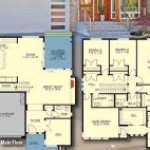
A house plan 2nd floor is a detailed architectural drawing that outlines the layout, dimensions, and features of the second story of a house. It provides a comprehensive view of the space, including the location and size of rooms, windows, doors, and other architectural elements.
House plan 2nd floor plans are essential for planning the construction or renovation of a home. They help architects, builders, and homeowners visualize the space, make informed decisions about the design and functionality of the second floor, and ensure that the structure complies with building codes and regulations.
In the following sections, we will explore the key components of a house plan 2nd floor, discuss the factors to consider when designing a second floor, and provide tips for creating a functional and aesthetically pleasing living space on the second level of your home.
When designing a house plan 2nd floor, several important points should be considered to ensure functionality, comfort, and aesthetic appeal:
- Room layout and size
- Window and door placement
- Staircase design and location
- Ceiling height and shape
- Structural support and load-bearing capacity
- Natural lighting and ventilation
- Storage and closet space
- Electrical and plumbing systems
- Fire safety and egress
- Energy efficiency and insulation
By carefully considering these factors and incorporating thoughtful design elements, homeowners can create a second floor that meets their specific needs and enhances the overall livability and enjoyment of their home.
Room layout and size
The layout and size of rooms on the second floor of a house plan are crucial for creating a functional and comfortable living space. Several factors need to be considered when determining the room layout, including the number of bedrooms and bathrooms required, the desired size and shape of each room, and the overall flow and connectivity of the space.
The most common room layout for a second floor includes a master bedroom with an en-suite bathroom, additional bedrooms, and one or more shared bathrooms. The size of the master bedroom will vary depending on the overall size of the house and the homeowner’s preferences, but it should be large enough to accommodate a bed, nightstands, dresser, and other furniture. Additional bedrooms should be sized to comfortably fit a bed, dresser, and desk or other necessary furniture.
The size and placement of bathrooms on the second floor are also important considerations. Bathrooms should be conveniently located near bedrooms and should be large enough to accommodate the necessary fixtures and provide comfortable use. Master bathrooms often include a shower, bathtub, and double vanity, while shared bathrooms may have a shower or bathtub and a single vanity.
The overall flow and connectivity of the second floor is also important. The layout should allow for easy movement between rooms and should avoid creating any awkward or inefficient spaces. Hallways should be wide enough to comfortably accommodate furniture and traffic, and doors should be placed to maximize space and functionality.
By carefully considering the room layout and size, homeowners can create a second floor that meets their specific needs and provides a comfortable and enjoyable living environment.
Window and door placement
The placement of windows and doors on the second floor of a house plan is crucial for maximizing natural light, ventilation, and views, while also ensuring privacy and security. Several factors need to be considered when determining window and door placement, including the orientation of the house on the lot, the surrounding environment, and the desired level of natural light and privacy.
Windows should be placed to take advantage of natural light and views. South-facing windows will provide the most sunlight, while north-facing windows will provide more diffused light. East-facing windows will provide morning light, while west-facing windows will provide afternoon light. The size and shape of windows will also affect the amount of natural light that enters a room. Larger windows will provide more light, while smaller windows will provide less light but can offer more privacy.
Doors should be placed for convenience and security. Exterior doors should be placed in well-lit areas and should be visible from the street. Interior doors should be placed to minimize noise and traffic flow. Pocket doors or sliding doors can be used to save space and create a more open feel.
The surrounding environment should also be considered when placing windows and doors. Windows and doors that overlook a busy street or noisy neighbor may need to be placed higher up on the wall or fitted with soundproof glass. Windows and doors that overlook a private backyard or garden can be placed lower down on the wall to provide better views and access to the outdoors.
By carefully considering the placement of windows and doors, homeowners can create a second floor that is filled with natural light, offers beautiful views, and provides a comfortable and secure living environment.
Staircase design and location
The design and location of the staircase on the second floor of a house plan are important considerations for both functionality and aesthetics. Several factors need to be considered when determining the staircase design and location, including the available space, the desired style of the staircase, and the overall flow and connectivity of the second floor.
- Space requirements: The staircase should be designed to fit comfortably within the available space on the second floor. The width of the stairs, the number of steps, and the height of the risers should all be carefully considered to ensure that the staircase is safe and easy to use.
- Style: The style of the staircase should complement the overall design of the house. Staircases can be made from a variety of materials, including wood, metal, and glass, and can be designed with different shapes and styles. The choice of staircase style will depend on the homeowner’s personal preferences and the overall aesthetic of the home.
- Flow and connectivity: The staircase should be located in a central and convenient location on the second floor. It should provide easy access to all of the rooms on the second floor and should not create any awkward or inefficient spaces. The staircase should also be designed to minimize noise and traffic flow.
- Safety: The staircase should be designed with safety in mind. The stairs should be slip-resistant, and the handrails should be securely attached. The staircase should also be well-lit to prevent accidents.
By carefully considering the design and location of the staircase, homeowners can create a second floor that is both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
Ceiling height and shape
The ceiling height and shape of the second floor of a house plan can have a significant impact on the overall feel and functionality of the space. Several factors need to be considered when determining the ceiling height and shape, including the desired ambiance, the architectural style of the home, and the overall flow and connectivity of the second floor.
Ceiling height can affect the perceived spaciousness of a room. Higher ceilings can make a room feel more open and airy, while lower ceilings can create a more cozy and intimate atmosphere. The height of the ceiling should be proportional to the size of the room. A small room with a high ceiling can feel disproportionate, while a large room with a low ceiling can feel cramped.
Ceiling shape can also be used to create different effects. A flat ceiling is the most common type of ceiling, but vaulted ceilings, tray ceilings, and coffered ceilings can add visual interest and architectural detail to a room. Vaulted ceilings create a sense of height and grandeur, while tray ceilings add a touch of elegance. Coffered ceilings are a classic architectural detail that can add a sense of depth and sophistication to a room.
The ceiling height and shape should be carefully considered in relation to the overall flow and connectivity of the second floor. A high ceiling in the entryway or living room can create a dramatic first impression, while a lower ceiling in the bedrooms can create a more cozy and intimate atmosphere. By carefully considering the ceiling height and shape, homeowners can create a second floor that is both visually appealing and functional.
In addition to the aesthetic considerations, the ceiling height and shape can also affect the energy efficiency of the home. Higher ceilings can allow for more natural light to enter the home, reducing the need for artificial lighting. Vaulted ceilings can also help to circulate air more efficiently, reducing the need for air conditioning.
Structural support and load-bearing capacity
The structural support and load-bearing capacity of the second floor of a house plan are crucial for ensuring the safety and stability of the structure. Several factors need to be considered when determining the structural support and load-bearing capacity, including the size and weight of the second floor, the materials used in construction, and the overall design of the house.
- Floor joists: Floor joists are the horizontal beams that support the floorboards and distribute the weight of the second floor. The size and spacing of the floor joists will depend on the span of the floor and the weight of the materials used. Floor joists are typically made of wood, but can also be made of steel or concrete.
- Beams: Beams are larger structural members that support the floor joists and transfer the weight of the second floor to the walls or foundation. Beams can be made of wood, steel, or concrete. The size and type of beams required will depend on the span of the floor and the weight of the materials used.
- Walls: The walls of the house provide lateral support to the second floor and help to resist wind and seismic forces. The walls should be constructed of strong and durable materials, such as concrete, brick, or wood. The thickness and height of the walls will depend on the size and weight of the second floor.
- Foundation: The foundation of the house provides support to the walls and transfers the weight of the entire structure to the ground. The foundation should be designed to withstand the weight of the second floor and the forces exerted by the soil and wind. Foundations are typically made of concrete or concrete blocks.
By carefully considering the structural support and load-bearing capacity of the second floor, homeowners can ensure that their home is safe and stable for years to come.
Natural lighting and ventilation
Natural lighting and ventilation are essential for creating a healthy and comfortable living environment on the second floor of a house. Natural light can help to reduce energy costs, improve mood, and boost productivity. Ventilation can help to improve air quality, reduce moisture, and prevent the growth of mold and mildew.
There are several ways to incorporate natural lighting and ventilation into a second-floor house plan. Windows are the most common way to bring natural light into a room. Windows should be placed to take advantage of natural light sources, such as south-facing windows for maximum sunlight. Skylights are another option for bringing natural light into a room, and they can be especially effective in rooms with limited wall space for windows.
Ventilation can be achieved through a variety of means, including windows, doors, and vents. Operable windows allow for cross-ventilation, which is the movement of air through a space from one side to the other. Doors can also be used for ventilation, especially when they lead to a balcony or patio. Vents can be installed in walls or ceilings to allow for the flow of air. It is important to ensure that there is adequate ventilation in all rooms on the second floor, especially in bathrooms and kitchens.
By carefully considering natural lighting and ventilation in the design of the second floor, homeowners can create a space that is both healthy and comfortable.
Storage and closet space
Adequate storage and closet space is essential for maintaining a well-organized and clutter-free second floor. Several factors need to be considered when planning for storage and closet space, including the number of bedrooms and bathrooms, the size and type of furniture, and the personal storage needs of the occupants.
Bedrooms should have ample closet space to accommodate clothing, shoes, and other personal belongings. The size and type of closet will depend on the size of the bedroom and the amount of storage space required. Walk-in closets are ideal for larger bedrooms, as they provide more space and organization options. Reach-in closets are a good option for smaller bedrooms, as they can be customized to fit the specific needs of the occupants.
Bathrooms should also have adequate storage space for toiletries, towels, and other bathroom essentials. Medicine cabinets are a good option for storing small items, while linen closets can be used to store larger items, such as towels and bedding. Built-in shelves and drawers can also be added to bathrooms to provide additional storage space.
In addition to bedroom and bathroom closets, other storage areas may be desired on the second floor, such as a linen closet in the hallway or a storage closet for seasonal items. The type and amount of storage space required will vary depending on the individual needs of the occupants.
By carefully considering storage and closet space in the design of the second floor, homeowners can create a space that is both functional and organized.
Electrical and plumbing systems
Electrical systems
The electrical system on the second floor of a house plan should be designed to meet the electrical needs of the occupants, including lighting, appliances, and electronics. The electrical system should be installed in accordance with local building codes and should be designed to provide safe and reliable service.
The electrical system on the second floor will typically include a main electrical panel, which is the central distribution point for electricity in the home. The main electrical panel will contain circuit breakers or fuses, which protect the electrical circuits from overloads and short circuits. The electrical system will also include a network of electrical wiring, which carries electricity from the main electrical panel to the various electrical outlets, switches, and fixtures on the second floor.
When designing the electrical system for the second floor, it is important to consider the following factors:
- The number and type of electrical devices that will be used on the second floor
- The location of the electrical outlets, switches, and fixtures
- The routing of the electrical wiring
- The need for dedicated circuits for high-power appliances
- The need for safety features, such as ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) and arc fault circuit interrupters (AFCIs)
By carefully considering these factors, homeowners can design an electrical system that meets their specific needs and provides safe and reliable service.
Plumbing systems
The plumbing system on the second floor of a house plan should be designed to meet the plumbing needs of the occupants, including water supply, drainage, and waste disposal. The plumbing system should be installed in accordance with local building codes and should be designed to provide safe and reliable service.
The plumbing system on the second floor will typically include a water supply system, which provides water to the various plumbing fixtures on the second floor. The water supply system will typically include a water heater, which heats the water for the plumbing fixtures. The plumbing system will also include a drainage system, which removes wastewater from the plumbing fixtures on the second floor. The drainage system will typically include a network of drainpipes, which carry wastewater to the main sewer line.
When designing the plumbing system for the second floor, it is important to consider the following factors:
- The number and type of plumbing fixtures that will be used on the second floor
- The location of the plumbing fixtures
- The routing of the water supply and drain pipes
- The need for dedicated water lines for high-water-usage fixtures
- The need for safety features, such as pressure-reducing valves and backflow preventers
By carefully considering these factors, homeowners can design a plumbing system that meets their specific needs and provides safe and reliable service.
Fire safety and egress
Fire safety and egress are critical considerations in the design of any house plan, and the second floor is no exception. In the event of a fire, it is essential to have a safe and efficient way to evacuate the second floor. There are several important factors to consider when planning for fire safety and egress on the second floor:
1. Staircase design
The staircase is the primary means of egress from the second floor in the event of a fire. It is important to design the staircase to be wide enough and have a shallow enough pitch to allow for easy and safe evacuation. The staircase should also be enclosed in fire-resistant materials, such as drywall or plasterboard, to help prevent the spread of fire.
2. Fire escape windows
Fire escape windows are another important egress option for the second floor. Fire escape windows must be large enough to allow for a person to escape through them and must be located in a place where they can be easily accessed in the event of a fire. Fire escape windows should also be equipped with a release mechanism that can be easily operated from the inside.
3. Smoke detectors and alarms
Smoke detectors and alarms are essential for providing early warning of a fire. Smoke detectors should be installed in all bedrooms and hallways on the second floor. Smoke alarms should be interconnected so that if one alarm sounds, all of the alarms in the house will sound.
4. Fire sprinklers
Fire sprinklers can help to control and extinguish fires on the second floor. Fire sprinklers should be installed in all bedrooms, hallways, and other enclosed spaces on the second floor. Fire sprinklers can help to reduce the risk of injury and property damage in the event of a fire.
By carefully considering fire safety and egress in the design of the second floor, homeowners can help to ensure the safety of their family and property in the event of a fire.
Energy efficiency and insulation
Energy efficiency and insulation are important considerations for the second floor of a house plan, as they can help to reduce energy costs and improve the comfort of the living space. There are several ways to improve the energy efficiency and insulation of the second floor, including:
- Insulating the attic: The attic is one of the most important areas to insulate, as it can account for a significant amount of heat loss. Attic insulation should be installed between the roof rafters and the ceiling joists, and it should be thick enough to provide an adequate level of insulation. The recommended R-value for attic insulation in most climate zones is R-38.
- Insulating the walls: The walls of the second floor should also be insulated to prevent heat loss. Wall insulation can be installed in a variety of ways, including batt insulation, spray foam insulation, and cellulose insulation. The type of insulation used will depend on the climate zone and the construction of the walls.
- Insulating the floors: The floors of the second floor should be insulated to prevent heat loss from the lower level of the house. Floor insulation can be installed between the floor joists, and it should be thick enough to provide an adequate level of insulation. The recommended R-value for floor insulation in most climate zones is R-19.
- Installing energy-efficient windows and doors: Windows and doors can be a significant source of heat loss, so it is important to install energy-efficient windows and doors on the second floor. Energy-efficient windows and doors are designed to minimize heat loss and maximize energy efficiency.
By taking these steps to improve the energy efficiency and insulation of the second floor, homeowners can reduce energy costs and improve the comfort of their living space.










Related Posts