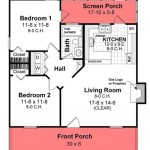
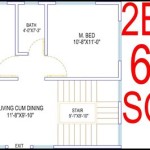
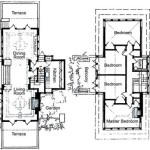
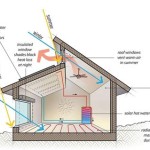
Multifamily housing plans are long-range plans that outline the development and management of multi-family residential properties, typically consisting of apartments, condominiums, or townhouses. These plans provide a framework for addressing housing needs, promoting community development, and enhancing the quality of life for residents.
For instance, the City of Los Angeles has implemented a multifamily housing plan to address its growing housing shortage and affordability crisis. The plan includes initiatives to increase the supply of affordable housing, preserve existing units, and incentivize the development of mixed-income communities.
The main body of this article will delve into the essential components of multifamily housing plans, explore best practices for their development and implementation, and examine their impact on urban development and community well-being.
Multifamily housing plans are comprehensive documents that guide the development and management of multi-family residential properties, such as apartments, condominiums, and townhouses. These plans typically address a range of important considerations, including:
- Housing needs assessment
- Land use and zoning
- Building design and construction
- Rental and ownership models
- Property management
- Community amenities and services
- Environmental sustainability
- Financial feasibility
- Public-private partnerships
- Community engagement
By addressing these and other relevant factors, multifamily housing plans can help to ensure that these developments meet the needs of the community, promote economic growth, and enhance the overall quality of life for residents.
Housing needs assessment
A housing needs assessment is a critical component of any multifamily housing plan. It provides a comprehensive understanding of the current and future housing needs of the community, including the demand for different types of housing, the affordability of housing, and the availability of supportive services.
- Demographic analysis: This involves examining the population characteristics of the community, including age, income, household size, and racial and ethnic composition. Understanding the demographic makeup of the community helps to identify the specific housing needs of different population groups.
- Housing market analysis: This analysis examines the supply and demand for housing in the community, including the availability of different types of housing, the rental and sale prices, and the vacancy rates. It helps to identify any imbalances in the housing market and areas where there is a shortage or surplus of housing.
- Affordability analysis: This analysis examines the affordability of housing in the community, taking into account the income levels of residents and the costs of housing. It helps to identify households that are cost-burdened, meaning they spend a large portion of their income on housing, and those who are at risk of homelessness.
- Analysis of supportive services: This analysis examines the availability of supportive services in the community, such as childcare, healthcare, and transportation. It helps to identify any gaps in services and areas where additional support is needed to ensure that residents have access to the resources they need to live independently.
By conducting a thorough housing needs assessment, communities can gain a clear understanding of their housing needs and develop multifamily housing plans that are tailored to meet those needs.
Land use and zoning
Land use and zoning play a critical role in guiding the development of multifamily housing. Zoning ordinances regulate the use of land and the types of buildings that can be constructed in different areas of a community. These regulations can have a significant impact on the supply of multifamily housing, its affordability, and its overall quality.
- Permitted uses: Zoning ordinances typically specify the types of uses that are permitted in different zoning districts. In order to build multifamily housing, developers must ensure that the land they have acquired is zoned for multifamily use. If the land is not currently zoned for multifamily use, they may need to apply for a zoning change.
- Density and setbacks: Zoning ordinances also regulate the density of development and the setbacks that must be maintained between buildings. Density is typically measured in terms of the number of dwelling units per acre. Setbacks are the minimum distances that buildings must be set back from property lines and other structures. These regulations can impact the number of multifamily units that can be built on a given parcel of land and the overall scale and character of the development.
- Parking requirements: Zoning ordinances often include parking requirements that specify the number of parking spaces that must be provided for different types of development. These requirements can impact the cost of developing multifamily housing and its affordability for residents.
- Design standards: Zoning ordinances may also include design standards that regulate the appearance of buildings and the overall character of the community. These standards can impact the architectural style of multifamily housing developments and the materials that are used in their construction.
By carefully considering land use and zoning regulations, communities can ensure that multifamily housing developments are compatible with the surrounding neighborhood, meet the needs of residents, and contribute to the overall quality of life in the community.
Building design and construction
The design and construction of multifamily housing developments is a complex process that involves a wide range of considerations, including the needs of residents, the surrounding community, and the overall goals of the development. Multifamily housing plans typically include detailed guidelines for building design and construction, covering aspects such as:
- Building type: Multifamily housing developments can include a variety of building types, such as apartments, condominiums, and townhouses. The choice of building type will depend on a number of factors, including the target market, the site constraints, and the overall design goals.
- Unit mix: Multifamily housing developments typically offer a mix of unit sizes and configurations to meet the needs of different households. The unit mix will be determined based on the results of the housing needs assessment and the target market for the development.
- Building height and density: The height and density of multifamily housing developments will be influenced by a number of factors, including the zoning regulations, the site constraints, and the desired scale and character of the development.
- Architectural style: The architectural style of multifamily housing developments can vary widely, depending on the preferences of the developer and the surrounding community. However, it is important to ensure that the architectural style is compatible with the surrounding neighborhood and contributes to the overall aesthetic appeal of the community.
In addition to these general considerations, multifamily housing plans also typically include specific requirements for building construction, such as:
- Building materials: The choice of building materials will impact the cost, durability, and energy efficiency of the development. Multifamily housing plans typically specify the minimum standards for building materials, such as the type of foundation, the exterior cladding, and the roofing materials.
- Energy efficiency: Multifamily housing plans often include energy efficiency requirements to reduce the environmental impact of the development and lower operating costs for residents. These requirements may include measures such as improved insulation, energy-efficient appliances, and renewable energy systems.
- Accessibility: Multifamily housing plans must comply with all applicable accessibility regulations to ensure that the development is accessible to people with disabilities. This may include features such as ramps, elevators, and accessible units.
- Safety and security: Multifamily housing plans typically include features to ensure the safety and security of residents. These features may include secure entrances, surveillance cameras, and emergency call systems.
By carefully considering all of these factors, multifamily housing plans can help to ensure that multifamily housing developments are safe, sustainable, and meet the needs of residents and the community.
Rental and ownership models
Multifamily housing plans typically include a mix of rental and ownership models to meet the diverse needs of residents. Rental housing is typically owned by a landlord or property management company and leased to tenants for a specified period of time. Ownership housing, on the other hand, is owned by the occupant and may include condominiums, townhouses, or single-family homes within a multifamily development.
There are several advantages to rental housing. First, it is typically more affordable than ownership housing, as tenants do not have to pay for the down payment, closing costs, or maintenance and repairs. Second, rental housing offers greater flexibility, as tenants can move more easily if their needs change. Third, rental housing often includes amenities that are not typically found in ownership housing, such as swimming pools, fitness centers, and clubhouses.
However, there are also some disadvantages to rental housing. First, tenants do not have the same level of control over their living space as homeowners. Second, tenants may be subject to rent increases, which can make it difficult to budget for housing costs. Third, tenants may have to deal with unresponsive landlords or property management companies.
Ownership housing offers several advantages over rental housing. First, homeowners have a greater level of control over their living space and can make modifications as they see fit. Second, homeowners can build equity in their homes, which can be a valuable financial asset. Third, homeowners may be eligible for tax breaks and other financial incentives.
However, there are also some disadvantages to ownership housing. First, it is typically more expensive than rental housing, as homeowners have to pay for the down payment, closing costs, and ongoing maintenance and repairs. Second, ownership housing is less flexible than rental housing, as homeowners may have to pay a penalty if they sell their home before the mortgage is paid off. Third, homeowners may be responsible for unexpected expenses, such as major repairs or renovations.
Ultimately, the decision of whether to rent or own a home is a personal one that depends on a variety of factors, including financial situation, lifestyle, and long-term goals.
Property management
Property management is a critical component of multifamily housing plans. It encompasses a wide range of responsibilities, including:
- Tenant relations: Property managers are responsible for building and maintaining positive relationships with tenants. This includes responding to tenant inquiries and requests, resolving conflicts, and enforcing lease agreements.
- Rent collection and accounting: Property managers are responsible for collecting rent from tenants and managing the property’s finances. This includes invoicing tenants, processing payments, and reconciling accounts.
- Maintenance and repairs: Property managers are responsible for maintaining the property in good condition and making necessary repairs. This includes both routine maintenance tasks, such as cleaning and landscaping, and major repairs, such as roof repairs or plumbing emergencies.
- Compliance with laws and regulations: Property managers are responsible for ensuring that the property complies with all applicable laws and regulations, including building codes, fair housing laws, and environmental regulations.
Effective property management is essential for the success of any multifamily housing development. By providing professional and responsive property management services, property managers can help to ensure that the development is well-maintained, financially sound, and attractive to tenants.
Community amenities and services
Community amenities and services play a vital role in the success of multifamily housing developments. They can help to create a sense of community, improve the quality of life for residents, and attract and retain tenants.
- Recreational amenities: Recreational amenities can include a variety of features, such as swimming pools, fitness centers, clubhouses, and playgrounds. These amenities can provide opportunities for residents to relax, socialize, and stay active.
- Community spaces: Community spaces can include common areas, such as lobbies, lounges, and courtyards. These spaces can provide opportunities for residents to gather and interact with each other, which can help to build a sense of community.
- Retail and commercial services: Retail and commercial services can include on-site stores, restaurants, and other businesses. These services can provide convenience and value for residents, and they can also help to create a more vibrant and active community.
- Transportation services: Transportation services can include shuttle buses, car sharing programs, and bike sharing programs. These services can help residents to get around more easily, which can be especially important in communities with limited public transportation options.
By providing a range of community amenities and services, multifamily housing developments can create more livable and desirable communities for residents.
Environmental sustainability
Environmental sustainability is a key consideration in multifamily housing plans. Multifamily housing developments can have a significant impact on the environment, both during construction and operation. By incorporating sustainable design and construction practices, multifamily housing developments can minimize their environmental impact and create healthier living environments for residents.
One important aspect of environmental sustainability in multifamily housing is energy efficiency. Energy-efficient buildings consume less energy, which reduces greenhouse gas emissions and operating costs. Multifamily housing plans can incorporate a variety of energy-efficient features, such as:
- High-performance windows and insulation
- Energy-efficient appliances and lighting
- Solar panels and other renewable energy systems
- Smart building controls
Water conservation is another important aspect of environmental sustainability in multifamily housing. Water-efficient fixtures and appliances can reduce water consumption and save money on utility bills. Multifamily housing plans can incorporate a variety of water-efficient features, such as:
- Low-flow toilets and faucets
- Water-efficient landscaping
- Rainwater harvesting systems
- Graywater reuse systems
Finally, it is important to consider the environmental impact of building materials and construction practices. Multifamily housing plans can incorporate sustainable building materials, such as recycled and renewable materials, and low-VOC (volatile organic compound) materials. Sustainable construction practices can also minimize waste and pollution.
By incorporating sustainable design and construction practices, multifamily housing developments can minimize their environmental impact and create healthier living environments for residents.
Financial feasibility
Financial feasibility is a critical consideration in multifamily housing plans. Multifamily housing developments are complex and expensive projects, and it is important to ensure that they are financially viable before proceeding with construction. Financial feasibility analysis typically includes the following steps:
- Market analysis: This analysis examines the demand for multifamily housing in the target market, including the rental rates that can be achieved and the occupancy rates that can be expected.
- Site analysis: This analysis examines the suitability of the development site, including the land costs, the zoning regulations, and the availability of infrastructure.
- Development costs: This analysis estimates the costs of developing the project, including the construction costs, the financing costs, and the soft costs.
- Operating costs: This analysis estimates the ongoing costs of operating the development, including the property taxes, the insurance costs, and the maintenance costs.
By carefully considering all of these factors, multifamily housing developers can assess the financial feasibility of their projects and make informed decisions about whether to proceed with construction.
Public-private partnerships
Public-private partnerships (PPPs) are a form of collaboration between the public and private sectors to develop and operate multifamily housing developments. PPPs can take a variety of forms, but they typically involve the public sector providing land or other resources, while the private sector provides the financing and expertise to develop and operate the project.
PPPs can be an effective way to finance and develop multifamily housing projects, especially in communities with limited public resources. PPPs can also allow the public sector to share the risks and rewards of development with the private sector, which can help to ensure the success of the project.
There are a number of factors to consider when developing a PPP for a multifamily housing project. These factors include the project’s scope and complexity, the financial capacity of the public and private partners, and the regulatory environment. It is important to carefully structure the PPP agreement to ensure that it is fair and equitable to both parties.
PPPs can be a valuable tool for developing and operating multifamily housing projects. By carefully considering the factors involved and structuring the PPP agreement appropriately, communities can use PPPs to create affordable and sustainable housing for their residents.
One of the key benefits of PPPs is that they can allow the public sector to access private sector expertise and innovation. The private sector often has a wealth of experience in developing and operating multifamily housing projects, and they can bring this expertise to bear on PPP projects.
Another benefit of PPPs is that they can help to reduce the financial burden on the public sector. PPPs allow the public sector to share the costs of development with the private sector, which can free up public resources for other priorities.
However, it is important to note that PPPs are not without their risks. One of the biggest risks is that the public sector may not be able to adequately oversee the private sector partner. This can lead to cost overruns, delays, and other problems.
Community engagement
Community engagement is a critical component of multifamily housing plans. It is important to involve the community in the planning process to ensure that the development meets the needs of the community and is compatible with the surrounding neighborhood.
There are a variety of ways to engage the community in the planning process. One common approach is to hold public meetings to discuss the proposed development and gather feedback from residents. Other methods of community engagement include surveys, focus groups, and workshops.
It is important to provide multiple opportunities for the community to participate in the planning process. This allows residents to provide their input at different stages of the process and helps to ensure that their concerns are addressed.
Community engagement can help to build support for the proposed development and can help to avoid potential conflicts down the road. By involving the community in the planning process, developers can create multifamily housing developments that are responsive to the needs of the community and that are compatible with the surrounding neighborhood.
One of the key benefits of community engagement is that it can help to identify potential problems early in the planning process. By involving the community in the planning process, developers can get feedback on the proposed development and can make changes to the plans to address any concerns that are raised.










Related Posts