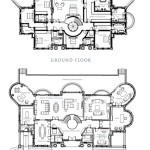
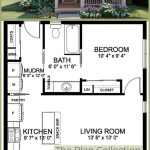
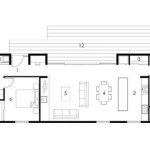
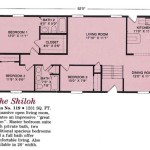
Site House Plans are comprehensive blueprints that guide the construction of a house, taking into account the specific characteristics of the building site. These plans provide detailed instructions for every aspect of the house’s construction, from the foundation to the roof, ensuring that the house is structurally sound and meets the needs of the occupants. For instance, a site house plan might include sections on the foundation, framing, electrical, plumbing, and roofing, each of which provides specific instructions for the materials and techniques to be used.
Site House Plans also consider the unique features of the building site, such as the slope of the land, the availability of utilities, and the presence of trees or other obstacles. This ensures that the house is designed to fit harmoniously into its surroundings and that potential challenges are addressed during the planning stage.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the various components of Site House Plans, exploring the essential elements that contribute to the successful construction of a house.
Here are 9 important points about Site House Plans:
- Define building codes
- Consider site conditions
- Outline foundation details
- Specify framing materials
- Detail electrical systems
- Plan plumbing layout
- Designate room dimensions
- Include window and door specs
- Provide roof framing details
These plans ensure that a house is built to meet specific requirements and is tailored to the unique characteristics of its building site.
Define building codes
Building codes are essential regulations that govern the construction of buildings to ensure safety, structural integrity, and energy efficiency. Site House Plans must adhere to these codes to comply with legal requirements and industry standards.
- Zoning codes establish regulations for land use, building setbacks, and height restrictions, ensuring that the house fits harmoniously into its surroundings.
- Building codes specify minimum standards for structural design, materials, and construction methods to ensure the safety and habitability of the house.
- Fire codes regulate fire safety measures such as smoke detectors, fire extinguishers, and emergency exits to protect occupants in the event of a fire.
- Energy codes promote energy efficiency by setting standards for insulation, windows, and appliances, reducing energy consumption and lowering utility costs for homeowners.
Site House Plans that comply with building codes provide peace of mind that the house is constructed according to established safety and quality standards, ensuring the well-being of occupants and the longevity of the structure.
Consider site conditions
Site conditions play a crucial role in determining the design and construction of a house. Site House Plans must carefully consider these conditions to ensure that the house is well-suited to its environment and meets the needs of the occupants.
- Slope of the land
The slope of the land can significantly impact the design of the house. Houses built on sloping lots may require special foundation designs, retaining walls, and drainage systems to ensure stability and prevent erosion. The slope can also affect the layout of the house, with rooms and living spaces often arranged to take advantage of views or minimize the impact of the slope. - Soil conditions
The type of soil on the building site can influence the foundation design and construction methods. Different soils have different bearing capacities, which determine the type of foundation required to support the weight of the house. Soil conditions can also affect drainage and landscaping, requiring specific measures to prevent water problems and maintain the health of plants. - Utilities
The availability of utilities such as water, electricity, gas, and sewer service must be considered when planning a house. Site House Plans should indicate the location of utility connections and specify the necessary infrastructure to bring these services to the house. The cost and feasibility of extending utilities to the site can impact the overall budget and design of the house. - Vegetation
Existing trees, shrubs, and other vegetation on the building site can affect the placement and design of the house. Site House Plans should consider the preservation of valuable trees and vegetation while also ensuring that they do not pose a hazard to the house or interfere with drainage and access.
By carefully considering site conditions, Site House Plans can create houses that are well-adapted to their surroundings, minimizing potential challenges and maximizing the benefits of the natural environment.
Outline foundation details
The foundation is the critical base of a house, providing support and stability to the entire structure. Site House Plans must outline the foundation details to ensure that the house is built on a solid and durable base.
Foundation type
The type of foundation used depends on several factors, including the soil conditions, the weight of the house, and the local building codes. Common foundation types include:
– Slab-on-grade foundations: A concrete slab poured directly on the ground, suitable for stable soil conditions and smaller houses.
– Basement foundations: A concrete foundation with walls extending below the ground level, providing additional space and protection from the elements.
– Crawl space foundations: A concrete foundation with a shallow crawlspace beneath the house, allowing access to utilities and providing ventilation.
Foundation materials
The materials used for the foundation include concrete, concrete blocks, and stone. Concrete is a popular choice due to its strength, durability, and resistance to moisture. Concrete blocks are also commonly used, as they are relatively inexpensive and easy to install. Stone foundations are less common but can provide a unique and aesthetically pleasing appearance.
Foundation depth
The depth of the foundation depends on the frost line in the area. The frost line is the depth to which the ground freezes during the winter months. Foundations must extend below the frost line to prevent damage from frost heave, which can occur when the ground freezes and expands, pushing the foundation upwards.
Foundation drainage
Proper drainage is essential to prevent water from accumulating around the foundation and causing damage. Site House Plans should include details on drainage systems, such as gutters, downspouts, and French drains, to direct water away from the foundation.
Specify framing materials
The framing of a house is the skeletal structure that provides support and shape to the building. Site House Plans must specify the framing materials to ensure that the house is structurally sound and meets the design requirements.
Framing lumber
The most common framing material is lumber, typically made from wood species such as pine, fir, or spruce. Lumber is used for framing walls, floors, and roofs, and comes in various sizes and grades. The size and grade of lumber used depends on the load-bearing requirements of the structure.
Engineered wood
Engineered wood products, such as plywood, oriented strand board (OSB), and laminated veneer lumber (LVL), are also commonly used in framing. These products are manufactured from wood strands or veneers and are glued together under pressure to create panels or beams. Engineered wood products offer advantages such as increased strength, dimensional stability, and resistance to warping and cracking.
Steel framing
Steel framing is another option for house framing, particularly for larger structures or those with complex designs. Steel framing is made from cold-formed steel sections, which are lightweight and easy to assemble. Steel framing is strong, durable, and resistant to fire and rot.
The choice of framing materials depends on several factors, including the size and complexity of the house, the local building codes, and the budget. Site House Plans should specify the framing materials and provide details on their installation, ensuring that the house is structurally sound and meets the design intent.
Detail electrical systems
Electrical systems are essential for the functionality and safety of a house. Site House Plans must detail the electrical systems to ensure that the house is equipped with a safe and efficient electrical infrastructure.
- Electrical service
The electrical service is the point of entry for electricity into the house. It consists of a meter, a service panel, and the main electrical wires that distribute electricity throughout the house. Site House Plans should specify the size of the electrical service, which is determined by the electrical load of the house, and the location of the service panel. - Branch circuits
Branch circuits are the individual circuits that supply electricity to different areas of the house, such as lighting, outlets, and appliances. Site House Plans should indicate the number and location of branch circuits, as well as the type of wiring and circuit breakers to be used. - Lighting
Site House Plans should include a lighting plan that specifies the location and type of lighting fixtures throughout the house. This includes general lighting, task lighting, and accent lighting. The lighting plan should also consider the energy efficiency of the fixtures and the use of natural light. - Outlets
Outlets are essential for powering appliances and devices. Site House Plans should indicate the location and number of outlets in each room, as well as the type of outlets required (e.g., standard outlets, GFCI outlets, USB outlets). The placement of outlets should consider the furniture layout and the accessibility of devices.
By detailing the electrical systems, Site House Plans ensure that the house has a safe and functional electrical infrastructure that meets the needs of the occupants and complies with electrical codes and standards.
Plan plumbing layout
The plumbing layout is a crucial aspect of Site House Plans, ensuring that the house has a functional and efficient water supply and drainage system.
- Water supply
The water supply system includes the pipes and fixtures that bring water into the house and distribute it to various fixtures, such as sinks, toilets, showers, and appliances. Site House Plans should indicate the location and size of the water supply pipes, as well as the type of fixtures and appliances to be used. The plans should also consider the water pressure and flow rate requirements of the fixtures and appliances. - Drainage system
The drainage system includes the pipes and fixtures that remove wastewater from the house and direct it to a septic tank or municipal sewer system. Site House Plans should indicate the location and size of the drainage pipes, as well as the type of fixtures and appliances that will be connected to the system. The plans should also consider the slope and capacity of the drainage pipes to ensure proper drainage. - Venting system
The venting system is an essential part of the plumbing system that allows air to circulate and prevents the buildup of sewer gases. Site House Plans should indicate the location and size of the vent pipes, as well as the type of fixtures and appliances that will be connected to the system. Proper venting ensures that the drainage system functions efficiently and prevents unpleasant odors. - Water heater
The water heater is responsible for providing hot water to the house. Site House Plans should indicate the location and type of water heater to be installed, as well as the fuel source and capacity requirements. The plans should also consider the energy efficiency and safety features of the water heater.
By planning the plumbing layout carefully, Site House Plans ensure that the house has a reliable and efficient water supply and drainage system that meets the needs of the occupants and complies with plumbing codes and standards.
Designate room dimensions
Room dimensions are crucial in Site House Plans as they determine the size, functionality, and overall layout of the house. Carefully planned room dimensions ensure that the house meets the specific needs and preferences of the occupants while adhering to building codes and industry standards.
- Functional requirements
Room dimensions shouldconsider the functional requirements of each space. For example, bedrooms should be large enough to accommodate a bed, nightstands, and dresser comfortably. Kitchens should provide ample space for cooking, food preparation, and storage. Bathrooms should have sufficient space for fixtures, toiletries, and movement. - Traffic flow
Room dimensions should also consider traffic flow within the house. There should be enough space to move around comfortably without feeling cramped or obstructed. Hallways and doorways should be wide enough to allow for easy passage of people and furniture. The placement of rooms and the flow between them should create a logical and efficient layout. - Furniture arrangement
Room dimensions should take into account the intended furniture arrangement. The size and shape of the room should allow for the placement of furniture in a way that maximizes space utilization and creates a comfortable and inviting atmosphere. The dimensions should consider the size and scale of furniture pieces, as well as the need for circulation space around them. - Building codes
Room dimensions must comply with local building codes and regulations. Building codes often specify minimum room sizes for different types of rooms, such as bedrooms, bathrooms, and living rooms. These codes are in place to ensure health, safety, and habitability standards.
By carefully designating room dimensions, Site House Plans create a house that is both functional and comfortable, meeting the specific needs of the occupants while adhering to industry standards and building codes.
Include window and door specs
Window and door specifications are crucial in Site House Plans as they determine the natural lighting, ventilation, and overall aesthetic appeal of the house. Carefully planned window and door specs ensure that the house meets the specific needs and preferences of the occupants while adhering to building codes and industry standards.
- Window types and sizes
Site House Plans should specify the types and sizes of windows to be installed. The choice of window types depends on factors such as the desired amount of natural light, ventilation, and energy efficiency. The size of the windows should be proportional to the room size and the desired level of natural lighting. - Window placement
The placement of windows is essential for maximizing natural light and creating a visually appealing faade. Site House Plans should indicate the location of windows on each exterior wall, considering factors such as the orientation of the house, views, and privacy concerns. - Door types and sizes
Site House Plans should specify the types and sizes of doors to be installed. The choice of door types depends on the intended use of the door, such as entry doors, interior doors, or patio doors. The size of the doors should be appropriate for the size of the doorway and the flow of traffic. - Door placement
The placement of doors is important for functionality and aesthetics. Site House Plans should indicate the location of doors on each exterior and interior wall, considering factors such as accessibility, privacy, and the overall layout of the house.
By carefully including window and door specs, Site House Plans create a house that is both functional and aesthetically pleasing, meeting the specific needs of the occupants while adhering to industry standards and building codes.
Provide roof framing details
Roof framing details are essential in Site House Plans as they determine the structural integrity, durability, and overall design of the roof. Carefully planned roof framing details ensure that the roof can withstand various loads and weather conditions while meeting the specific needs and preferences of the occupants.
- Roof type and pitch
Site House Plans should specify the type of roof to be installed, such as gable roof, hip roof, or flat roof. The choice of roof type depends on factors such as the architectural style of the house, the local climate, and the desired aesthetic appeal. The roof pitch, which is the angle of the roof slope, should also be indicated as it affects the drainage of rainwater and the overall appearance of the house.
- Rafter design and spacing
Site House Plans should detail the design and spacing of the roof rafters. Rafters are the structural members that support the roof decking and provide the shape to the roof. The size and spacing of the rafters depend on the roof span, the roof load requirements, and the type of roofing material to be used. Proper rafter design ensures the structural integrity of the roof and its ability to withstand wind and snow loads.
- Roof decking and underlayment
Site House Plans should specify the type of roof decking and underlayment to be installed. Roof decking provides a solid base for the roofing material, while underlayment protects the roof from moisture and air infiltration. The choice of decking material depends on factors such as the roof pitch and the type of roofing material to be used. Proper installation of roof decking and underlayment is crucial for the durability and performance of the roof.
- Roofing material
Site House Plans should indicate the type of roofing material to be installed, such as asphalt shingles, metal roofing, or tile roofing. The choice of roofing material depends on factors such as the climate, the architectural style of the house, and the budget. The roofing material should be durable, weather-resistant, and aesthetically pleasing.
By providing detailed roof framing details, Site House Plans ensure that the roof is structurally sound, durable, and meets the specific needs and preferences of the occupants. A well-designed roof protects the house from the elements, enhances its curb appeal, and contributes to the overall longevity of the structure.










Related Posts