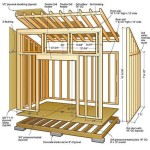
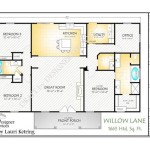
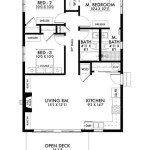
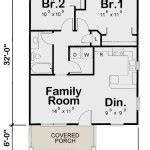
Off Grid Housing Plans are blueprints that provide detailed instructions for constructing a dwelling that is independent from traditional utility connections such as the electrical grid, water mains, or sewer systems. These homes are designed to be self-sufficient, minimizing reliance on external resources and maximizing energy efficiency.
In remote areas where access to utilities is limited or nonexistent, off grid housing plans offer a viable solution for building sustainable and livable homes. They empower individuals and communities to create dwellings that are tailored to their specific needs and resources, fostering greater independence and resilience.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the key considerations for designing and implementing off grid housing plans, including site selection, energy generation systems, water management strategies, and waste disposal methods. By understanding the principles and techniques involved, individuals can embark on the journey of creating their own self-sustaining homes that harmonize with their environmental surroundings.
When considering off grid housing plans, several key points should be taken into account to ensure a sustainable and livable dwelling:
- Site selection
- Energy generation
- Water management
- Waste disposal
- Building materials
- Energy efficiency
- Financial planning
- Legal requirements
- Community involvement
By carefully considering these aspects, off grid housing plans can provide a path towards self-reliance and a harmonious relationship with the environment.
Site selection
Site selection is a crucial step in off grid housing planning, as it determines the viability and sustainability of the future dwelling. Careful consideration should be given to factors such as access to resources, environmental conditions, and legal regulations.
- Proximity to resources: The site should be located near sources of water, such as a river, lake, or aquifer. It should also have access to sunlight for solar energy generation and wind for wind energy generation, if desired.
- Slope and soil conditions: The slope of the land can affect the cost and ease of construction, as well as the potential for erosion and water drainage. Soil conditions should be evaluated to ensure the stability of the foundation and the suitability for gardening or agriculture.
- Climate and weather patterns: The local climate and weather patterns should be taken into account to determine the appropriate building materials and design features. For example, in areas with heavy snowfall, a steeply pitched roof may be necessary to prevent snow accumulation.
- Legal considerations: Zoning regulations and building codes may restrict the construction of off grid homes in certain areas. It is important to research local regulations and obtain necessary permits before purchasing land or beginning construction.
By carefully considering these factors during site selection, individuals can increase the likelihood of creating a sustainable and livable off grid home that meets their specific needs and aspirations.
Energy generation
Energy generation is a critical aspect of off grid housing plans, as it determines the availability of electricity and heat for the dwelling. Several renewable energy sources can be utilized to power off grid homes, each with its own advantages and considerations.
- Solar energy: Solar photovoltaic (PV) panels convert sunlight directly into electricity. They are a popular choice for off grid homes due to their reliability, low maintenance requirements, and scalability. The number of solar panels required depends on the energy needs of the home and the amount of sunlight available at the site.
- Wind energy: Wind turbines harness the kinetic energy of the wind to generate electricity. They are suitable for sites with consistent wind patterns and sufficient open space. The size and type of wind turbine will depend on the wind resources available.
- Hydropower: Hydroelectric systems use the energy of flowing water to generate electricity. They can range from small micro-hydro systems to larger-scale installations. The viability of hydropower depends on the availability of a suitable water source with sufficient flow rate.
- Biomass energy: Biomass energy systems utilize organic materials, such as wood or agricultural waste, to produce heat or electricity. Biomass can be burned in stoves or boilers to generate heat, or converted into biogas through anaerobic digestion to produce electricity.
The choice of energy generation system(s) for an off grid home will depend on factors such as the site’s resources, energy needs, and financial constraints. Hybrid systems that combine multiple renewable energy sources can provide increased reliability and redundancy.
Water management
Water management is essential for off grid living, as access to clean and reliable water is crucial for human health and well-being. Off grid housing plans should incorporate strategies for collecting, storing, and treating water from a variety of sources.
- Rainwater harvesting: Rainwater harvesting systems collect rainwater from rooftops or other surfaces and store it in tanks or cisterns for later use. Rainwater is naturally soft and free of impurities, making it an ideal source of drinking water. The size of the rainwater harvesting system will depend on the amount of rainfall in the area and the water consumption needs of the household.
- Groundwater wells: Groundwater wells tap into underground aquifers to access water. The depth and yield of a well will depend on the local geology and groundwater conditions. Wells require regular maintenance and testing to ensure the quality and safety of the water.
- Surface water sources: Surface water sources, such as rivers, lakes, or ponds, can be used for water supply if properly treated. However, surface water is more susceptible to contamination and requires filtration and disinfection before it is safe for drinking.
- Water conservation: Water conservation measures can reduce the overall water consumption of a household, making it more sustainable to live off grid. This can include installing low-flow appliances and fixtures, practicing water-efficient gardening techniques, and reducing water waste.
By implementing a comprehensive water management plan, off grid homes can ensure a reliable and safe water supply, even in remote or water-scarce areas.
Waste disposal
Waste disposal is an important consideration for off grid housing plans, as proper waste management is essential for protecting human health and the environment. Off grid homes cannot rely on municipal waste collection services, so alternative waste disposal methods must be implemented.
- Composting: Composting is the natural process of breaking down organic waste, such as food scraps, yard waste, and paper products, into a nutrient-rich soil amendment. Composting can be done in a variety of ways, including using a compost bin, pile, or trench. The resulting compost can be used to fertilize gardens and improve soil health.
- Incineration: Incineration involves burning waste at high temperatures to reduce its volume and kill pathogens. Incinerators can be used to dispose of non-recyclable and non-compostable waste, such as plastics and certain types of hazardous waste. However, incineration can also release pollutants into the air, so it is important to use incinerators that meet environmental regulations and to minimize the amount of waste burned.
- Landfills: Landfills are designated areas where waste is buried and compacted. Landfills are typically used to dispose of waste that cannot be recycled, composted, or incinerated. However, landfills can have negative environmental impacts, such as groundwater contamination and methane gas emissions. Therefore, it is important to minimize the amount of waste sent to landfills.
- Waste reduction: The most effective way to manage waste off grid is to reduce the amount of waste produced in the first place. This can be done by choosing reusable products over disposable products, buying in bulk to reduce packaging waste, and repairing or repurposing items instead of throwing them away.
By implementing a comprehensive waste disposal plan, off grid homes can minimize their environmental impact and protect the health of their inhabitants.
Building materials
The choice of building materials for off grid housing plans is crucial for ensuring the durability, sustainability, and energy efficiency of the dwelling. Off grid homes are often located in remote areas with limited access to conventional building materials, so it is important to consider alternative and sustainable options.
- Recycled and reclaimed materials: Recycled and reclaimed materials, such as reclaimed wood, salvaged bricks, and used windows, can be used to reduce the environmental impact of construction and create unique and characterful homes. These materials are often available at a lower cost than new materials and can help to reduce waste.
- Natural and local materials: Natural and local materials, such as stone, timber, and earth, can be used to create homes that are in harmony with the surrounding environment. These materials are often more sustainable than manufactured materials and can help to reduce the carbon footprint of the home.
- Energy-efficient materials: Energy-efficient materials, such as insulated concrete forms (ICFs), straw bales, and triple-glazed windows, can help to reduce the energy consumption of the home and improve its thermal performance. These materials can help to keep the home warm in winter and cool in summer, reducing the need for heating and cooling systems.
- Durable and low-maintenance materials: Durable and low-maintenance materials, such as metal roofing, fiber cement siding, and composite decking, can help to reduce the long-term maintenance costs of the home. These materials are designed to withstand harsh weather conditions and require less frequent repairs and replacements.
By carefully selecting building materials that are sustainable, energy-efficient, and durable, off grid homeowners can create homes that are both environmentally friendly and cost-effective to maintain.
Energy efficiency
Energy efficiency is a key consideration for off grid housing plans, as it can significantly reduce the energy consumption of the home and increase its sustainability. By implementing energy-efficient measures, off grid homeowners can reduce their reliance on fossil fuels, lower their energy bills, and minimize their environmental impact.
- Insulation: Proper insulation is essential for reducing heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer. Insulation can be installed in walls, ceilings, and floors to create a thermal barrier between the interior and exterior of the home. Common insulation materials include fiberglass, cellulose, and spray foam.
- Air sealing: Air sealing involves sealing any gaps or cracks in the building envelope to prevent the infiltration of outside air. This can be done using caulk, weatherstripping, and expanding foam. Air sealing helps to reduce heat loss and improve the efficiency of the home’s heating and cooling systems.
- Energy-efficient windows and doors: Energy-efficient windows and doors are designed to minimize heat loss and heat gain. They typically have double or triple glazing, low-e coatings, and tight-fitting seals. Energy-efficient windows and doors can significantly reduce the energy consumption of the home, especially in climates with extreme temperatures.
- Energy-efficient appliances: Energy-efficient appliances use less energy to perform the same tasks as conventional appliances. Look for appliances with the Energy Star label, which indicates that they meet certain energy efficiency standards. Energy-efficient appliances can help to reduce the overall energy consumption of the home and lower energy bills.
By implementing these energy efficiency measures, off grid homeowners can create homes that are more comfortable, sustainable, and cost-effective to operate.
Financial planning
Financial planning is crucial for the success of any off grid housing project. Off grid homes typically require a significant financial investment, and it is important to carefully consider all of the costs involved before beginning construction. Failure to properly plan for the financial aspects of an off grid home can lead to unexpected expenses, delays, and even abandonment of the project.
- Land acquisition: The cost of land will vary depending on the location, size, and topography of the property. It is important to factor in the cost of land when creating a budget for an off grid home.
- Construction costs: The cost of construction will depend on the size, complexity, and materials used to build the home. Off grid homes often require specialized construction techniques and materials, which can increase the cost of construction.
- Energy system installation: The cost of installing an off grid energy system will depend on the type of system chosen and the size of the home. Renewable energy systems can be expensive to install, but they can save money on energy bills in the long run.
- Water system installation: The cost of installing a water system will depend on the source of water and the type of system chosen. Drilling a well or installing a rainwater harvesting system can be expensive, but it is essential to have a reliable source of water for an off grid home.
In addition to these major costs, there are also a number of other expenses that should be considered when budgeting for an off grid home, such as the cost of appliances, furniture, and tools. It is also important to factor in the ongoing costs of living off grid, such as the cost of fuel for generators, propane for appliances, and maintenance of the home and energy system.
Legal requirements
Before building an off grid home, it is important to research and understand the legal requirements that apply to your specific location. Off grid homes are often subject to different regulations than traditional homes, so it is important to ensure that your plans comply with all applicable laws.
- Building codes: Building codes are regulations that govern the construction of buildings to ensure that they are safe and habitable. Off grid homes may be subject to different building codes than traditional homes, so it is important to check with your local building department to determine what codes apply to your project.
- Zoning laws: Zoning laws regulate the use of land and property. Off grid homes may be restricted in certain zoning districts, so it is important to check with your local zoning department to determine if your property is zoned for off grid use.
- Environmental regulations: Environmental regulations may apply to off grid homes, especially if they are located in sensitive areas such as wetlands or floodplains. It is important to check with your local environmental agency to determine what regulations apply to your project.
- Permit requirements: Building permits are typically required for the construction of any new building, including off grid homes. The permit process ensures that your plans comply with all applicable building codes and zoning laws. It is important to apply for a building permit before beginning construction.
Failure to comply with legal requirements can result in fines, delays, or even the demolition of your off grid home. It is important to do your research and understand the legal requirements that apply to your project before beginning construction.
Community involvement
Community involvement is an important consideration for off grid housing plans, as it can help to ensure the success and sustainability of the project. Off grid homes are often located in remote areas, and community involvement can help to create a sense of belonging and support for the residents.
- Community planning: Involving the community in the planning process can help to ensure that the off grid housing project is compatible with the needs and values of the community. This can involve holding public meetings, conducting surveys, and forming community working groups to gather input and feedback.
- Community ownership: Giving the community a sense of ownership over the off grid housing project can help to ensure its long-term success. This can be done by involving the community in the design and construction of the homes, as well as in the ongoing management and maintenance of the project.
- Community resources: Off grid communities can benefit from sharing resources and knowledge. This can involve creating community gardens, tool libraries, and other shared spaces. It can also involve organizing workshops and training sessions on topics such as renewable energy, water conservation, and sustainable living.
- Community resilience: Off grid communities are often more resilient than traditional communities in the face of challenges such as natural disasters and economic downturns. This is because they have developed strong social networks and are able to rely on each other for support.
By involving the community in the planning and implementation of off grid housing plans, it is possible to create more sustainable, resilient, and livable communities.










Related Posts