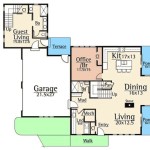
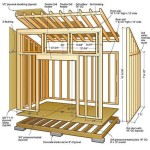
House on stilts plans refer to architectural blueprints that outline the construction of a house elevated above the ground, supported by vertical posts or columns. These plans provide detailed instructions and specifications for building a house that is partially or entirely suspended off the ground, typically for reasons related to flood protection, challenging terrain, or aesthetic preferences.
In flood-prone areas, for instance, houses on stilts offer an effective solution by elevating the living spaces above potential floodwaters. They allow water to flow underneath the house without causing structural damage or compromising the safety of the occupants. Additionally, in areas with uneven or sloping terrain, stilts can help level the foundation and provide a stable base for the house.
Transition Paragraph:
The following sections will explore the various considerations involved in designing and building a house on stilts, including factors such as site selection, foundation design, material choices, and structural integrity. We will also provide practical tips and insights to help you navigate the complexities of stilt house construction.
When planning a house on stilts, several important considerations must be taken into account:
- Site selection
- Foundation design
- Material choices
- Structural integrity
- Flood protection
- Access and egress
- Maintenance and repairs
- Cost and budget
- Building codes
- Aesthetic preferences
These factors will influence the overall design and construction of your stilt house, ensuring its safety, functionality, and durability.
Site selection
Selecting the right site for your house on stilts is crucial for its safety, functionality, and overall success. Here are some key factors to consider when choosing a site:
- Flood risk: If you’re building in a flood-prone area, it’s essential to choose a site that is elevated enough to avoid potential flooding. Determine the flood risk level of the area and select a site that is above the expected flood elevation.
- Soil conditions: The soil conditions of the site will impact the type of foundation required for your stilt house. Conduct a soil test to determine the soil bearing capacity and identify any potential issues that may require special foundation design considerations.
- Slope and topography: If the site has a slope or uneven topography, you may need to consider additional measures such as terracing or retaining walls to ensure the stability of the stilt house. Proper site preparation and grading will be crucial to create a level and stable base for the structure.
- Access and egress: Consider the accessibility of the site both during construction and after the house is built. Ensure that there is adequate space for construction equipment and materials, as well as convenient access for vehicles and pedestrians.
Thoroughly evaluating these site selection factors will help you choose a suitable location for your house on stilts, ensuring its safety, functionality, and long-term durability.
Foundation design
The foundation design for a house on stilts is crucial for its stability, safety, and long-term durability. Unlike traditional foundations that rest directly on the ground, stilt houses require specialized foundation systems to support the elevated structure.
The most common types of foundations for stilt houses include:
- Concrete piers: Concrete piers are widely used for stilt houses due to their strength and durability. They are typically made of reinforced concrete and extend from the ground to the underside of the house, providing support for the stilts.
- Steel piers: Steel piers are another popular option, offering high strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to corrosion. They are typically made of galvanized steel and can be driven into the ground or screwed into place.
- Timber piles: Timber piles are traditional foundation elements for stilt houses. They are made of pressure-treated wood and driven deep into the ground to provide support. Timber piles are suitable for areas with stable soil conditions.
The choice of foundation type will depend on factors such as soil conditions, flood risk, and the overall design of the house. It’s essential to consult with a qualified structural engineer to determine the most appropriate foundation system for your specific project.
In addition to the type of foundation, the design must also consider the height of the stilts, the spacing between them, and the overall load-bearing capacity of the foundation. Proper engineering calculations and design are necessary to ensure the stability of the stilt house under various load conditions, including wind, seismic forces, and the weight of the structure itself.
A well-designed foundation is the cornerstone of a safe and durable stilt house. By carefully considering the factors discussed above and working with qualified professionals, you can ensure that your stilt house stands strong for generations to come.
Material choices
The choice of materials for a house on stilts is crucial for its durability, functionality, and aesthetic appeal. Here are some key considerations when selecting materials for your stilt house:
- Structural materials: The primary structural materials used for stilt houses include wood, steel, and concrete. Wood is a traditional choice for stilt houses, offering strength, durability, and ease of construction. Steel is another popular option, providing high strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to corrosion. Concrete, while less common, can be used for stilt houses in areas with high wind or seismic activity.
- Decking materials: The decking of a stilt house is exposed to the elements and requires durable materials that can withstand moisture, rot, and wear. Common decking materials include pressure-treated wood, composite decking, and aluminum. Pressure-treated wood is a cost-effective option that provides good durability, while composite decking offers low maintenance and high resistance to rot and fading. Aluminum decking is lightweight, durable, and resistant to corrosion.
- Roofing materials: The roofing material for a stilt house should be able to withstand the elements and provide adequate insulation. Popular roofing materials include asphalt shingles, metal roofing, and tile roofing. Asphalt shingles are a cost-effective option that provides good durability and a variety of styles. Metal roofing is lightweight, durable, and energy-efficient. Tile roofing is a high-end option that offers durability, longevity, and aesthetic appeal.
- Exterior cladding materials: The exterior cladding of a stilt house protects the structure from the elements and contributes to its overall aesthetic. Common exterior cladding materials include vinyl siding, wood siding, and fiber cement siding. Vinyl siding is a low-maintenance option that comes in a variety of colors and styles. Wood siding offers a natural look and can be painted or stained to match any dcor. Fiber cement siding is durable, fire-resistant, and resistant to moisture damage.
By carefully selecting the right materials for your stilt house, you can ensure its durability, functionality, and aesthetic appeal for years to come.
Structural integrity
Structural integrity is of paramount importance in house on stilts plans. The elevated nature of these structures requires careful consideration of load distribution, material strength, and connection details to ensure the safety and stability of the building. Here are some key aspects related to structural integrity in house on stilts plans:
Load distribution
Houses on stilts are subjected to various loads, including the weight of the structure itself, live loads (occupants, furniture, etc.), wind loads, and seismic forces. The stilts and foundation system must be designed to effectively distribute these loads to the ground without compromising the stability of the structure. Structural engineers use calculations and analysis to determine the appropriate spacing and dimensions of the stilts, as well as the required strength of the foundation.
Material strength
The materials used for the stilts and other structural components of a house on stilts must possess adequate strength to withstand the applied loads. Common materials include wood, steel, and concrete. Wood is a traditional choice for stilts due to its strength, durability, and ease of construction. Steel is another popular option, offering high strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to corrosion. Concrete stilts are less common but can provide exceptional strength and durability, especially in areas with high wind or seismic activity.
Connection details
The connections between the stilts, beams, and other structural elements are critical for the overall stability of a house on stilts. These connections must be designed to transfer loads effectively and prevent any movement or failure that could compromise the integrity of the structure. Engineers use various techniques to create strong and reliable connections, such as bolts, welds, and specialized connectors.
Lateral stability
In addition to vertical loads, houses on stilts must also resist lateral forces, such as wind and seismic loads. These forces can cause the structure to sway or overturn if not properly addressed. To ensure lateral stability, engineers employ various strategies, including the use of shear walls, bracing systems, and moment-resisting frames. These elements work together to distribute lateral loads throughout the structure and prevent excessive movement.
By carefully considering these aspects of structural integrity, architects and engineers can design and build houses on stilts that are safe, stable, and able to withstand the rigors of their environment.
Flood protection
Houses on stilts offer a unique solution for flood protection, elevating living spaces above potential floodwaters and minimizing the risk of damage to the structure and its contents. Here are some key details related to flood protection in house on stilts plans:
Elevation above flood levels
The primary goal of flood protection in house on stilts plans is to elevate the living spaces above the expected flood elevation. This involves determining the base flood elevation (BFE) for the area, which is the elevation of the floodwaters during a 100-year flood event. The stilts and foundation system are then designed to raise the house to a height that is at least one foot above the BFE. This elevation helps ensure that the living spaces remain dry and habitable even during severe flooding.
Open space below the house
Houses on stilts are designed with open space beneath the structure, allowing floodwaters to flow through without causing significant damage. This open space also provides a buffer zone between the floodwaters and the living quarters, reducing the risk of water intrusion and damage to the structure.
Flood-resistant materials
In addition to elevation and open space, the materials used in the construction of a house on stilts should be resistant to flood damage. Pressure-treated wood, galvanized steel, and concrete are commonly used for stilts and other structural components due to their durability and resistance to moisture and rot.
Access during flooding
Consideration should be given to access during flooding when designing a house on stilts. Elevated walkways or stairs can provide safe access to the house during flood events, allowing occupants to enter and exit without having to wade through floodwaters.
By incorporating these flood protection measures into house on stilts plans, homeowners can significantly reduce the risk of damage to their property and ensure the safety of their families during flood events.
Access and egress
Access and egress are important considerations in house on stilts plans, particularly during emergencies or situations when the surrounding area is flooded. Here are some key details related to access and egress:
Elevated walkways or stairs
Elevated walkways or stairs provide safe and convenient access to the house during normal conditions and flood events. These elevated pathways are typically constructed using durable materials such as pressure-treated wood, galvanized steel, or concrete. They are designed to be wide enough for comfortable passage and may include handrails for added safety.
Multiple access points
Incorporating multiple access points into the house on stilts plans is essential for safety and convenience. This ensures that occupants have alternative ways to enter and exit the house, especially during emergencies. Multiple access points can include elevated walkways or stairs located at different sides of the house.
Flood-resistant access
The access points to the house on stilts should be designed to be flood-resistant, ensuring that they remain usable even during flood events. This may involve elevating the walkways or stairs to a height above the expected flood elevation and using flood-resistant materials in their construction.
Emergency escape routes
In addition to regular access points, it is crucial to consider emergency escape routes in house on stilts plans. These escape routes should be clearly marked and easily accessible from all areas of the house. Emergency escape routes may include ladders or designated windows that lead to the ground level.
By carefully planning and incorporating these access and egress considerations into house on stilts plans, homeowners can ensure the safety and convenience of occupants, both during normal conditions and in the event of emergencies or flooding.
Maintenance and repairs
Maintaining and repairing a house on stilts requires regular attention to specific areas to ensure its longevity and safety. Here are some key details related to maintenance and repairs:
Inspection and cleaning
Regular inspection and cleaning are crucial for maintaining a house on stilts. Inspect the stilts, beams, and other structural components for any signs of damage, rot, or insect infestation. Clean the stilts and surrounding areas to remove dirt, debris, and vegetation that can trap moisture and lead to decay.
Repairs and replacements
As needed, repairs or replacements of structural components may be necessary to maintain the integrity of the house on stilts. Repairs may involve replacing damaged stilts, beams, or decking. In some cases, entire sections of the structure may need to be replaced to ensure safety.
Painting and sealing
Painting or sealing the stilts and other exposed structural components helps protect them from moisture, rot, and insects. Regularly applying a fresh coat of paint or sealant can extend the lifespan of these components and maintain the overall appearance of the house.
Foundation maintenance
The foundation of a house on stilts requires regular maintenance to ensure its stability and prevent any settlement or shifting. Inspect the foundation for cracks, erosion, or any signs of movement. Address any issues promptly to maintain the integrity of the foundation.
By following these maintenance and repair guidelines, homeowners can ensure the longevity, safety, and structural integrity of their house on stilts for years to come.
Cost and budget
The cost of building a house on stilts can vary depending on several factors, including the size and complexity of the design, the materials used, and the local labor costs. Here are some key considerations related to cost and budget in house on stilts plans:
Size and complexity
The size and complexity of the house on stilts design significantly impact the overall cost. Larger houses with more intricate designs typically require more materials, labor, and time to build, resulting in higher costs. Factors such as the number of stilts, the height of the structure, and the presence of additional features like decks or balconies can also contribute to the cost.
Materials
The choice of materials used for the stilts, foundation, decking, and other structural components can influence the cost of building a house on stilts. Pressure-treated wood, galvanized steel, and concrete are commonly used materials, each with its own cost implications. The type of roofing material, siding, and windows selected can also affect the overall cost.
Labor costs
Labor costs can vary depending on the location and availability of skilled labor. Regions with higher labor costs may result in a more expensive build. The complexity of the design and the need for specialized skills, such as those required for electrical and plumbing work, can also impact labor costs.
Foundation costs
The type of foundation required for a house on stilts can also affect the cost. Concrete piers, steel piers, and timber piles are common foundation options, with varying costs depending on the soil conditions, flood risk, and the size of the structure. In areas with challenging soil conditions or high flood risk, more extensive foundation systems may be necessary, leading to increased costs.
To ensure accurate cost estimates, it is advisable to consult with local contractors and material suppliers. They can provide detailed quotes based on the specific requirements of your house on stilts plans, taking into account factors such as size, materials, labor costs, and local building codes.
Building codes
Building codes are a set of regulations that govern the construction, alteration, and maintenance of buildings to ensure public safety, health, and welfare. When it comes to house on stilts plans, there are specific building codes that need to be considered to ensure the structural integrity and safety of these elevated structures.
- Foundation requirements: Building codes specify the minimum requirements for the foundation of a house on stilts, including the depth, width, and spacing of the stilts, as well as the type of materials that can be used. These requirements are based on factors such as soil conditions, flood risk, and seismic activity in the area.
- Structural design: Building codes outline the structural requirements for houses on stilts, including the size and spacing of the beams, joists, and other structural members. These requirements are intended to ensure that the structure can withstand the weight of the building, as well as lateral forces such as wind and seismic loads.
- Fire safety: Building codes include fire safety provisions for houses on stilts, such as the use of fire-resistant materials and the installation of smoke detectors and sprinklers. These measures are designed to minimize the risk of fire and protect the occupants in the event of a fire.
- Accessibility: Building codes may also include accessibility requirements for houses on stilts, such as the provision of ramps or elevators to ensure that the building is accessible to individuals with disabilities.
Adhering to building codes is crucial for ensuring the safety and structural integrity of a house on stilts. By following these codes, homeowners can be confident that their elevated home is built to withstand the elements and provide a safe and comfortable living environment.
Aesthetic preferences
In addition to functional considerations, aesthetic preferences also play a significant role in house on stilts plans. Homeowners can customize their elevated homes to reflect their personal style and create a visually appealing living space. Here are some key aesthetic considerations:
- Exterior design: The exterior design of a house on stilts can vary greatly, from traditional to modern styles. Homeowners can choose from a range of materials, colors, and architectural elements to create a unique look for their home. The shape and size of the stilts, the type of decking, and the overall form of the house can all be tailored to suit the desired aesthetic.
- Color schemes: Color plays a vital role in enhancing the visual appeal of a house on stilts. Homeowners can select colors for the exterior siding, trim, and stilts that complement each other and create a harmonious look. Bright colors can create a cheerful and inviting atmosphere, while neutral tones may lend a more sophisticated and elegant feel.
- Architectural details: Architectural details can add character and interest to a house on stilts. Decorative elements such as railings, latticework, and moldings can enhance the visual appeal of the structure. Homeowners can choose architectural details that align with the overall style of their home, whether it be traditional, contemporary, or coastal.
- Landscaping: The landscaping around a house on stilts can complement and enhance its aesthetic appeal. Planting trees, shrubs, and flowers around the stilts can create a visually pleasing environment and provide privacy. Homeowners can also incorporate outdoor lighting to highlight the architectural features of their home and create a warm and inviting ambiance.
By carefully considering these aesthetic elements, homeowners can create a house on stilts that not only meets their functional requirements but also reflects their personal style and creates a visually stunning living space.









Related Posts