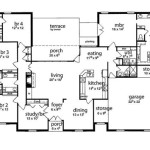
House plans with elevator are architectural designs that incorporate a lift or elevator within the structure of a house. These elevators typically run vertically through multiple floors, providing convenient and accessible transportation between levels for occupants.
They are particularly beneficial for individuals with mobility impairments or for those seeking to age in place in their homes. The installation of an elevator can enhance accessibility, reduce the risk of falls, and promote independence and comfort within the home.
In the following sections, we will explore the various considerations involved in designing and constructing house plans with elevator, including factors such as space requirements, safety features, and aesthetic integration.
When considering house plans with elevator, it’s crucial to keep several important points in mind:
- Space requirements
- Safety features
- Accessibility
- Design integration
- Electrical and mechanical systems
- Maintenance and repair
- Cost
- Building codes
These factors should be carefully evaluated during the planning and construction phases to ensure a functional, safe, and aesthetically pleasing elevator system.
Space requirements
Space requirements for house plans with elevator are a crucial consideration during the design and construction process. The elevator shaft, machine room, and any necessary support structures all require dedicated space within the house.
The size of the elevator shaft is determined by the dimensions of the elevator cab and the required clearances for safety and maintenance. The machine room, which houses the elevator’s motor, controller, and other mechanical components, typically requires a space of at least 50 square feet. Additionally, space may be needed for electrical panels, control systems, and other ancillary equipment.
The location of the elevator within the house should be carefully planned to minimize disruption to the overall floor plan and ensure accessibility to all levels. It is important to consider the proximity of the elevator to stairs, doorways, and other architectural features to ensure smooth traffic flow and avoid potential conflicts.
In multi-story houses, it is important to ensure that the elevator shaft extends through all levels, including the basement or garage, if applicable. This requires careful coordination with structural engineers to ensure that the shaft is properly supported and integrated into the overall building structure.
Overall, the space requirements for house plans with elevator should be carefully evaluated during the planning and design phases to ensure that the elevator system is functional, safe, and aesthetically integrated into the home.
Safety features
Safety features are paramount in house plans with elevator. These features are designed to prevent accidents, protect occupants, and ensure the reliable operation of the elevator system.
Emergency stop button
All elevators must be equipped with an emergency stop button located inside the elevator cab. This button allows passengers to stop the elevator immediately in the event of an emergency, such as a power failure, mechanical malfunction, or a sudden drop.
Interlocks
Interlocks are safety devices that prevent the elevator from moving if certain conditions are not met. For example, door interlocks prevent the elevator from moving if the elevator door is not fully closed and locked. Hoistway interlocks prevent the elevator from moving if there is an obstruction in the elevator shaft.
Overload protection
Overload protection systems prevent the elevator from operating if it is overloaded with passengers or cargo. These systems typically use sensors to measure the weight of the load in the elevator cab and prevent the elevator from moving if the weight exceeds the maximum allowable limit.
Fire safety
Elevators must be equipped with fire safety features to prevent the spread of fire and smoke in the event of a fire. These features include fire-rated doors and walls, smoke detectors, and sprinkler systems.
Regular inspections and maintenance
Regular inspections and maintenance are crucial for ensuring the safety and reliability of elevators. Inspections should be performed by qualified elevator technicians to identify and address any potential issues or hazards.
Accessibility
Barrier-free access
House plans with elevators promote accessibility by providing barrier-free access to different levels of the home. This is especially beneficial for individuals with mobility impairments, such as those using wheelchairs or walkers, as well as for elderly individuals who may have difficulty navigating stairs.
Universal design principles
Elevators can be designed to adhere to universal design principles, which aim to create spaces and products that are accessible to people of all abilities. This includes features such as wide doorways, accessible controls, and tactile surfaces to assist individuals with visual impairments.
Multi-story homes
In multi-story homes, elevators provide a convenient and safe way for occupants to move between floors, eliminating the need to climb stairs. This can be particularly important for individuals with mobility challenges, as well as for families with young children or elderly members who may require assistance.
Aging in place
House plans with elevators can support aging in place, allowing individuals to remain in their homes as they age. By providing accessibility to all levels of the home, elevators can help reduce the risk of falls and injuries, and promote independence and quality of life for seniors.
Design integration
Aesthetic considerations
Elevators can be seamlessly integrated into the overall design of the house to complement the architectural style and interior dcor. The elevator cab, shaft, and landing doors can be customized to match the aesthetic of the home, using materials such as wood, metal, glass, and stone.
Space optimization
Elevators can be designed to optimize space utilization within the home. For example, they can be placed in corners or along walls to minimize the impact on the floor plan. Compact elevator designs are available to fit into smaller spaces, making them suitable for a wider range of homes.
Multi-purpose spaces
Elevators can be incorporated into multi-purpose spaces to maximize functionality. For instance, the elevator shaft can be enclosed within a closet or storage area, providing additional storage space without compromising the elevator’s accessibility.
Visual impact
Elevators can be designed to create a visual impact within the home. They can become a focal point or a statement piece, adding architectural interest and enhancing the overall aesthetic appeal of the space.
Electrical and mechanical systems
House plans with elevator require careful consideration of electrical and mechanical systems to ensure the safe and efficient operation of the elevator.
- Electrical systems
The electrical system for an elevator includes the power supply, control system, and wiring. The power supply provides the electrical power required to operate the elevator motor, drive system, and other components. The control system manages the elevator’s operation, including door opening and closing, level selection, and emergency stop functions. The wiring connects all of the electrical components and ensures the proper flow of electricity throughout the system.
- Mechanical systems
The mechanical systems for an elevator include the elevator cab, shaft, hoistway, and drive system. The elevator cab is the passenger compartment that moves up and down the shaft. The shaft is the vertical space through which the elevator cab travels. The hoistway is the area surrounding the shaft that contains the elevator machinery and equipment. The drive system powers the elevator cab’s movement and ensures its safe and controlled operation.
- Safety features
Elevators must be equipped with various safety features to prevent accidents and protect passengers. These features include emergency stop buttons, interlocks, overload protection systems, and fire safety systems. Emergency stop buttons allow passengers to stop the elevator immediately in the event of an emergency. Interlocks prevent the elevator from moving if certain conditions are not met, such as if the elevator door is not fully closed. Overload protection systems prevent the elevator from operating if it is overloaded with passengers or cargo. Fire safety systems help to prevent the spread of fire and smoke in the event of a fire.
- Maintenance and inspection
Regular maintenance and inspection are crucial for ensuring the safe and reliable operation of an elevator. Maintenance tasks include lubricating moving parts, checking electrical connections, and testing safety features. Inspections should be performed by qualified elevator technicians to identify and address any potential issues or hazards.
Proper design, installation, and maintenance of electrical and mechanical systems are essential for the safe and efficient operation of elevators in house plans.
Maintenance and repair
Regular maintenance
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring the safe and reliable operation of an elevator. Maintenance tasks should be performed by qualified elevator technicians and typically include the following:
- Lubricating moving parts
- Checking electrical connections
- Testing safety features
- Inspecting the elevator cab, shaft, and hoistway for any signs of wear or damage
- Cleaning the elevator cab and shaft
Regular maintenance helps to identify and address potential issues before they become major problems, reducing the risk of breakdowns and accidents.
Repairs
Despite regular maintenance, elevators may occasionally require repairs. Repairs should always be performed by qualified elevator technicians to ensure the safety and reliability of the elevator system. Common repairs include:
- Replacing worn or damaged components
- Fixing electrical faults
- Adjusting the elevator’s control system
- Repairing the elevator cab, shaft, or hoistway
The cost of repairs can vary depending on the nature of the problem and the extent of the damage. It is important to have a regular maintenance plan in place to help prevent major repairs and extend the lifespan of the elevator.
Emergency repairs
In the event of an elevator breakdown or emergency, it is crucial to contact a qualified elevator technician immediately. Emergency repairs may be necessary to restore the elevator to working order and ensure the safety of passengers. Common emergency repairs include:
- Resetting the elevator’s control system
- Freeing trapped passengers
- Repairing damaged doors or gates
- Addressing electrical or mechanical faults that pose an immediate safety hazard
Emergency repairs should be performed as soon as possible to minimize the risk of further damage or injury.
Cost
Initial installation cost
The initial installation cost of an elevator in a house can vary widely depending on several factors, including the type of elevator, size of the elevator, number of floors served, and complexity of the installation. Generally, the cost of a residential elevator can range from $20,000 to $100,000 or more.
Type of elevator
The type of elevator chosen can significantly impact the installation cost. Hydraulic elevators are typically the most affordable option, followed by traction elevators and pneumatic elevators. The choice of elevator type depends on factors such as the height of the building, the number of floors served, and the desired speed and capacity of the elevator.
Size of the elevator
The size of the elevator cab, as well as the capacity and weight rating, can also affect the installation cost. Larger elevators with higher weight capacities require more powerful motors and support structures, which can increase the overall cost.
Number of floors served
The number of floors served by the elevator is another important factor that influences the installation cost. Each additional floor requires additional shaft height, wiring, and controls, which can add to the overall cost.
Building codes
Importance of building codes
Building codes are essential regulations that govern the design, construction, and maintenance of buildings, including house plans with elevator. These codes are established to ensure the safety, structural integrity, and accessibility of buildings, and they vary across different regions and jurisdictions.
Elevator-specific building codes
Building codes typically include specific requirements for the design and installation of elevators in residential buildings. These requirements cover various aspects of elevator systems, including:
- Shaft dimensions: Building codes specify the minimum dimensions for elevator shafts to ensure adequate space for the elevator cab, machinery, and maintenance access.
- Doorway clearances: Codes regulate the minimum width and height of elevator doorways to allow for safe and accessible entry and exit.
- Cab size and capacity: Codes establish minimum cab sizes and weight capacities to accommodate a specified number of passengers and any necessary mobility devices.
- Safety features: Building codes mandate the inclusion of essential safety features such as emergency stop buttons, interlocks, and overload protection systems.
- Fire safety: Codes require elevators to be equipped with fire-rated doors and walls, smoke detectors, and sprinkler systems to prevent the spread of fire and smoke in the event of a fire.
Compliance with building codes
Compliance with building codes is mandatory for all construction projects, including those involving house plans with elevator. Failure to comply with building codes can result in safety hazards, construction delays, and legal consequences. It is essential to work with qualified architects, engineers, and contractors who are familiar with the applicable building codes to ensure that the elevator system is designed and installed according to the required standards.










Related Posts