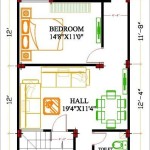
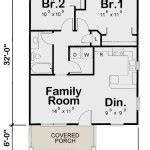
Multi-Family House Floor Plans are architectural drawings that outline the layout and design of a building intended for accommodating multiple families or households. These floor plans are crucial for constructing multi-unit residential structures, such as apartments, condominiums, townhouses, and duplexes.
Floor plans for multi-family houses typically include detailed specifications for each individual unit within the building, encompassing the arrangement of rooms, placement of doors and windows, kitchen and bathroom layouts, and any designated common areas or facilities. By providing a comprehensive blueprint, these plans facilitate the efficient planning, construction, and management of multi-family housing projects.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the intricacies of Multi-Family House Floor Plans, exploring their various types, design considerations, and the role they play in modern urban planning and architectural practices.
Multi-family house floor plans are essential for planning and constructing buildings that accommodate multiple families or households. Here are 10 important points to consider:
- Determine unit mix and size
- Plan for efficient circulation
- Maximize natural light and ventilation
- Design functional and livable spaces
- Consider accessibility and universal design
- Incorporate sustainable features
- Optimize common areas and amenities
- Comply with building codes and regulations
- Involve stakeholders in the design process
- Create adaptable and flexible floor plans
By following these guidelines, architects and developers can create multi-family house floor plans that meet the needs of residents and contribute to the overall livability and sustainability of our communities.
Determine unit mix and size
The unit mix refers to the variety of different unit types and sizes within a multi-family house. This is a crucial decision that will impact the overall design, marketability, and financial viability of the project.
- Studio units: Typically ranging from 400 to 600 square feet, studio units consist of a single main room that combines living, sleeping, and cooking areas.
- One-bedroom units: These units typically measure between 600 and 800 square feet and include a separate bedroom, a living room, a kitchen, and a bathroom.
- Two-bedroom units: With an average size of 800 to 1,200 square feet, two-bedroom units offer two separate bedrooms, a living room, a kitchen, and one or more bathrooms.
- Three-bedroom units: These units are usually larger, ranging from 1,200 to 1,600 square feet, and feature three separate bedrooms, a living room, a kitchen, and two or more bathrooms.
Determining the appropriate unit mix and size involves considering factors such as market demand, target renter demographic, and the overall goals of the development. A diverse unit mix can appeal to a wider range of tenants, while larger units tend to command higher rents.
Plan for efficient circulation
Efficient circulation in multi-family house floor plans is crucial for ensuring the smooth and convenient movement of residents and visitors throughout the building. Well-planned circulation patterns reduce congestion, improve accessibility, and enhance the overall livability of the space.
Here are four key considerations for planning efficient circulation:
- Minimize dead-end corridors: Dead-end corridors are long, narrow hallways that lead to a single destination. They can create a sense of confinement and make it difficult to navigate the building, especially during emergencies.
- Provide multiple access points: Units should have multiple access points to reduce reliance on a single entrance or exit. This is especially important for larger buildings with multiple stories.
- Create clear and intuitive wayfinding: The layout of the building should be easy to understand and navigate. Clear signage and visual cues can help residents and visitors find their way around, reducing confusion and frustration.
- Consider the flow of traffic: The circulation pattern should take into account the natural flow of traffic, such as the movement of residents from their units to common areas or the entry and exit points of the building.
By carefully considering these factors, architects can create multi-family house floor plans that promote efficient circulation and enhance the overall functionality and livability of the building.
Maximize natural light and ventilation
Maximizing natural light and ventilation in multi-family house floor plans is essential for creating healthy, comfortable, and sustainable living spaces. Natural light reduces the need for artificial lighting, saving energy and improving overall well-being. Proper ventilation ensures a constant supply of fresh air, reducing indoor air pollution and promoting good health.
- Position windows and doors strategically: Place windows and doors on opposite sides of rooms to create cross-ventilation, allowing air to flow freely and naturally ventilate the space. Consider the orientation of the building to take advantage of prevailing winds and sunlight.
- Use light-colored finishes: Light-colored walls, ceilings, and floors reflect light, making spaces feel brighter and more inviting. Dark colors absorb light, creating a more somber and enclosed atmosphere.
- Incorporate skylights and clerestory windows: Skylights and clerestory windows allow natural light to penetrate deeper into the building, illuminating interior spaces that may not have direct access to exterior windows.
- Design outdoor spaces that promote airflow: Balconies, patios, and courtyards can provide additional natural ventilation and create a sense of connection to the outdoors.
By incorporating these strategies, architects can create multi-family house floor plans that maximize natural light and ventilation, enhancing the overall health, comfort, and sustainability of the building.
Design functional and livable spaces
Creating functional and livable spaces in multi-family house floor plans is paramount for ensuring the comfort, well-being, and satisfaction of residents. This involves carefully considering the layout, flow, and use of each space within the unit.
Maximize space utilization: Every square foot of space in a multi-family unit should be used efficiently. Clever space-saving solutions, such as built-in storage, multi-purpose furniture, and open floor plans, can help maximize space utilization without compromising comfort or functionality.
Create flexible and adaptable spaces: Multi-family units should be designed to accommodate the changing needs of residents over time. Flexible and adaptable spaces can be easily reconfigured to suit different lifestyles and preferences. For example, a spare bedroom can be converted into a home office or a guest room as needed.
Provide ample storage: Adequate storage space is essential for keeping units organized and clutter-free. Built-in closets, pantries, and under-bed storage can help residents store their belongings efficiently and maintain a sense of order throughout the unit.
Consider accessibility and universal design
Accessibility and universal design principles ensure that multi-family house floor plans are inclusive and equitable, accommodating the needs of individuals with disabilities and the elderly. By incorporating these principles, architects can create living spaces that are safe, comfortable, and accessible to all.
Provide accessible entrances and exits: All entrances and exits should be step-free and wide enough to accommodate wheelchairs and other mobility devices. Ramps or elevators should be provided to ensure access to all levels of the building.
Design accessible bathrooms: Bathrooms should be designed with accessible features such as roll-in showers, grab bars, and adjustable sinks. Doorways should be wide enough to accommodate wheelchairs, and mirrors should be placed at an accessible height.
Incorporate universal design principles: Universal design principles go beyond accessibility requirements to create spaces that are usable by all, regardless of age or ability. This includes features such as lever handles on doors and faucets, adjustable countertops, and non-slip flooring.
Incorporate sustainable features
Incorporating sustainable features into multi-family house floor plans is crucial for reducing the environmental impact of these buildings and promoting the well-being of occupants. Sustainable design strategies can help conserve energy, water, and resources, while also creating healthier and more comfortable living spaces.
Energy efficiency: Energy-efficient features can significantly reduce the energy consumption of multi-family buildings. This can be achieved through measures such as high-performance insulation, energy-efficient windows and appliances, and the use of renewable energy sources like solar panels or geothermal heating and cooling systems.
Water conservation: Water conservation strategies help reduce water usage and protect precious water resources. Low-flow fixtures, drought-tolerant landscaping, and rainwater harvesting systems are all effective ways to conserve water in multi-family developments.
Sustainable materials: Using sustainable building materials can minimize the environmental impact of multi-family construction. These materials may include recycled content, rapidly renewable resources like bamboo or cork, and low-toxicity materials that promote indoor air quality.
Optimize common areas and amenities
Optimizing common areas and amenities in multi-family house floor plans is essential for creating a sense of community and enhancing the overall livability of the building. These shared spaces provide opportunities for residents to socialize, relax, and pursue various activities.
Design inviting and functional common areas: Common areas should be welcoming and encourage interaction among residents. Comfortable seating, ample lighting, and visually appealing dcor can create a pleasant and inviting atmosphere. Multi-purpose spaces that can accommodate a variety of activities, such as game rooms, lounges, or fitness centers, can add value to the building.
Provide outdoor amenities: Outdoor amenities, such as courtyards, balconies, or rooftop terraces, extend the living space beyond individual units and offer opportunities for residents to enjoy the outdoors. These spaces can be designed for relaxation, recreation, or socializing, providing a sense of community and enhancing the overall well-being of residents.
Incorporate amenities that cater to specific needs: Consider the specific needs and preferences of the target resident demographic when planning common areas and amenities. For example, a building with a large number of families might benefit from a dedicated play area or a community garden, while a building geared towards seniors might prioritize accessible features and amenities that promote health and well-being.
By carefully considering the design and functionality of common areas and amenities, architects can create multi-family house floor plans that foster a sense of community, enhance the quality of life for residents, and add value to the overall development.
Comply with building codes and regulations
Adhering to building codes and regulations is paramount when designing multi-family house floor plans. These codes and regulations are established to ensure the safety, habitability, and structural integrity of buildings. By complying with these requirements, architects and developers can create multi-family housing that meets the minimum standards set forth by local authorities.
Building codes typically address a wide range of aspects related to the design and construction of multi-family buildings, including:
- Structural requirements: These codes specify the minimum structural requirements for buildings to ensure their stability and resistance to various forces, such as earthquakes and high winds.
- Fire safety: Building codes include detailed regulations regarding fire safety measures, such as fire-rated walls and doors, smoke detectors, and sprinkler systems.
- Accessibility: Building codes mandate accessibility features for individuals with disabilities, including ramps, elevators, and accessible units.
- Energy efficiency: Many building codes now incorporate energy efficiency requirements to promote sustainable design and reduce energy consumption.
In addition to local building codes, architects must also comply with relevant national or regional building standards and regulations. These may include guidelines for specific construction methods, material specifications, and environmental sustainability.
Complying with building codes and regulations not only ensures the safety and habitability of multi-family housing but also protects the interests of occupants, investors, and the community as a whole. By adhering to these requirements, architects can create responsible and sustainable multi-family developments that meet the needs of present and future generations.
Involve stakeholders in the design process
Actively involving stakeholders in the design process of multi-family house floor plans is crucial for creating living spaces that meet the diverse needs and preferences of the intended occupants. By engaging with stakeholders early on, architects can gain valuable insights, address potential concerns, and ensure that the final design aligns with the desired outcomes.
Stakeholders in the design process typically include:
- Developers and investors: They have a vested interest in the financial viability and marketability of the project.
- Future residents: Their input is essential for creating living spaces that meet their functional and aesthetic needs.
- Property managers: They will be responsible for the day-to-day operations and maintenance of the building, so their insights can help optimize efficiency and reduce future maintenance costs.
- Local authorities: They ensure that the design complies with building codes and zoning regulations.
Effective stakeholder involvement involves ongoing communication and collaboration throughout the design process. This can be achieved through various methods, such as:
- Workshops and focus groups: These provide a platform for stakeholders to share their ideas, discuss concerns, and provide feedback on design proposals.
- Surveys and questionnaires: They can be used to gather quantitative data on stakeholder preferences and priorities.
- Site visits and mock-ups: These allow stakeholders to experience the design firsthand and provide input on spatial relationships and functionality.
Create adaptable and flexible floor plans
In today’s rapidly changing housing market, adaptability and flexibility are essential qualities for multi-family house floor plans. By designing spaces that can easily be reconfigured to meet evolving needs, architects can create multi-family developments that remain relevant and desirable over the long term.
There are several key strategies for creating adaptable and flexible floor plans:
- Use movable partitions and walls: Movable partitions and walls allow spaces to be easily reconfigured to create different room layouts. This is especially useful for creating flexible living spaces that can adapt to changing needs, such as a home office that can be converted into a guest room.
- Incorporate multi-purpose spaces: Multi-purpose spaces can serve multiple functions, depending on the needs of the occupants. For example, a dining room can also be used as a home office or a playroom.
- Provide ample storage: Adequate storage space allows occupants to keep their belongings organized and out of sight, creating a more flexible and adaptable living space.
- Consider future expansion: When designing multi-family house floor plans, it is important to consider the potential for future expansion. This may involve designing spaces that can be easily expanded or reconfigured to accommodate additional bedrooms, bathrooms, or other living areas.
By incorporating these strategies, architects can create multi-family house floor plans that are adaptable and flexible, allowing occupants to customize their living spaces to meet their changing needs and preferences.










Related Posts