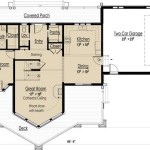
House Plans Colonial refer to the architectural designs and blueprints for constructing residential buildings inspired by the colonial era, particularly in the United States. These plans typically incorporate elements of traditional colonial architecture, characterized by symmetrical facades, gabled roofs, and formal interiors.
The popularity of house plans colonial stems from their timeless aesthetic and historical significance. They offer a classic and elegant look that evokes the charm and grandeur of the colonial era. Homeowners who choose house plans colonial often desire a residence that reflects the historical heritage and architectural traditions of their region.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the key features and variations of house plans colonial. We will explore the different types of colonial styles, provide tips for selecting the right plan, and showcase examples of beautiful colonial homes that demonstrate the enduring appeal of this architectural style.
Here are 9 important points about House Plans Colonial:
- Inspired by colonial era architecture
- Symmetrical facades
- Gabled roofs
- Formal interiors
- Timeless aesthetic
- Historical significance
- Reflects regional heritage
- Variety of colonial styles
- Enduring appeal
House Plans Colonial offer a classic and elegant look, steeped in history and architectural tradition.
Inspired by colonial era architecture
House Plans Colonial draw inspiration from the architectural styles prevalent during the colonial era in the United States, primarily from the 17th to the 19th centuries. These styles reflect the cultural influences of European settlers, particularly those from England, France, Spain, and the Netherlands.
- Georgian: Georgian architecture, popular in the 18th century, is characterized by its symmetrical facades, rectangular shape, and hipped or gabled roofs. Georgian houses often feature prominent entryways with pediments and Palladian windows.
- Federal: Federal architecture, which emerged in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, is known for its delicate details and restrained ornamentation. Federal houses typically have square or rectangular shapes, with symmetrical facades and sidelights flanking the main entrance.
- Cape Cod: Cape Cod architecture, originating in the 17th century, is a simple and practical style that is well-suited to coastal regions. Cape Cod houses are typically one-and-a-half stories tall, with a steeply pitched gabled roof and a central chimney.
- Colonial Revival: Colonial Revival architecture, which emerged in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, is a blend of elements from various colonial styles. Colonial Revival houses often feature asymmetrical facades, porches, and a mix of gabled and hipped roofs.
By incorporating these historical elements into their designs, House Plans Colonial evoke a sense of nostalgia and connection to the past. They capture the charm and elegance of colonial-era architecture, while also providing modern amenities and conveniences.
Symmetrical facades
Symmetrical facades are a defining characteristic of House Plans Colonial. Symmetry is achieved when the architectural elements on one side of the facade mirror those on the other side, creating a sense of balance and harmony.
This symmetry is often achieved through the use of windows, doors, and other architectural features that are arranged in a mirrored fashion. For example, a colonial-style house may have a central front door flanked by two windows on each side, creating a symmetrical composition.
Symmetrical facades are not only aesthetically pleasing, but they also contribute to the overall structural integrity of the house. By distributing the weight of the building evenly across the facade, symmetry helps to prevent the house from settling unevenly and developing structural problems.
In addition to their aesthetic and structural benefits, symmetrical facades also convey a sense of order and formality. This is why they have been a popular choice for centuries, both in colonial-era architecture and in modern-day house plans.
Benefits of symmetrical facades
- Aesthetically pleasing
- Contribute to structural integrity
- Convey a sense of order and formality
Examples of symmetrical facades in House Plans Colonial
Here are some examples of House Plans Colonial that feature symmetrical facades:
- The Camden: This 1435-square-foot colonial-style house features a symmetrical facade with a central front door flanked by two windows on each side.
- The Williamsburg: This 2527-square-foot colonial-style house has a symmetrical facade with a central front door flanked by two Palladian windows on each side.
- The Jefferson: This 3157-square-foot colonial-style house features a symmetrical facade with a central front door flanked by two sidelights and two windows on each side.
These are just a few examples of the many beautiful House Plans Colonial that feature symmetrical facades. With their timeless appeal and enduring popularity, colonial-style homes continue to be a popular choice for homeowners who desire a classic and elegant residence.
Gabled roofs
Gabled roofs are another defining characteristic of House Plans Colonial. A gable is a triangular portion of a wall that is formed by the intersection of two sloping roof planes. Gabled roofs are typically symmetrical, with two sloping sides that meet at a ridge line.
Benefits of gabled roofs
- Structural stability: Gabled roofs are inherently strong and stable, making them well-suited for regions with high winds or heavy snow loads.
- Energy efficiency: The sloped sides of a gabled roof allow for proper ventilation, which helps to reduce heat gain in the summer and heat loss in the winter.
- Architectural versatility: Gabled roofs can be used in a variety of architectural styles, from traditional colonial to modern farmhouse.
Types of gabled roofs
There are several different types of gabled roofs, including:
- Front gable: A front gable roof has two sloping sides that meet at a ridge line parallel to the front of the house.
- Side gable: A side gable roof has two sloping sides that meet at a ridge line perpendicular to the front of the house.
- Cross gable: A cross gable roof has two gables that intersect at a right angle, forming a T-shape.
- Dutch gable: A Dutch gable roof has a curved or stepped gable end, creating a distinctive silhouette.
Examples of gabled roofs in House Plans Colonial
Here are some examples of House Plans Colonial that feature gabled roofs:
- The Camden: This 1435-square-foot colonial-style house features a front gable roof with a central dormer.
- The Williamsburg: This 2527-square-foot colonial-style house has a side gable roof with two dormers on each side.
- The Jefferson: This 3157-square-foot colonial-style house features a cross gable roof with a central chimney.
These are just a few examples of the many beautiful House Plans Colonial that feature gabled roofs. With their timeless appeal and enduring popularity, colonial-style homes continue to be a popular choice for homeowners who desire a classic and elegant residence.
Formal interiors
Formal interiors are another defining characteristic of House Plans Colonial. These interiors are characterized by their symmetry, balance, and use of elegant furnishings and finishes.
- Symmetry: Formal interiors often feature symmetrical arrangements of furniture and other decorative elements. This symmetry creates a sense of order and harmony within the space.
- Balance: Formal interiors also strive for balance, both in terms of the placement of furniture and the use of colors and patterns. This balance helps to create a visually pleasing and inviting space.
- Elegant furnishings and finishes: Formal interiors typically feature elegant furnishings and finishes, such as fine woods, rich fabrics, and elaborate moldings. These elements add a touch of luxury and sophistication to the space.
- Purposeful spaces: Formal interiors often have designated spaces for different activities, such as entertaining guests, dining, and relaxing. This purposeful use of space helps to create a more comfortable and functional living environment.
Formal interiors are not only beautiful to look at, but they also serve a practical purpose. By creating a sense of order and harmony, formal interiors can help to reduce stress and promote relaxation. Additionally, the use of elegant furnishings and finishes can create a sense of luxury and sophistication, which can be both inviting and impressive.
Timeless aesthetic
House Plans Colonial have a timeless aesthetic that transcends trends and generations. This enduring appeal can be attributed to several key factors:
- Classic proportions and symmetry: Colonial-style homes are characterized by their classic proportions and symmetrical facades. These elements create a sense of balance and harmony that is both pleasing to the eye and timeless in its appeal.
- Natural materials and finishes: Colonial-style homes often incorporate natural materials such as wood, brick, and stone. These materials age gracefully over time, adding to the home’s charm and character.
- Traditional detailing: Colonial-style homes feature traditional detailing such as moldings, cornices, and wainscoting. These details add a touch of elegance and sophistication to the home’s interior and exterior.
- Versatile floor plans: Colonial-style homes typically have versatile floor plans that can be adapted to a variety of lifestyles and needs. This flexibility ensures that colonial-style homes remain relevant and desirable over time.
As a result of these factors, House Plans Colonial continue to be popular choices for homeowners who desire a classic and elegant residence that will stand the test of time.
Historical significance
House Plans Colonial hold significant historical value as they embody the architectural styles and traditions of the colonial era in the United States. These plans provide a tangible connection to the past, offering a glimpse into the lives and aspirations of early American settlers.
The colonial era, spanning from the 17th to the 19th centuries, was a period of great social, political, and economic change in the United States. As European settlers established colonies along the Atlantic coast, they brought with them their own cultural influences and architectural traditions. These traditions blended with local materials and craftsmanship to create a unique American style of architecture.
House Plans Colonial often reflect the architectural styles of the countries that colonized the United States, such as England, France, Spain, and the Netherlands. For example, Georgian-style homes, popular in the 18th century, are characterized by their symmetrical facades, rectangular shape, and hipped roofs, all of which are hallmarks of British architecture.
In addition to their architectural significance, House Plans Colonial also provide insights into the social and economic conditions of the colonial era. The size and grandeur of a colonial home often reflected the wealth and status of its owner. For example, wealthy merchants and plantation owners typically lived in large, elaborate homes, while farmers and laborers lived in more modest dwellings.
Reflects regional heritage
House Plans Colonial not only evoke the architectural styles of the colonial era, but they also reflect the regional heritage of the United States. The vast and diverse landscape of the country, coupled with the influence of different European cultures, resulted in a wide range of regional variations in colonial architecture.
For example, in the New England region, where the influence of British architecture was strong, colonial homes are characterized by their clapboard siding, gabled roofs, and central chimneys. In the Mid-Atlantic region, where Dutch and German influences were more pronounced, colonial homes often feature stone or brick exteriors, gambrel roofs, and large porches.
In the Southern region, where the climate is warmer, colonial homes are typically larger and more elaborate, with wide verandas, high ceilings, and plantation shutters. In the Western region, where Spanish and Mexican influences were prevalent, colonial homes often incorporate elements such as stucco walls, tile roofs, and arched doorways.
These regional variations in House Plans Colonial reflect the diverse cultural heritage of the United States and add to the charm and character of these historic homes.
Here are some specific examples of how House Plans Colonial reflect regional heritage:
- New England: The Cape Cod style house is a classic example of New England colonial architecture. These homes are typically one-and-a-half stories tall, with a steeply pitched gabled roof, a central chimney, and clapboard siding.
- Mid-Atlantic: The Dutch Colonial style house is a popular choice in the Mid-Atlantic region. These homes are characterized by their stone or brick exteriors, gambrel roofs, and large porches.
- Southern: The plantation style house is a grand and elegant example of Southern colonial architecture. These homes are typically large and spacious, with wide verandas, high ceilings, and plantation shutters.
- Western: The Spanish Colonial style house is a unique blend of Spanish and Mexican influences. These homes often feature stucco walls, tile roofs, and arched doorways.
Variety of colonial styles
House Plans Colonial encompass a wide range of architectural styles that reflect the diverse cultural influences and regional variations of the colonial era in the United States. These styles can be broadly categorized into four main types:
Georgian: Georgian architecture, popular in the 18th century, is characterized by its symmetrical facades, rectangular shape, and hipped or gabled roofs. Georgian houses often feature prominent entryways with pediments and Palladian windows.
Federal: Federal architecture, which emerged in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, is known for its delicate details and restrained ornamentation. Federal houses typically have square or rectangular shapes, with symmetrical facades and sidelights flanking the main entrance.
Cape Cod: Cape Cod architecture, originating in the 17th century, is a simple and practical style that is well-suited to coastal regions. Cape Cod houses are typically one-and-a-half stories tall, with a steeply pitched gabled roof and a central chimney.
Colonial Revival: Colonial Revival architecture, which emerged in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, is a blend of elements from various colonial styles. Colonial Revival houses often feature asymmetrical facades, porches, and a mix of gabled and hipped roofs.
Enduring appeal
House Plans Colonial continue to captivate homeowners with their enduring appeal. This timeless style transcends trends and generations, offering a harmonious blend of classic elegance and modern functionality.
- Timeless aesthetic
Colonial-style homes possess a timeless aesthetic characterized by their symmetrical facades, gabled roofs, and elegant detailing. These elements create a visually pleasing and harmonious design that never goes out of style.
- Historical significance
House Plans Colonial embody the architectural traditions of the colonial era in the United States. They provide a tangible link to the past, offering insights into the lives and aspirations of early American settlers.
- Versatility and adaptability
Colonial-style homes offer versatile floor plans that can be adapted to a variety of lifestyles and needs. They can be expanded or modified to accommodate growing families or changing tastes, ensuring their relevance over time.
- Regional diversity
House Plans Colonial reflect the diverse regional heritage of the United States. Different regions developed their own unique variations of colonial architecture, showcasing the influence of local materials, craftsmanship, and cultural traditions.
Furthermore, colonial-style homes are known for their durability and low maintenance requirements. Their classic materials and construction methods ensure longevity, while their timeless designs minimize the need for frequent renovations or updates.
In conclusion, House Plans Colonial endure because they offer a timeless aesthetic, historical significance, versatility, regional diversity, and practical advantages. These qualities continue to resonate with homeowners who desire a classic and elegant residence that stands the test of time.








Related Posts