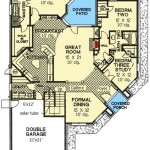
House Design With Floor Plan, also known as Residential Floor Planning, is the process of creating a diagrammatic representation of a house’s interior layout. It serves as a blueprint for the arrangement of rooms, hallways, and other spaces within a house. Floor plans provide essential information about the size, shape, and relationships between different areas of a house, enabling architects, builders, and homeowners to visualize and plan the functionality and aesthetics of the living space.
For instance, in the design of a single-family home, a floor plan might include an entryway leading to a spacious living room with an open kitchen and dining area, connected by a hallway leading to bedrooms, bathrooms, and other private spaces. The floor plan would specify the dimensions of each room, the location of windows and doors, and the placement of furniture and fixtures.
Floor plans are crucial for planning and constructing houses as they allow for efficient use of space, optimal lighting and ventilation, and seamless transitions between different areas of the house. They help ensure that the house meets the functional needs of its occupants while adhering to building codes and regulations.
House design with floor plan involves several important considerations:
- Space planning
- Traffic flow
- Lighting and ventilation
- Privacy and security
- Accessibility
- Energy efficiency
- Building codes
- Personal preferences
By addressing these aspects, floor plans help create functional, comfortable, and aesthetically pleasing living spaces.
Space planning
Space planning is the process of determining the size, shape, and arrangement of rooms and other spaces within a house. It involves allocating space for different functions, such as living, sleeping, cooking, dining, and storage. The goal of space planning is to create a functional and comfortable living environment that meets the needs of the occupants.
- Efficient use of space
Space planning helps ensure that the available space is used efficiently. By carefully considering the size and shape of rooms, as well as the placement of walls, doors, and windows, architects can create floor plans that maximize space utilization and minimize wasted areas.
- Functional layout
Space planning also involves creating a functional layout that allows for easy and efficient movement between different areas of the house. The arrangement of rooms and spaces should facilitate daily activities and minimize disruptions. For example, locating the kitchen and dining areas near each other can improve convenience and efficiency during meal preparation and serving.
- Natural lighting and ventilation
Space planning takes into account the placement of windows and doors to maximize natural lighting and ventilation. By positioning windows strategically, architects can create brighter and more inviting spaces while reducing the need for artificial lighting during the day. Proper ventilation is also essential for maintaining a healthy and comfortable indoor environment.
- Privacy and noise control
Space planning also considers privacy and noise control. The arrangement of rooms and the use of soundproofing materials can help create private spaces for bedrooms and bathrooms. Separating noisy areas, such as the laundry room or utility room, from quieter areas can minimize noise disturbances.
Overall, space planning is a critical aspect of house design with floor plan. By carefully planning the size, shape, and arrangement of spaces, architects can create functional, comfortable, and aesthetically pleasing living environments that meet the specific needs and preferences of the occupants.
Traffic flow
Traffic flow refers to the movement of people and objects within a house. It is important to consider traffic flow when designing a floor plan to ensure that the movement of occupants is smooth, efficient, and safe.
- Main circulation paths
The main circulation paths are the primary pathways through which people move within a house. These paths should be wide enough to accommodate the movement of people and objects, and they should be free of obstacles. Common main circulation paths include hallways, corridors, and stairways.
- Secondary circulation paths
Secondary circulation paths are less frequently used pathways that connect different areas of the house. These paths can be narrower than main circulation paths, but they should still be wide enough to allow for comfortable movement. Examples of secondary circulation paths include doorways and passages between rooms.
- Avoidance of congestion
Traffic flow planning aims to avoid congestion and bottlenecks in the movement of people and objects. By carefully considering the placement of rooms, doors, and hallways, architects can create floor plans that minimize the likelihood of people getting stuck or having to backtrack.
- Safety considerations
Traffic flow planning also takes into account safety considerations. The arrangement of spaces and the placement of circulation paths should minimize the risk of accidents, such as falls or collisions. For example, stairs should be well-lit and have handrails, and hallways should be free of tripping hazards.
Overall, traffic flow is an important aspect of house design with floor plan. By carefully planning the movement of people and objects within a house, architects can create floor plans that are functional, efficient, and safe.
Lighting and ventilation
Lighting and ventilation are essential aspects of house design with floor plan. They contribute to the overall comfort, health, and well-being of the occupants.
Natural lighting
Natural lighting refers to the use of sunlight to illuminate the interior of a house. It is an important consideration in floor plan design as it can reduce the need for artificial lighting, saving energy and creating a more inviting and healthier living environment.
- Placement of windows
The placement of windows is crucial for maximizing natural lighting. Architects carefully consider the orientation of the house and the position of the sun to ensure that rooms receive adequate sunlight throughout the day. South-facing windows, for example, allow for maximum sunlight exposure in the Northern Hemisphere.
- Size and shape of windows
The size and shape of windows also affect the amount of natural light entering a space. Larger windows allow for more light, while smaller windows provide more privacy. The shape of the window can also be used to control the direction and distribution of light.
- Skylights and solar tubes
Skylights and solar tubes are effective ways to bring natural light into interior spaces that do not have access to exterior walls. Skylights are installed on the roof, while solar tubes are reflective tubes that channel sunlight from the roof to other parts of the house.
Ventilation
Ventilation refers to the exchange of air between the interior and exterior of a house. It is essential for maintaining a healthy indoor environment by removing stale air, moisture, and pollutants.
- Cross-ventilation
Cross-ventilation is a passive ventilation technique that involves placing windows and doors on opposite sides of a room to create a flow of air. This helps to remove stale air and bring in fresh air from the outside.
- Mechanical ventilation
Mechanical ventilation systems use fans or ducts to circulate air throughout a house. These systems can be used to supplement natural ventilation or provide ventilation in areas where cross-ventilation is not possible.
- Exhaust fans
Exhaust fans are installed in areas where moisture and pollutants are generated, such as bathrooms and kitchens. They help to remove these contaminants from the air and improve indoor air quality.
By carefully considering lighting and ventilation in floor plan design, architects can create houses that are not only energy-efficient but also healthy and comfortable to live in.
Privacy and security
Privacy and security are important considerations in house design with floor plan. The arrangement of rooms and spaces, as well as the placement of windows and doors, can impact the privacy and security of the occupants.
Privacy
Privacy refers to the ability of occupants to control access to and use of different areas of the house. Floor plans can be designed to create private spaces for bedrooms, bathrooms, and other areas where occupants may desire privacy.
- Placement of bedrooms
Bedrooms are typically placed in private areas of the house, away from common areas and entrances. This helps to ensure that occupants can sleep and relax without disturbances.
- En suite bathrooms
En suite bathrooms are private bathrooms that are directly accessible from bedrooms. This provides occupants with a private and convenient way to use the bathroom, without having to share it with other members of the household or guests.
- Separate living areas
Separate living areas, such as a living room and a family room, can provide occupants with private spaces to relax and entertain guests.
Security
Security refers to the protection of occupants and their property from unauthorized access or harm. Floor plans can be designed to incorporate security features that deter crime and improve the safety of the occupants.
- Secure entrances
Secure entrances are designed to prevent unauthorized access to the house. This can be achieved through the use of strong doors, locks, and security systems.
- Visibility from the street
Houses that are visible from the street are less likely to be targeted by burglars. Floor plans should consider the placement of windows and doors to maximize visibility from the street.
- Landscaping for security
Landscaping can be used to improve security by creating barriers around the house and providing visibility. Planting thorny shrubs or installing a fence can deter intruders.
- Security lighting
Security lighting can be used to deter crime by illuminating dark areas around the house. Motion-activated lights can be particularly effective in deterring intruders.
By carefully considering privacy and security in floor plan design, architects can create houses that are not only functional and comfortable but also safe and secure for the occupants.
Accessibility
Accessibility in house design with floor plan refers to the ability of all individuals, regardless of their physical abilities, to safely and independently use and enjoy the spaces within a house. Accessibility considerations are particularly important for individuals with disabilities, such as those who use wheelchairs or have difficulty walking or climbing stairs.
- Universal design principles
Universal design principles aim to create spaces that are accessible and usable by people of all abilities. When applied to house design, universal design principles can include features such as wide doorways, ramps instead of stairs, and accessible bathroom fixtures.
- Zero-step entry
Zero-step entry refers to the design of entrances and doorways that are level with the ground, eliminating the need for steps or ramps. This feature is essential for individuals who use wheelchairs or have difficulty walking.
- Accessible hallways and doorways
Hallways and doorways should be wide enough to allow for easy movement of wheelchairs and other mobility aids. Doorways should also have lever handles instead of knobs, which can be difficult to operate for individuals with limited hand mobility.
- Accessible bathrooms
Accessible bathrooms include features such as roll-in showers, grab bars, and raised toilets. These features make it easier for individuals with disabilities to use the bathroom safely and independently.
By incorporating accessibility considerations into floor plan design, architects can create houses that are not only functional and comfortable but also accessible and inclusive for all.
Energy efficiency
Energy efficiency in house design with floor plan refers to the use of design strategies and technologies to minimize the amount of energy required to operate a house. By incorporating energy-efficient features into the floor plan, architects can create houses that are more environmentally friendly and less expensive to operate.
- Building envelope
The building envelope is the physical separator between the interior and exterior of a house. It includes the roof, walls, windows, and doors. A well-designed building envelope can significantly reduce heat loss and gain, leading to improved energy efficiency.
- Insulation
Insulation is a material that is installed in the building envelope to resist heat flow. It can be used in walls, ceilings, and floors to minimize heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer. Proper insulation can greatly improve the energy efficiency of a house.
- Windows and doors
Windows and doors are major sources of heat loss in a house. Energy-efficient windows and doors are designed to minimize heat transfer, reducing the amount of energy required to heat or cool the house.
By carefully considering energy efficiency in floor plan design, architects can create houses that are not only comfortable and functional but also environmentally friendly and economical to operate.
Building codes
Building codes are regulations that govern the design, construction, and alteration of buildings. They are established to ensure the safety, health, and welfare of the public. Building codes related to house design with floor plan include:
- Zoning codes
Zoning codes regulate the use of land and the types of buildings that can be constructed in different areas. They may specify the minimum lot size, building height, and setbacks from property lines. Zoning codes help to ensure that new houses are compatible with the surrounding neighborhood and that there is adequate space for infrastructure and public services.
- Building codes
Building codes set minimum standards for the structural integrity, fire safety, and accessibility of buildings. They specify requirements for the design and construction of foundations, walls, roofs, electrical systems, plumbing systems, and other building components. Building codes help to ensure that houses are safe and habitable.
- Energy codes
Energy codes regulate the energy efficiency of buildings. They specify requirements for insulation, windows, doors, and other building components that affect energy consumption. Energy codes help to reduce the environmental impact of buildings and lower energy costs for occupants.
- Accessibility codes
Accessibility codes ensure that buildings are accessible to people with disabilities. They specify requirements for ramps, elevators, accessible bathrooms, and other features that make it easier for people with disabilities to use and enjoy buildings.
By complying with building codes, architects and builders can create houses that are safe, healthy, energy-efficient, and accessible. Building codes help to protect the public and ensure that houses are built to a minimum standard of quality.
Personal preferences
Lifestyle and needs
Personal preferences play a significant role in house design with floor plan. The arrangement of rooms and spaces should reflect the lifestyle and needs of the occupants. For example, a family with young children may prefer a floor plan with a large open-plan living area where they can spend time together. A couple who loves to entertain may prefer a floor plan with a formal dining room and a separate living room for guests. A person who works from home may prefer a floor plan with a dedicated home office.
Architectural style
Personal preferences also extend to the architectural style of the house. Some people prefer traditional styles, such as Colonial or Victorian, while others prefer more modern styles, such as Contemporary or Mid-Century Modern. The architectural style of the house should complement the personal taste of the occupants and the surrounding neighborhood.
Interior design
Interior design is another important aspect of personal preference in house design. The colors, finishes, and furnishings of the house should reflect the personal style of the occupants. Some people prefer a minimalist aesthetic with clean lines and neutral colors, while others prefer a more eclectic style with bold colors and patterns. The interior design of the house should create a space that is both comfortable and inviting.
Outdoor living
For many people, outdoor living is an important part of their lifestyle. A well-designed floor plan should include spaces for outdoor living, such as a patio, deck, or porch. These spaces can be used for relaxing, entertaining, or simply enjoying the outdoors. The design of the outdoor living spaces should complement the architectural style of the house and the personal preferences of the occupants.
By considering personal preferences in floor plan design, architects can create houses that are not only functional and comfortable but also reflect the unique style and personality of the occupants.









Related Posts