and metal roofing offer enhanced durability and longevity. Wood shakes provide a natural and aesthetically pleasing look but require more maintenance. The roofing material must be properly installed to ensure weatherproofing and prevent leaks.
Another crucial consideration is the design and construction of the roof structure. The structure must be strong enough to support the weight of the roofing materials, as well as anticipated snow and wind loads. The design should also incorporate proper ventilation to prevent moisture buildup and ensure adequate insulation. The structural components of the roof, such as rafters, trusses, and sheathing, must be properly sized and connected to ensure stability. PDF documents containing slanted roof house plans typically include detailed structural drawings and specifications to guide the construction process.
Proper insulation is essential for maximizing the energy efficiency of a slanted roof. Insulation can be installed in the attic space, between the rafters, or on top of the roof deck. The type and amount of insulation should be determined based on the climate and the desired level of energy performance. Adequate ventilation is also important for preventing moisture buildup and ensuring the effectiveness of the insulation. Ventilation systems can include soffit vents, ridge vents, and gable vents. These vents allow air to circulate through the attic space, removing moisture and preventing condensation.
Finally, it is important to comply with all applicable building codes and regulations. Building codes specify minimum requirements for roof pitch, roofing materials, structural support, and fire resistance. These codes are designed to ensure the safety and durability of buildings. It is essential to obtain all necessary permits and inspections before beginning construction. PDF documents containing slanted roof house plans should be reviewed by a qualified building official to ensure compliance with all applicable codes and regulations. Failure to comply with building codes can result in costly delays and potentially dangerous structural problems.

House Plans 3d 9 12 Meter 30 39 Feet 3 Bed 2 Bath Shed Roof

House Plans 3d 9 12 Meter 30 39 Feet 3 Bed 2 Bath Shed Roof

Elegant Contemporary House With A Shed Roof Pinoy Eplans

Small House Plan 7x7 Meter Design 23x23 Feet 2 Bed Plans 3d

10 2 Bedroom Shed House Plans And Designs Tiny Craft

Small House Plans 8x10 Meter Design 26x33 Feet 2 Bed 3d
Skillion Roof Types Uses Design

Home Design Ideas And Inspiration For Your Maramani Com

Modern Style House Plan 4 Beds 3 Baths 2448 Sq Ft 497 37 Houseplans Com

Small House Design 6x9 Meter 2 Beds 20x30 Feet Shed Roof Samhouseplans
Related Posts