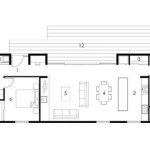
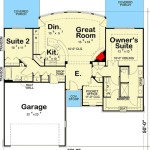
House Plan Design refers to the process of creating a detailed visual representation of a house, including its structure, layout, and floor plan. It serves as a blueprint, guiding the construction and development of the house. Architects and homeowners collaborate to design a plan that meets the specific requirements and preferences of the occupants, ensuring functionality, aesthetics, and comfort.
From sprawling mansions to cozy cottages, house plan design is indispensable in the realm of architecture. It establishes the framework for the house, dictating the flow of rooms, the placement of windows and doors, and the overall spatial arrangement. Whether it’s a renovation project or a new construction, a well-crafted house plan ensures that the resulting structure is not only aesthetically pleasing but also functional and enduring.
In the following sections, we will delve into the various aspects of house plan design, exploring the key considerations, design styles, and emerging trends. We will examine the role of architects and the importance of collaboration, and provide practical guidance for homeowners seeking to create their dream home.
House Plan Design: 10 Important Points
- Functionality
- Aesthetics
- Layout
- Space planning
- Structural integrity
- Energy efficiency
- Building codes
- Homeowner needs
- Architectural style
- Sustainability
When designing a house plan, it’s crucial to consider these factors to ensure a well-rounded and successful project.
Functionality
Functionality lies at the heart of house plan design, ensuring that the resulting structure meets the practical needs and lifestyle of its occupants. A well-designed house should be efficient, comfortable, and adaptable to changing circumstances, fostering a sense of well-being and ease of living.
Functional house plans prioritize the flow of movement throughout the house, creating seamless connections between spaces and minimizing wasted space. They consider the relationship between rooms, ensuring that they are appropriately sized and positioned to meet the intended use. For example, placing the kitchen adjacent to the dining room and outdoor entertaining areas enhances convenience and functionality.
Storage solutions are another crucial aspect of functionality. Well-planned storage spaces, such as closets, pantries, and built-in cabinetry, help maintain order and maximize space utilization. Ample storage prevents clutter and ensures that belongings are easily accessible, contributing to a comfortable and organized living environment.
Functionality also encompasses the consideration of accessibility and universal design principles. This involves creating spaces that are easily navigable and adaptable to the needs of individuals with disabilities or age-related limitations. Wider doorways, ramps, and accessible bathrooms are examples of features that enhance the functionality and inclusivity of a house.
Aesthetics
Aesthetics play a pivotal role in house plan design, influencing the overall appeal, character, and curb appeal of the structure. A well-designed house not only meets functional requirements but also embodies a cohesive aesthetic vision, reflecting the tastes and aspirations of its occupants.
- Architectural Style
The architectural style of a house is a defining characteristic that influences its overall appearance and aesthetic appeal. From traditional styles like Victorian and Colonial to contemporary styles like Modern and Minimalist, there is a wide range of architectural styles to choose from. Each style has its own unique set of design elements, such as rooflines, window shapes, and exterior finishes, that contribute to the overall aesthetic.
- Exterior Design
The exterior design of a house encompasses all elements visible from the outside, including the facade, roofing, siding, and landscaping. It plays a crucial role in creating a visually appealing and inviting home. Factors such as color, texture, and material selection contribute to the overall aesthetic impact. For example, a house with a stone facade and a pitched roof exudes a classic and elegant charm, while a house with a sleek glass facade and a flat roof conveys a modern and minimalist aesthetic.
- Interior Design
Interior design focuses on the aesthetic and functional aspects of the interior spaces of a house. It involves selecting finishes, furnishings, and decorative elements that reflect the occupants’ tastes and lifestyle. Interior design can range from traditional and ornate to modern and minimalist, and can significantly impact the overall ambiance and comfort of a home.
- Curb Appeal
Curb appeal refers to the aesthetic appeal of a house as viewed from the street. It is influenced by factors such as the overall design, landscaping, and exterior maintenance. A house with good curb appeal is visually inviting and creates a positive first impression. It can also contribute to the property value and neighborhood aesthetics.
By carefully considering aesthetic principles and incorporating cohesive design elements, architects and homeowners can create houses that are not only functional but also visually stunning and enduringly appealing.
Layout
The layout of a house plan refers to the arrangement of rooms, spaces, and other structural elements within the structure. It plays a crucial role in determining the functionality, flow, and overall livability of a house. A well-designed layout optimizes space utilization, creates a cohesive flow between rooms, and enhances the overall comfort and enjoyment of the occupants.
- Open Floor Plan
An open floor plan is characterized by a spacious, interconnected layout where multiple functional areas, such as the living room, dining room, and kitchen, flow seamlessly into one another. This design concept promotes a sense of openness, encourages interaction, and maximizes natural light penetration. Open floor plans are particularly popular in modern and contemporary homes.
- Closed Floor Plan
In contrast to an open floor plan, a closed floor plan features separate, enclosed rooms for different functions. This traditional layout provides greater privacy and noise isolation between rooms. Closed floor plans are often found in older homes and are preferred by those who value traditional design and separate spaces for different activities.
- Split-Level Floor Plan
A split-level floor plan is characterized by different levels or half-levels within the house. This layout allows for separation of spaces while maintaining a sense of connection. Split-level floor plans can be particularly effective in homes built on sloping lots, as they can accommodate the natural grade of the land.
- Multi-Story Floor Plan
A multi-story floor plan features two or more stories, connected by stairs. This layout allows for a more compact footprint and can be a space-saving solution for smaller lots. Multi-story floor plans can also offer separation of spaces, with private areas like bedrooms typically located on upper floors, while common areas and living spaces are on the main level.
The choice of layout depends on a variety of factors, including the size and shape of the lot, the desired level of privacy and separation of spaces, and the lifestyle and preferences of the occupants. A well-planned layout can significantly enhance the overall functionality, comfort, and aesthetic appeal of a house.
Space planning
Space planning is a fundamental aspect of house plan design that involves the efficient and functional allocation of space within a structure. It encompasses the thoughtful arrangement of rooms, hallways, closets, and other elements to create a comfortable, livable, and aesthetically pleasing environment.
Effective space planning considers the size, shape, and orientation of the available space, as well as the specific needs and preferences of the occupants. It involves optimizing the use of natural light, maximizing storage capacity, and ensuring a smooth flow of movement throughout the house. Well-planned spaces promote a sense of harmony and balance, while poorly planned spaces can feel cramped, cluttered, and inefficient.
One key aspect of space planning is the efficient use of square footage. This involves carefully considering the size and shape of each room, ensuring that they are appropriately proportioned and optimized for their intended use. For example, a living room should be spacious enough to accommodate furniture and allow for comfortable movement, while a kitchen should be designed to maximize counter and storage space without feeling cramped.
Another important consideration in space planning is the relationship between different spaces. The flow of movement between rooms should be smooth and logical, avoiding awkward transitions or wasted space. Common areas, such as the living room and kitchen, should be easily accessible from other parts of the house, while private areas, such as bedrooms and bathrooms, should be afforded a sense of privacy and separation. Careful attention to the placement of doors, windows, and hallways can significantly enhance the overall functionality and livability of a house.
Structural integrity
Structural integrity refers to the ability of a house to withstand and distribute loads and forces while maintaining its stability and safety. It is a crucial consideration in house plan design, as it ensures the long-term durability and resilience of the structure.
Structural integrity is achieved through the careful selection and arrangement of building materials, as well as the proper design of structural elements such as foundations, walls, roofs, and framing. The foundation, which is the base of the house, must be strong enough to support the weight of the entire structure and transfer loads to the ground. Walls provide vertical support and resist lateral forces, such as wind and seismic activity. The roof protects the house from the elements and transfers loads to the walls and foundation. Framing, which consists of beams, joists, and studs, provides the skeletal framework of the house and distributes loads throughout the structure.
In addition to the main structural elements, other factors that contribute to structural integrity include the use of proper construction techniques, adherence to building codes, and regular maintenance. Poor construction practices, such as using substandard materials or cutting corners, can compromise the structural integrity of a house. Building codes provide minimum standards for structural design and construction, ensuring that houses are built to withstand the expected loads and forces in their specific location. Regular maintenance, such as inspecting and repairing structural components, helps to identify and address potential issues before they become major problems.
A house with good structural integrity is safe, durable, and resistant to damage from natural disasters and other external forces. It provides peace of mind to the occupants and ensures that the house will stand the test of time.
Energy efficiency
Energy efficiency in house plan design refers to the practice of creating homes that minimize energy consumption while maintaining a comfortable and healthy indoor environment. By incorporating energy-efficient features and strategies, homeowners can reduce their energy bills, lessen their environmental impact, and enhance the long-term value of their property.
One of the key aspects of energy-efficient house plan design is the building envelope, which includes the walls, roof, windows, and doors. A well-insulated building envelope helps to reduce heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer, minimizing the need for heating and cooling. This can be achieved through the use of high-performance insulation materials, energy-efficient windows and doors, and proper air sealing to prevent drafts.
Another important consideration is the orientation of the house on the building lot. By carefully positioning the house to take advantage of natural sunlight and prevailing breezes, architects can reduce the need for artificial lighting and cooling. For example, placing large windows on the south side of the house allows for passive solar heating in the winter, while strategically placed overhangs can shade the house from the sun during the summer.
The selection of energy-efficient appliances and systems also plays a significant role in reducing energy consumption. Modern appliances, such as refrigerators, dishwashers, and washing machines, are available with Energy Star ratings, indicating that they meet strict energy efficiency standards. Additionally, energy-efficient lighting systems, such as LED and CFL bulbs, use less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs and last longer.
Building codes
Building codes are a set of regulations that govern the design, construction, and alteration of buildings to ensure their safety, structural integrity, and energy efficiency. They are established by local, state, and national authorities and provide minimum standards that must be met in order to obtain a building permit and construct a house.
Building codes cover a wide range of aspects related to house plan design, including structural requirements, fire safety, energy efficiency, accessibility, and environmental protection. Structural requirements specify the minimum strength and stability standards that the house must meet to withstand various loads and forces, such as gravity, wind, and seismic activity. Fire safety codes regulate the use of fire-resistant materials, the installation of smoke detectors and sprinkler systems, and the design of escape routes to minimize the risk of fire and protect the occupants in case of a fire.
Energy efficiency codes set standards for the thermal performance of the building envelope, including insulation levels, window and door efficiency, and air sealing. These codes aim to reduce energy consumption and improve the overall energy performance of the house, resulting in lower energy bills and a reduced carbon footprint. Accessibility codes ensure that buildings are accessible to people with disabilities, including those who use wheelchairs or have other mobility impairments. These codes specify requirements for accessible entrances, ramps, elevators, and other features that facilitate access and movement throughout the house.
Environmental protection codes regulate the use of environmentally friendly materials and practices in construction. They may include requirements for the use of recycled materials, energy-efficient appliances, and low-VOC (volatile organic compound) paints and finishes to minimize the environmental impact of the house and protect the health of the occupants.
Adherence to building codes is essential for ensuring the safety, functionality, and durability of a house. By complying with these regulations, architects and homeowners can create houses that meet the minimum standards for habitability, protect the occupants from potential hazards, and contribute to a more sustainable built environment.
Homeowner needs
The design of a house plan should prioritize the needs and preferences of the homeowners. By understanding their lifestyle, aspirations, and functional requirements, architects can create a house that truly meets their unique needs. Here are some key homeowner needs to consider in house plan design:
- Number of bedrooms and bathrooms
The number of bedrooms and bathrooms required depends on the size of the family, their sleeping arrangements, and their privacy preferences. For example, a family with young children may need more bedrooms to accommodate their growing needs, while a couple may prefer a master suite with a luxurious bathroom.
- Living space requirements
The amount and type of living space required depends on the homeowner’s lifestyle and how they use their home. A family that enjoys entertaining guests may need a spacious living room and dining room, while a couple who prefers cozy evenings at home may opt for a smaller, more intimate space.
- Functional areas
In addition to bedrooms and living spaces, homeowners may have specific functional areas that they need to incorporate into their house plan. These could include a home office, a dedicated craft room, a playroom for children, or a home gym. The design should accommodate these functional areas in a way that supports the homeowner’s daily routines and hobbies.
- Outdoor space
Outdoor space can significantly enhance the livability and enjoyment of a home. Homeowners should consider their outdoor needs and preferences when designing their house plan. This could include a patio for entertaining, a deck for grilling and dining, a garden for growing vegetables or flowers, or a play area for children.
By carefully considering the homeowner’s needs and preferences, architects can create a house plan that not only meets their functional requirements but also reflects their unique lifestyle and aspirations.
Architectural style
Architectural style refers to the distinctive visual characteristics and design principles that define a building. It encompasses a wide range of elements, including the overall form and massing of the structure, the choice of materials, the design of windows and doors, and the ornamentation and detailing. Architectural style is influenced by various factors, such as the historical period, cultural context, geographic location, and the personal preferences of the architect and client.
In house plan design, architectural style plays a crucial role in determining the overall appearance and character of the home. It sets the tone for the interior and exterior spaces, guiding the selection of materials, finishes, and decorative elements. The choice of architectural style should be carefully considered, as it will have a lasting impact on the aesthetic appeal and functionality of the house.
There are numerous architectural styles to choose from, each with its own unique set of characteristics. Some popular architectural styles for houses include:
- Traditional styles, such as Victorian, Colonial, and Craftsman, are characterized by their timeless appeal and historical references. They often feature symmetrical facades, pitched roofs, and intricate detailing.
- Modern styles, such as Contemporary, Mid-Century Modern, and Bauhaus, emphasize clean lines, simplicity, and the use of innovative materials. They often feature open floor plans, large windows, and flat roofs.
- Rustic styles, such as Log Cabin, Farmhouse, and Adirondack, draw inspiration from natural materials and vernacular architecture. They often feature exposed beams, stone fireplaces, and cozy interiors.
- Mediterranean styles, such as Spanish Colonial, Italian Renaissance, and Greek Revival, are characterized by their warm colors, arched openings, and tiled roofs. They often evoke a sense of relaxed elegance and outdoor living.
The choice of architectural style is ultimately a matter of personal preference. However, it is important to consider the context of the surrounding environment and the desired lifestyle of the occupants when making this decision. A well-chosen architectural style can enhance the overall appeal of the house, increase its value, and create a home that is both beautiful and functional.
Sustainability
Sustainability in house plan design refers to the practice of creating homes that minimize their environmental impact and promote the well-being of occupants. By incorporating sustainable features and strategies, architects and homeowners can reduce the carbon footprint of their homes, conserve natural resources, and create healthier and more resilient living environments.
One of the key aspects of sustainable house plan design is energy efficiency. This involves designing homes that consume less energy for heating, cooling, and lighting. Energy-efficient features can include high-performance insulation, energy-efficient windows and doors, and the use of renewable energy sources such as solar panels and geothermal heating and cooling systems.
Another important aspect of sustainability is water conservation. Sustainable house plan designs incorporate water-saving fixtures and appliances, such as low-flow toilets and faucets, and rainwater harvesting systems. These features can significantly reduce water consumption and help to protect local water resources.
Sustainable house plan designs also prioritize the use of environmentally friendly materials and construction practices. This includes using sustainably harvested wood, recycled materials, and low-VOC (volatile organic compound) paints and finishes. These materials and practices help to reduce the environmental impact of the home and improve indoor air quality.
In addition to these specific features, sustainable house plan design also considers the overall orientation and placement of the home on the building lot. By taking advantage of natural sunlight and prevailing breezes, architects can reduce the need for artificial lighting and cooling, and create more comfortable and energy-efficient living spaces.
By incorporating sustainable principles into house plan design, architects and homeowners can create homes that are not only beautiful and functional but also environmentally responsible and healthy for occupants. Sustainable homes have a lower impact on the planet, reduce energy and water consumption, and promote the well-being of those who live in them.








Related Posts