Mountain house plans serve as blueprints for residential structures designed to withstand mountainous environments. These plans incorporate specific architectural elements that cater to the challenges posed by rugged terrain, elevation, and climate conditions. For instance, mountain houses often feature steeply pitched roofs to shed snow and wind-resistant materials to endure inclement weather.
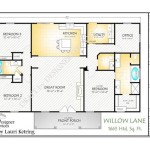
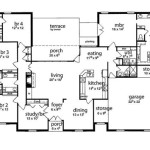
The design of mountain house plans necessitates careful consideration of available space, as mountainous areas frequently have limited buildable land. Compact floor plans and efficient use of space are therefore crucial. Additionally, these plans prioritize natural light and ventilation through strategic placement of windows and skylights to maximize the benefits of the surrounding environment.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the essential components of mountain house plans and explore the key factors to consider when designing and constructing a mountain home.
When designing mountain house plans, several crucial factors must be taken into account:
- Roof pitch
- Wind resistance
- Compact floor plan
- Efficient space use
- Natural light
- Ventilation
- Building materials
- Available space
These elements ensure that mountain homes are both aesthetically pleasing and well-suited to their unique environment.
Roof pitch
Roof pitch, referring to the angle of a roof’s slope, plays a critical role in mountain house plans. In mountainous regions with heavy snowfall, a steep roof pitch is essential for preventing snow accumulation and potential roof collapse. A steeper pitch allows snow to slide off easily, reducing the risk of structural damage. Additionally, a steep roof provides better drainage during rainfall, preventing water from pooling and seeping into the house.
The optimal roof pitch for mountain homes varies depending on the climate and snowfall patterns of the specific location. However, a pitch of 30 degrees or more is generally recommended to ensure effective snow shedding. In areas with extreme snowfall, a pitch of 45 degrees or higher may be necessary. It is important to consult with local building codes and experienced professionals to determine the appropriate roof pitch for the specific mountain environment.
In addition to snow shedding, roof pitch also influences other aspects of mountain house design. A steeper roof pitch can create a more spacious and airy interior, as it allows for higher ceilings and larger windows. However, it is important to consider the increased cost and complexity of constructing a steeper roof, as well as the potential impact on the home’s overall appearance and energy efficiency.
Overall, roof pitch is a crucial design element in mountain house plans, as it directly affects the home’s ability to withstand snow loads, manage water drainage, and create a comfortable and visually appealing living space.
Wind resistance
In mountainous regions, homes are often exposed to strong winds and turbulent weather conditions. Therefore, wind resistance is a crucial factor to consider in mountain house plans.
- Roof shape and design
The shape and design of the roof significantly impact a mountain home’s wind resistance. Roofs with simple, symmetrical shapes, such as gable or hip roofs, are generally more wind-resistant than complex or irregular roof designs. Additionally, avoiding dormers, skylights, and other roof protrusions can help reduce wind resistance and potential damage.
- Roofing materials and installation
The choice of roofing materials and proper installation techniques play a vital role in wind resistance. Metal roofing, such as steel or aluminum, is a popular option for mountain homes due to its durability and ability to withstand high winds. Asphalt shingles and concrete tiles are also commonly used, but they require careful installation and maintenance to ensure wind resistance.
- Wall construction and bracing
The walls of a mountain home must be strong enough to resist wind loads and prevent structural damage. Proper framing and bracing techniques, such as using hurricane ties and shear walls, help to distribute wind forces evenly throughout the structure. Additionally, reinforcing wall corners and openings with additional framing or steel plates can enhance wind resistance.
- Window and door selection and installation
Windows and doors are potential weak points in a mountain home’s defense against wind. Choosing impact-resistant windows and doors, designed to withstand high winds and flying debris, is essential. Proper installation, including the use of weatherstripping and flashing, is also crucial to prevent wind infiltration and damage.
By incorporating these wind-resistant design features into mountain house plans, homeowners can ensure the safety and longevity of their homes in challenging mountain environments.
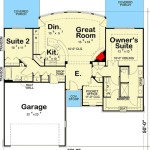
Compact floor plan
In mountainous regions, where buildable land is often limited and valuable, compact floor plans are essential in mountain house plans. A compact floor plan maximizes space efficiency by minimizing hallways,, and other non-essential areas, allowing for a more efficient use of the available space.
Compact floor plans prioritize open and flexible living areas that can serve multiple functions. For example, a combined living room and dining area can create a spacious and inviting gathering space, while a kitchen with an island can double as a dining and food preparation area.
Multi-purpose rooms are another clever space-saving strategy. A room that can serve as both a guest bedroom and a home office, for instance, eliminates the need for a dedicated guest room that may only be used occasionally.
Vertical space is also utilized in compact floor plans. Lofts and mezzanines can add extra sleeping or living space without increasing the home’s footprint. Built-in storage solutions, such as under-stair storage or pull-out drawers, further optimize space utilization.
By adopting a compact floor plan, mountain homes can achieve both space efficiency and a comfortable, livable environment, even within limited square footage.
Efficient space use
Efficient space use is paramount in mountain house plans, where maximizing every square foot is crucial. Here are some key strategies employed to achieve optimal space utilization:
- Multi-purpose rooms
Assigning multiple functions to a single room is a clever way to save space in mountain homes. For example, a guest bedroom can double as a home office or a playroom. Built-in furniture, such as Murphy beds or sofa beds, allows for flexible use of space without sacrificing comfort or style.
- Vertical space utilization
Taking advantage of vertical space is essential in compact mountain homes. Lofts and mezzanines can create additional sleeping or living areas without increasing the home’s footprint. Built-in shelves and cabinets make use of vertical space for storage and display, reducing clutter and maximizing floor space.
- Open floor plans
Open floor plans eliminate unnecessary walls and partitions, creating a more spacious and airy feel. Combining living, dining, and kitchen areas into one large space allows for multiple functions to occur simultaneously without feeling cramped. Open floor plans also facilitate natural light penetration, making the home feel brighter and more inviting.
- Built-in storage solutions
Incorporating built-in storage solutions throughout the mountain home optimizes space utilization and keeps clutter at bay. Custom cabinetry, drawers under stairs, and pull-out shelves maximize storage capacity without taking up valuable floor space. Utilizing the vertical space above cabinets with additional shelves or storage units further increases storage capacity.
By implementing these efficient space use techniques, mountain house plans can create comfortable and functional living spaces, even within limited square footage.
Natural light
Natural light plays a vital role in the design of mountain house plans. In mountainous regions, where homes are often nestled amidst dense forests or surrounded by towering peaks, maximizing natural light can be challenging yet essential for creating comfortable and inviting living spaces.
One key strategy employed in mountain house plans is the use of large windows and skylights. By strategically placing windows on multiple walls and incorporating skylights into the roof, architects can capture natural light from various angles throughout the day. This not only brightens the interior but also reduces the need for artificial lighting, saving energy and creating a more natural and healthy living environment.
Another important consideration is the orientation of the house. In the Northern Hemisphere, south-facing windows allow for maximum sunlight exposure during the winter months, when the sun is lower in the sky. By orienting the house to take advantage of southern exposure, homeowners can harness natural light to warm and illuminate their homes.
In addition to windows and skylights, reflective surfaces can be used to bounce natural light deeper into the interior of mountain homes. Light-colored walls, ceilings, and flooring reflect and distribute natural light, making rooms feel more spacious and. Mirrors can also be strategically placed to reflect light into darker areas or to create the illusion of larger spaces.
By incorporating these natural light design strategies into mountain house plans, architects can create homes that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also healthy and energy-efficient.
Ventilation
Proper ventilation is crucial in mountain house plans to maintain a healthy and comfortable indoor environment. Here are some key considerations and strategies for effective ventilation:
- Cross-ventilation
Cross-ventilation involves strategically placing windows and vents on opposite sides of the house to create airflow. This allows fresh air to enter from one side and stale air to exit from the other, naturally ventilating the home. Cross-ventilation is particularly effective in mountain regions where breezes are common.
- Exhaust fans
Exhaust fans are installed in areas that generate moisture and odors, such as kitchens, bathrooms, and laundry rooms. These fans help remove excess moisture and pollutants from the air, preventing mold growth and ensuring good indoor air quality.
- Ridge vents
Ridge vents are installed along the peak of the roof to allow warm, moist air to escape from the attic. This helps prevent heat buildup and condensation in the attic, which can damage the roof and insulation.
- Passive ventilation
Passive ventilation techniques, such as operable windows and skylights, allow for natural airflow without the use of mechanical systems. By opening windows and skylights when weather permits, homeowners can take advantage of natural breezes and temperature differences to ventilate their homes.
Incorporating these ventilation strategies into mountain house plans is essential for maintaining a healthy and comfortable indoor environment, preventing moisture problems, and ensuring good air quality for the occupants.
Building materials
The choice of building materials for mountain homes is crucial, as they must withstand the unique challenges of mountainous environments, including harsh weather conditions, moisture, and potential seismic activity. Here are some key considerations and commonly used materials for mountain house plans:
Durability and resilience
Mountain homes require durable and resilient building materials that can endure the elements. These materials should be able to withstand extreme temperatures, high winds, heavy snow loads, and moisture. Common choices include:
- Pressure-treated lumber
- Fiber cement siding
- Metal roofing
Insulation and energy efficiency
Insulation is essential for mountain homes to maintain comfortable temperatures year-round and reduce energy consumption. High-performance insulation materials, such as spray foam insulation or cellulose insulation, help minimize heat loss and improve energy efficiency. Additionally, energy-efficient windows and doors with double or triple glazing can further enhance thermal performance.
Moisture resistance
Mountain homes are prone to moisture from rain, snow, and condensation. Choosing moisture-resistant building materials is crucial to prevent rot, mold growth, and structural damage. Materials like pressure-treated lumber, vinyl siding, and moisture-resistant drywall are commonly used in mountain construction.
Fire resistance
In areas with high wildfire risk, fire resistance is a critical consideration for mountain house plans. Non-combustible materials, such as metal roofing, stone veneer, and fire-resistant siding, are recommended to minimize the risk of ignition and spread of fire.
Sustainability and environmental impact
Sustainable building materials are becoming increasingly popular for mountain homes. These materials minimize environmental impact and promote energy efficiency. Examples include recycled materials, bamboo flooring, and solar panels. By incorporating sustainable practices into mountain house plans, homeowners can reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to a greener built environment.
Available space
In mountainous regions, available space for construction is often limited due to steep slopes, rocky terrain, and environmental. Mountain house plans must carefully consider the available space and make the most of every square foot.
One strategy is to utilize vertical space by designing multi-level homes. Split-level designs, lofts, and mezzanines can add additional living areas without increasing the home’s footprint. Built-in shelves, cabinets, and storage units can also be incorporated to maximize vertical space.
Another approach is to design compact floor plans that prioritize essential living areas and eliminate unnecessary spaces. Open floor plans, where multiple functions occur in one large space, can create a sense of spaciousness in smaller homes. Multi-purpose rooms that serve multiple functions, such as a guest bedroom that doubles as a home office, can also save space.
Additionally, careful site planning is crucial in maximizing available space. Orienting the house to take advantage of natural light and views can reduce the need for large windows, saving valuable wall space. Decks and patios can be designed to extend the living area outdoors, creating the illusion of more space.
By employing these strategies, mountain house plans can create comfortable and functional living spaces, even within limited available space.










Related Posts