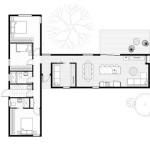
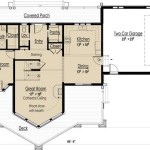
A master plan of house refers to a comprehensive document that outlines the overall design and layout of a residential property. It serves as a blueprint for the construction and development of the house, ensuring that all aspects, from architectural style to functional spaces, are carefully considered and integrated.
Master plans are essential for homeowners who intend to design and build customized houses that meet their specific needs and preferences. By providing a detailed plan, homeowners can visualize the final outcome of their project and make informed decisions regarding materials, construction methods, and space allocation.
In the following sections, we will explore the key elements of a master plan of house, its benefits, and how it contributes to the successful execution of a residential construction project.
A master plan of house is a comprehensive document that outlines the overall design and layout of a residential property. It serves as a blueprint for the construction and development of the house, ensuring that all aspects, from architectural style to functional spaces, are carefully considered and integrated.
- Defines overall design concept
- Determines architectural style
- Outlines room layout and flow
- Specifies material selections
- Integrates structural elements
- Addresses mechanical systems
- Considers energy efficiency
- Ensures code compliance
By providing a detailed plan, homeowners can visualize the final outcome of their project and make informed decisions regarding materials, construction methods, and space allocation. A well-crafted master plan is essential for the successful execution of any residential construction project.
Defines overall design concept
The overall design concept is the foundation of a master plan of house. It establishes the aesthetic direction and functional goals of the project, ensuring that all elements of the house work together harmoniously.
- Architectural style: The design concept defines the architectural style of the house, whether it be traditional, modern, contemporary, or a blend of styles. This decision influences the exterior appearance, rooflines, window and door designs, and overall character of the house.
- Functional flow: The design concept also considers the functional flow of the house, ensuring that spaces are arranged in a logical and efficient manner. This includes the placement of rooms, hallways, and staircases, as well as the relationship between indoor and outdoor spaces.
- Material selections: The design concept guides the selection of materials used in the construction of the house. This includes the choice of siding, roofing, windows, doors, and interior finishes. The materials selected should complement the architectural style and enhance the overall aesthetic of the house.
- Integration of structural elements: The design concept must integrate structural elements into the overall design of the house. This includes the placement of load-bearing walls, columns, and beams, as well as the design of the roof structure. The structural elements must be carefully considered to ensure the safety and stability of the house.
By defining the overall design concept, the master plan of house establishes a clear vision for the project and ensures that all subsequent decisions are made in accordance with the desired aesthetic and functional goals.
Determines architectural style
The architectural style of a house is a defining characteristic that influences its overall appearance, functionality, and character. The master plan of house plays a crucial role in determining the architectural style, ensuring that the design is cohesive and visually appealing.
- Traditional style: Traditional architectural styles, such as Colonial, Victorian, and Craftsman, are characterized by their timeless appeal and familiar design elements. Master plans for traditional houses typically incorporate symmetrical facades, pitched roofs, and decorative details such as moldings, columns, and bay windows.
- Modern style: Modern architectural styles, such as Mid-Century Modern and Contemporary, emphasize clean lines, open floor plans, and large windows. Master plans for modern houses often feature flat roofs, asymmetrical facades, and the use of natural materials such as wood, stone, and glass.
- Contemporary style: Contemporary architectural styles are characterized by their innovative designs and use of cutting-edge materials. Master plans for contemporary houses may incorporate unique geometric shapes, bold colors, and sustainable features such as solar panels and green roofs.
- Eclectic style: Eclectic architectural styles combine elements from different periods and styles to create a unique and personalized design. Master plans for eclectic houses allow for flexibility and creativity, incorporating a mix of traditional, modern, and contemporary elements to achieve a distinctive look.
By carefully considering the architectural style in the master plan of house, homeowners can ensure that the final design reflects their personal preferences and creates a cohesive and visually appealing living environment.
Outlines room layout and flow
The master plan of house outlines the room layout and flow, ensuring that the spaces within the house are arranged in a logical and efficient manner. This involves determining the placement and size of each room, as well as the relationship between different spaces.
- Functional adjacencies: The master plan considers functional adjacencies, which refers to the placement of rooms that are frequently used together in close proximity to each other. For example, the kitchen may be placed adjacent to the dining room, and the master bedroom may be located near the master bathroom.
- Traffic flow: The master plan also addresses traffic flow, ensuring that people can move easily and safely throughout the house. This involves creating clear pathways between rooms and avoiding bottlenecks or obstructions.
- Privacy and separation: The master plan considers privacy and separation by creating distinct zones for different activities. For example, the living room and dining room may be separated from the bedrooms by a hallway, and the master suite may be located in a private wing of the house.
- Natural light and ventilation: The master plan maximizes natural light and ventilation by strategically placing windows and doors. This helps to create a healthy living environment and reduces the need for artificial lighting and ventilation.
By carefully outlining the room layout and flow in the master plan of house, homeowners can create a functional and comfortable living space that meets their specific needs and preferences.
Specifies material selections
The master plan of house specifies the materials that will be used in the construction of the house, including the exterior siding, roofing, windows, doors, and interior finishes. The selection of materials is guided by several factors, including the architectural style of the house, the climate, and the homeowner’s personal preferences.
- Exterior siding: The exterior siding protects the house from the elements and contributes to its overall appearance. Common siding materials include vinyl, fiber cement, wood, and brick. The choice of siding material depends on factors such as durability, maintenance requirements, and cost.
- Roofing: The roofing material protects the house from rain, snow, and other weather conditions. Common roofing materials include asphalt shingles, metal roofing, and tile roofing. The choice of roofing material depends on factors such as durability, energy efficiency, and aesthetic appeal.
- Windows and doors: Windows and doors provide natural light and ventilation, as well as access to the outdoors. The choice of window and door materials depends on factors such as energy efficiency, durability, and security. Common window and door materials include wood, vinyl, and aluminum.
- Interior finishes: Interior finishes, such as flooring, paint, and cabinetry, contribute to the overall aesthetic and functionality of the house. The choice of interior finishes depends on factors such as durability, maintenance requirements, and personal style.
By carefully specifying the material selections in the master plan of house, homeowners can ensure that the final design meets their specific needs and preferences, while also ensuring the durability and functionality of the house.
Integrates structural elements
The master plan of house integrates structural elements into the overall design of the house, ensuring the safety and stability of the structure. This involves carefully considering the placement of load-bearing walls, columns, beams, and the roof structure.
- Load-bearing walls: Load-bearing walls are structural walls that support the weight of the roof and upper floors. The master plan determines the location and orientation of load-bearing walls to ensure that the weight of the house is distributed evenly and safely.
- Columns: Columns are vertical structural elements that support the weight of beams and other structural elements. The master plan specifies the placement and size of columns to ensure that they can adequately support the loads imposed on them.
- Beams: Beams are horizontal structural elements that span between columns or walls to support the weight of the roof and upper floors. The master plan determines the size and spacing of beams to ensure that they can safely carry the loads imposed on them.
- Roof structure: The roof structure is a critical structural element that protects the house from the elements. The master plan specifies the type of roof structure, such as a gable roof, hip roof, or flat roof, as well as the materials and construction methods to be used.
By carefully integrating structural elements into the master plan of house, homeowners can ensure that the final design is structurally sound and can withstand the forces of nature, such as wind, snow, and earthquakes.
Addresses mechanical systems
The master plan of house addresses mechanical systems, which are essential for the comfort, safety, and functionality of the home. These systems include heating, ventilation, air conditioning (HVAC), plumbing, and electrical systems.
- Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems: HVAC systems regulate the temperature and air quality within the house. The master plan determines the type of HVAC system to be installed, such as a central forced-air system, a heat pump, or a geothermal system. The plan also specifies the location and size of HVAC equipment, such as furnaces, air conditioners, and ductwork.
- Plumbing systems: Plumbing systems provide water to fixtures and appliances throughout the house, and remove wastewater. The master plan determines the location and size of water pipes, drains, and fixtures. The plan also specifies the type of plumbing fixtures to be installed, such as sinks, toilets, and bathtubs.
- Electrical systems: Electrical systems provide power to lighting, appliances, and other electrical devices throughout the house. The master plan determines the location and size of electrical panels, wiring, and outlets. The plan also specifies the type of electrical fixtures to be installed, such as light fixtures, switches, and dimmers.
- Fire protection systems: Fire protection systems are essential for the safety of the occupants of the house. The master plan determines the type of fire protection systems to be installed, such as smoke detectors, fire sprinklers, and fire extinguishers. The plan also specifies the location and number of fire protection devices to be installed.
By carefully addressing mechanical systems in the master plan of house, homeowners can ensure that the final design meets their specific needs and preferences, while also ensuring the comfort, safety, and functionality of the home.
Considers energy efficiency
The master plan of house considers energy efficiency to minimize the environmental impact of the home and reduce energy costs. This involves incorporating various energy-efficient measures into the design, such as:
- Insulation: Insulation is a critical energy-efficient measure that reduces heat loss and gain through the walls, roof, and floor of the house. The master plan specifies the type and thickness of insulation to be installed, ensuring that the house meets or exceeds energy efficiency standards.
- Windows and doors: Windows and doors are another important source of heat loss and gain. The master plan specifies the use of energy-efficient windows and doors, which are designed to minimize air leakage and heat transfer.
- Appliances: The master plan also considers the energy efficiency of appliances, such as refrigerators, dishwashers, and washing machines. The plan specifies the use of Energy Star appliances, which meet strict energy efficiency criteria.
- Lighting: Lighting can account for a significant portion of a home’s energy consumption. The master plan specifies the use of energy-efficient lighting fixtures and bulbs, such as LED and CFL bulbs.
By carefully considering energy efficiency in the master plan of house, homeowners can create a home that is not only comfortable and functional but also environmentally friendly and cost-effective to operate.
In addition to the measures listed above, the master plan may also consider other energy-efficient features, such as the use of renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and geothermal heating and cooling systems. By incorporating these features into the design, homeowners can further reduce their environmental impact and energy costs.
Ensures code compliance
The master plan of house ensures code compliance, which is essential for the safety and habitability of the home. Building codes are regulations that establish minimum standards for the design, construction, and alteration of buildings. These codes are in place to protect the health, safety, and welfare of the occupants and the general public.
- Structural safety: Building codes specify requirements for structural safety, ensuring that the house can withstand the forces of nature, such as wind, snow, and earthquakes. The master plan must comply with these requirements to ensure the structural integrity of the house.
- Fire safety: Building codes also specify requirements for fire safety, such as the installation of smoke detectors, fire sprinklers, and fire-resistant materials. The master plan must comply with these requirements to minimize the risk of fire and protect the occupants in the event of a fire.
- Energy efficiency: Building codes may also include requirements for energy efficiency, such as insulation standards and the use of energy-efficient appliances and lighting. The master plan must comply with these requirements to reduce the environmental impact of the home and lower energy costs.
- Accessibility: Building codes may also include requirements for accessibility, such as the provision of ramps and elevators for individuals with disabilities. The master plan must comply with these requirements to ensure that the home is accessible to all occupants.
By ensuring code compliance, the master plan of house helps to ensure that the final design meets the minimum standards for safety, habitability, and accessibility. This is essential for the well-being of the occupants and the protection of the public.










Related Posts