House plans design encompasses the conceptualization and detailed representation of a building’s structure, layout, and functionality. It provides a blueprint for the construction of a home, ensuring compliance with building codes, aesthetics, and the homeowner’s desired features. For instance, a family opting for a spacious and energy-efficient residence will heavily rely on house plans design to guide their construction.
The design process typically begins with a consultation between the architect or designer and the homeowner to establish their requirements. The plans include floor plans, elevations, cross-sections, and other drawings that precisely define the home’s dimensions, room arrangements, window placements, and structural elements. House plans design serves as a crucial communication tool between architects, builders, and contractors, ensuring that the finished home aligns with the initial vision.
In the following sections, we will delve into the intricacies of house plans design, exploring its various aspects, including types of house plans, considerations for design, and the latest trends shaping the industry. By understanding the principles and nuances of house plans design, homeowners can actively participate in creating a dream home that meets their unique needs and preferences.
House plans design encompasses various important aspects that contribute to the overall success of a building project. Here are eight key points to consider:
- Site Planning: Optimizing the home’s placement on the lot.
- Floor Plan Design: Arranging rooms for functionality and flow.
- Exterior Design: Determining the home’s architectural style and curb appeal.
- Structural Design: Ensuring the home’s safety and stability.
- Mechanical Design: Planning for heating, cooling, plumbing, and electrical systems.
- Interior Design: Selecting finishes, fixtures, and furnishings.
- Energy Efficiency: Incorporating sustainable features to reduce energy consumption.
- Code Compliance: Adhering to building codes and regulations.
By carefully considering these points, homeowners and architects can work together to create house plans that meet their specific needs and aspirations.
Site Planning: Optimizing the home’s placement on the lot.
Site planning is a crucial aspect of house plans design that involves carefully positioning the home on the lot to maximize its potential and address various factors. It encompasses considerations such as maximizing natural light, optimizing views, minimizing environmental impact, and ensuring proper drainage.
- Orientation: Determining the best orientation of the home on the lot to take advantage of natural light, prevailing breezes, and views. By strategically placing windows and outdoor spaces, homeowners can create a comfortable and energy-efficient living environment.
- Grading and Drainage: Proper grading and drainage are essential to prevent water accumulation around the home’s foundation. Site planning involves designing a grading plan that ensures water flows away from the home, protecting it from moisture damage and potential flooding.
- Landscaping: The placement of trees, shrubs, and other landscaping elements can significantly impact the home’s appearance and functionality. Site planning considers the integration of landscaping to enhance privacy, provide shade, and create a cohesive outdoor living space.
- Access and Circulation: Site planning also involves designing driveways, walkways, and other access points to ensure convenient and safe movement around the property. Proper circulation planning enhances the functionality and accessibility of the home.
By carefully considering these factors during site planning, homeowners can create a well-integrated home that harmonizes with its surroundings and maximizes its potential for comfort, energy efficiency, and aesthetic appeal.
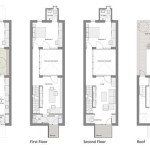
Floor Plan Design: Arranging rooms for functionality and flow.
Floor plan design is a fundamental aspect of house plans design that focuses on the arrangement of rooms within the home to ensure optimal functionality and flow. It involves carefully considering the relationships between different spaces, traffic patterns, and the overall livability of the home.
One of the key principles of floor plan design is the concept of adjacencies. This refers to the placement of rooms that are frequently used together in close proximity to each other. For example, the kitchen, dining room, and living room are often arranged in an open floor plan to facilitate easy movement and interaction between these common areas. Similarly, bedrooms are typically positioned near bathrooms for convenience.
Another important consideration in floor plan design is traffic flow. The layout of the home should allow for smooth and efficient movement throughout the space. Wide hallways, clear sightlines, and well-defined entrances and exits help prevent congestion and create a more comfortable living environment. Designers also consider the placement of doors and windows to maximize natural light and ventilation, reducing the need for artificial lighting and improving the overall ambiance of the home.
Finally, floor plan design should take into account the specific needs and preferences of the homeowners. Factors such as family size, lifestyle, and personal tastes should be reflected in the layout of the home. For example, a family with young children may prefer a floor plan with a separate playroom or family room, while a couple may opt for a more open and spacious design. By carefully considering these factors, architects and designers can create floor plans that not only meet the functional requirements of the home but also enhance the overall quality of life for its occupants.
Well-designed floor plans are essential for creating homes that are comfortable, efficient, and enjoyable to live in. They form the foundation for a successful house plans design and set the stage for a harmonious and functional living space.
Exterior Design: Determining the home’s architectural style and curb appeal.
Exterior design is a crucial aspect of house plans design that encompasses the overall appearance and architectural style of the home. It involves carefully selecting materials, colors, textures, and architectural elements to create a visually appealing and cohesive exterior that complements the surrounding environment and reflects the homeowner’s personal preferences.
One of the primary considerations in exterior design is the choice of architectural style. The architectural style refers to the overall aesthetic and design principles that guide the home’s exterior appearance. Common architectural styles include traditional, modern, contemporary, rustic, and craftsman, each with its own distinct characteristics and elements. Homeowners should carefully consider the architectural style that best aligns with their tastes and the overall character of the neighborhood.
Another important aspect of exterior design is curb appeal. Curb appeal refers to the attractiveness and desirability of a home from the street view. It encompasses factors such as the home’s facade, landscaping, and overall presentation. To enhance curb appeal, designers consider the use of inviting colors, attractive landscaping, well-maintained lawns, and architectural details that create a visually appealing and welcoming exterior.
Exterior design also involves selecting appropriate materials and finishes. The choice of materials can significantly impact the home’s durability, energy efficiency, and overall appearance. Common exterior materials include brick, stone, stucco, siding, and wood. Designers carefully consider the combination of materials and finishes to create a cohesive and visually appealing exterior that complements the home’s architectural style and enhances its curb appeal.
Well-designed exteriors not only enhance the aesthetic appeal of the home but also contribute to its overall functionality and value. By carefully considering factors such as architectural style, curb appeal, and material selection, homeowners can create exteriors that are both beautiful and practical, reflecting their personal tastes and enhancing the overall character of their home.
Structural Design: Ensuring the home’s safety and stability.
Structural design is a critical aspect of house plans design that focuses on ensuring the safety and stability of the home. It involves carefully calculating and designing the structural elements of the home to withstand various loads and forces, including gravity, wind, and seismic activity. Structural design aims to create a home that is strong, durable, and able to withstand the rigors of everyday use and potential environmental challenges.
One of the primary tasks of structural design is to determine the appropriate foundation system for the home. The foundation is the base of the home and is responsible for transferring the weight of the structure to the ground. The type of foundation system selected will depend on factors such as the soil conditions at the building site and the overall design of the home. Common foundation systems include slab-on-grade foundations, crawl space foundations, and basement foundations.
Once the foundation system is determined, the structural designer will design the framing system for the home. The framing system is the skeleton of the home and provides the support for the walls, roof, and other structural elements. The framing system typically consists of beams, columns, joists, and trusses, which are carefully engineered to carry the loads imposed on the home.
In addition to designing the foundation and framing system, structural designers also consider other structural elements, such as shear walls, moment frames, and braced frames. These elements are designed to resist lateral forces, such as those caused by wind and earthquakes. The structural designer will carefully calculate the size and placement of these elements to ensure that the home can withstand the anticipated lateral loads.
Well-designed structural systems are essential for creating homes that are safe and durable. By carefully considering factors such as foundation systems, framing systems, and lateral force resistance, structural designers ensure that homes can withstand the various loads and forces they may encounter, providing peace of mind and protection for the occupants.
Mechanical Design: Planning for heating, cooling, plumbing, and electrical systems.
Mechanical design is a crucial aspect of house plans design that focuses on planning and integrating the mechanical systems essential for the comfort and functionality of the home. These systems include heating, cooling, plumbing, and electrical systems, which are carefully designed to meet the specific needs of the homeowners and the unique characteristics of the home.
- Heating and Cooling Systems:
Heating and cooling systems are designed to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature throughout the year. The choice of heating and cooling system depends on factors such as the climate, the size of the home, and the homeowner’s budget. Common heating systems include furnaces, heat pumps, and radiant floor heating, while cooling systems include central air conditioning, ductless mini-splits, and evaporative coolers.
- Plumbing Systems:
Plumbing systems are responsible for supplying water to the home’s fixtures and appliances, as well as removing wastewater. The design of the plumbing system includes determining the location and size of water pipes, drains, and fixtures, as well as ensuring compliance with plumbing codes and regulations. Proper plumbing design ensures a reliable and efficient water supply and drainage system for the home.
- Electrical Systems:
Electrical systems provide power to the home’s lighting, appliances, and other electrical devices. The design of the electrical system involves calculating the electrical load, determining the appropriate wiring and circuit breaker sizes, and ensuring that the system meets electrical codes and safety standards. A well-designed electrical system ensures a safe and reliable power supply for the home.
- Ventilation Systems:
Ventilation systems are designed to circulate air throughout the home, removing stale air and introducing fresh air. Proper ventilation helps maintain indoor air quality, prevents moisture buildup, and reduces the risk of mold and mildew growth. Ventilation systems can include natural ventilation, mechanical ventilation, or a combination of both.
By carefully considering and integrating these mechanical systems during the house plans design process, architects and designers can create homes that are not only comfortable and functional but also energy-efficient and safe.
Interior Design: Selecting finishes, fixtures, and furnishings.
Interior design encompasses the selection of finishes, fixtures, and furnishings that define the aesthetic and functional aspects of a home’s interior spaces. It involves carefully considering the interplay of colors, textures, patterns, and materials to create a cohesive and visually appealing living environment that reflects the homeowners’ personal style and meets their functional needs.
One of the key aspects of interior design is the selection of finishes, which include flooring, wall coverings, and ceiling treatments. Flooring options range from hardwood and tile to carpet and laminate, each with its own unique characteristics and suitability for different rooms. Wall coverings can include paint, wallpaper, or decorative panels, and play a significant role in setting the tone and ambiance of a space. Ceiling treatments can enhance the overall aesthetic appeal and functionality of a room, with options such as coffered ceilings, tray ceilings, or simply painted or textured finishes.
Fixtures, such as lighting, plumbing fixtures, and hardware, are another important consideration in interior design. Lighting fixtures provide both functional illumination and aesthetic appeal, and come in a wide variety of styles and types, including chandeliers, pendants, recessed lighting, and sconces. Plumbing fixtures, including sinks, faucets, and toilets, should be selected not only for their functionality but also for their aesthetic compatibility with the overall design scheme. Hardware, such as door handles, cabinet knobs, and drawer pulls, can add subtle yet impactful details to a space, and should be chosen to complement the finishes and fixtures.
Finally, furnishings, including furniture, textiles, and accessories, complete the interior design scheme. Furniture selection involves choosing pieces that are not only comfortable and functional but also aesthetically pleasing and in harmony with the overall design concept. Textiles, such as curtains, rugs, and upholstery fabrics, add warmth, texture, and color to a space, and should be carefully selected to complement the finishes and furnishings. Accessories, such as artwork, plants, and decorative objects, provide the finishing touches that personalize a space and reflect the homeowners’ unique style.
By carefully considering and integrating these elements, interior designers create living spaces that are not only visually appealing but also highly functional and reflective of the homeowners’ personalities and lifestyles.
Well-executed interior design enhances the overall quality of life within a home, creating spaces that are both beautiful and comfortable. It is a collaborative process that involves the homeowner, interior designer, and other professionals, working together to transform a house into a dream home.
Energy Efficiency: Incorporating sustainable features to reduce energy consumption.
Energy efficiency is a crucial aspect of house plans design that focuses on incorporating sustainable features and design strategies to minimize the home’s energy consumption and environmental impact. By carefully considering factors such as insulation, window placement, and the use of renewable energy sources, architects and designers can create homes that are not only comfortable and affordable to operate but also contribute to a greener and more sustainable future.
- Proper Insulation:
Insulation plays a vital role in reducing heat transfer through the home’s envelope, minimizing energy loss and improving thermal comfort. Proper insulation in walls, ceilings, and floors helps maintain a stable indoor temperature, reducing the need for heating and cooling systems to work harder.
- Energy-Efficient Windows and Doors:
Windows and doors are potential sources of heat gain and loss. Energy-efficient windows and doors feature double or triple glazing, low-e coatings, and tight seals to minimize heat transfer and improve insulation. This helps reduce the load on HVAC systems and lowers energy consumption.
- Passive Solar Design:
Passive solar design utilizes the sun’s energy to heat and light the home naturally. By carefully positioning windows and incorporating thermal mass, homes can capture and store solar heat during the day, reducing the need for artificial heating sources. This strategy is particularly effective in climates with ample sunlight.
- Renewable Energy Sources:
Incorporating renewable energy sources, such as solar panels or geothermal systems, can significantly reduce the home’s reliance on fossil fuels. Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity, while geothermal systems harness the earth’s natural heat to provide heating and cooling. These renewable energy sources contribute to energy independence and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
By implementing these energy-efficient features and design strategies, house plans can create homes that are more sustainable, environmentally friendly, and cost-effective to operate. Energy-efficient homes not only reduce energy consumption and lower utility bills but also contribute to a cleaner and healthier environment for present and future generations.
Code Compliance: Adhering to building codes and regulations.
Code compliance is a fundamental aspect of house plans design that ensures the home adheres to all applicable building codes and regulations. Building codes are established by local, state, and national authorities to safeguard the health, safety, and welfare of building occupants. Compliance with these codes is not only a legal requirement but also essential for a safe and habitable home.
- Structural Safety:
Building codes specify minimum requirements for structural integrity to withstand various loads and forces, such as gravity, wind, and seismic activity. Code-compliant designs ensure the home is structurally sound and can resist potential hazards, providing a safe living environment for the occupants.
- Fire Safety:
Building codes include stringent fire safety regulations to minimize the risk of fire and protect occupants in the event of a fire. These regulations cover aspects such as fire-resistant materials, smoke detectors, sprinkler systems, and emergency exits, ensuring that the home is equipped to prevent and mitigate fire hazards.
- Health and Sanitation:
Codes address health and sanitation concerns by regulating aspects such as ventilation, plumbing, and sewage systems. Proper ventilation ensures air quality and prevents moisture buildup, while adequate plumbing and sewage systems maintain a sanitary environment and prevent the spread of disease.
- Energy Efficiency:
Building codes increasingly incorporate energy efficiency standards to promote sustainable building practices. These standards may include requirements for insulation, energy-efficient appliances, and renewable energy sources, contributing to reduced energy consumption and environmental impact.
By adhering to building codes and regulations, house plans design ensures the home meets the minimum safety, health, and energy efficiency standards required by law. Code compliance not only protects the occupants but also enhances the home’s value and marketability, demonstrating that it has been constructed according to established best practices and industry standards.







Related Posts