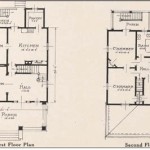
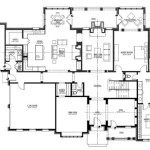
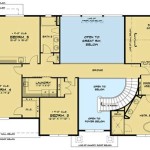
House design plans serve as blueprints that outline the architectural layout and specifications of a residential building. They provide a detailed roadmap for the construction process, encompassing aspects such as room dimensions, structural elements, electrical wiring, and plumbing systems. These plans are essential for ensuring the integrity, functionality, and aesthetic appeal of the final structure.
The development of house design plans typically involves collaboration between architects, engineers, and homeowners. Architects conceptualize the overall design and space utilization, while engineers ensure structural stability and compliance with building codes. Homeowners provide their desired specifications and preferences, influencing the layout, room sizes, and exterior features of the house. By integrating these diverse perspectives, house design plans serve as a comprehensive guide for transforming architectural visions into tangible living spaces.
In the subsequent sections of this article, we will delve into the various types of house design plans available, their advantages and disadvantages, and essential considerations for homeowners when selecting the most suitable plan for their needs.
Consider these crucial aspects when evaluating house design plans:
- Site analysis: Study the land’s topography, orientation, and environmental factors.
- Space planning: Optimize the flow and functionality of interior spaces.
- Exterior design: Choose a style that complements the surroundings and personal preferences.
- Structural integrity: Ensure the plan adheres to building codes and provides stability.
- Energy efficiency: Design for optimal insulation, natural lighting, and sustainable features.
- Cost estimation: Determine the financial implications of the plan’s materials and construction.
- Zoning compliance: Verify that the plan aligns with local building regulations.
- Flexibility: Consider future modifications or expansions.
- Personalization: Tailor the plan to suit individual needs and preferences.
- Professional expertise: Seek guidance from qualified architects and engineers.
By addressing these points, homeowners can make informed decisions and select a house design plan that meets their unique requirements and aspirations.
Site analysis: Study the land’s topography, orientation, and environmental factors.
Site analysis is a crucial step in house design planning, as it involves carefully studying the land’s topography, orientation, and environmental factors to optimize the building’s design and functionality. Topography refers to the shape and elevation of the land, which can influence factors such as drainage, foundation design, and views from the house. Orientation refers to the direction in which the house faces, which affects natural lighting, solar heat gain, and prevailing winds. Environmental factors include vegetation, soil conditions, and access to utilities, which can impact landscaping, drainage, and overall sustainability.
Understanding the topography of the land is essential for determining the most suitable building site and foundation type. Sloping land may require special engineering considerations to ensure stability and prevent erosion, while flat land may offer more flexibility in terms of placement and drainage. The orientation of the house should be carefully planned to maximize natural lighting and minimize heat gain during summer months. South-facing orientations are generally preferred in the Northern Hemisphere, as they receive the most sunlight throughout the day. Prevailing winds should also be considered, as they can affect ventilation and energy efficiency.
In addition to topography and orientation, environmental factors such as vegetation, soil conditions, and access to utilities should be carefully evaluated. Mature trees can provide shade and privacy, but they can also interfere with solar access and drainage. Soil conditions can impact the type of foundation required and the cost of construction. Access to utilities such as water, electricity, and sewer is essential for the functionality of the house and should be considered during site analysis.
By conducting a thorough site analysis, architects and homeowners can make informed decisions about the placement, orientation, and design of the house to ensure that it is well-suited to the specific characteristics of the land and minimizes potential challenges during construction and throughout the life of the building.
Space planning: Optimize the flow and functionality of interior spaces.
Space planning is a critical aspect of house design, as it involves optimizing the flow and functionality of interior spaces to create a comfortable, efficient, and aesthetically pleasing living environment. It encompasses the arrangement of rooms, the placement of fixtures and furniture, and the creation of spaces that meet the specific needs and preferences of the occupants.
Effective space planning begins with understanding the activities that will take place in each room and how they relate to each other. For example, the kitchen should be designed to facilitate food preparation, storage, and dining, while the living room should provide a comfortable and inviting space for relaxation and entertainment. By considering the intended use of each room, architects and homeowners can create a layout that promotes smooth transitions between spaces and minimizes disruptions to daily routines.
In addition to the functional aspects of space planning, aesthetic considerations also play an important role. The placement of windows, doors, and other architectural elements can be used to create visually appealing spaces that maximize natural light and offer pleasing views. The use of color, texture, and materials can further enhance the aesthetics of interior spaces and create a cohesive and inviting atmosphere.
Space planning should also take into account the specific needs and preferences of the occupants. For example, families with young children may require a more open floor plan to facilitate supervision and interaction. Individuals with mobility impairments may need wider doorways and accessible fixtures. By tailoring the space plan to the unique requirements of the occupants, architects and homeowners can create a truly personalized and functional living space.
Exterior design: Choose a style that complements the surroundings and personal preferences.
Exterior design plays a crucial role in the overall appeal and functionality of a house. It encompasses the architectural style, materials, colors, and landscaping that define the building’s external appearance and its relationship to the surrounding environment.
- Curb appeal:
The exterior design should create an inviting and visually pleasing impression from the street. This can be achieved through a harmonious combination of architectural elements, materials, and landscaping.
- Contextual harmony:
The exterior design should complement the architectural styles and materials of the surrounding neighborhood while still maintaining a unique identity. This can be achieved by incorporating similar design elements or materials, or by using a complementary color scheme.
- Personal expression:
The exterior design should reflect the personal tastes and preferences of the homeowners. This can be achieved through the choice of architectural style, materials, colors, and landscaping that align with their individual aesthetic sensibilities.
- Functional considerations:
In addition to aesthetics, the exterior design should also consider functional aspects such as weather resistance, energy efficiency, and outdoor living spaces. The choice of materials and architectural elements should be appropriate for the local climate and should minimize energy consumption.
By carefully considering these factors, architects and homeowners can create an exterior design that not only enhances the beauty and value of their home but also complements the surrounding environment and reflects their personal style.
Structural integrity: Ensure the plan adheres to building codes and provides stability.
Structural integrity is paramount in house design, as it ensures the safety and stability of the building throughout its lifespan. To achieve this, house design plans must adhere to established building codes and incorporate sound engineering principles to withstand various loads and forces.
- Compliance with building codes:
Building codes are regulations set by local authorities to ensure the structural safety and habitability of buildings. House design plans must comply with these codes to guarantee that the building meets minimum safety standards for materials, construction methods, and structural design.
- Load analysis:
Structural engineers carefully analyze the various loads that the house will be subjected to, including dead loads (permanent fixtures and materials), live loads (occupants and furniture), wind loads, seismic loads (in earthquake-prone areas), and snow loads (in climates). The plan must account for these loads and incorporate appropriate structural elements to resist them.
- Foundation design:
The foundation is the base of the house and plays a critical role in its stability. The plan must specify the type of foundation (e.g., slab-on-grade, crawlspace, basement) that is suitable for the soil conditions and the anticipated loads.
- Structural framing:
The structural framing, which includes elements such as beams, columns, and trusses, provides the skeletal framework of the house. The plan must specify the materials, dimensions, and connections of these elements to ensure adequate strength and rigidity.
By addressing these points, house design plans provide a roadmap for constructing a structurally sound and safe building that can withstand the test of time and environmental factors.
Energy efficiency: Design for optimal insulation, natural lighting, and sustainable features.
Energy efficiency is a key consideration in modern house design, as it can significantly reduce energy consumption, lower utility bills, and minimize the environmental impact of the building. House design plans should incorporate strategies to optimize insulation, utilize natural lighting, and integrate sustainable features to create energy-efficient and eco-friendly homes.
- Insulation:
Insulation is a crucial factor in reducing heat loss and gain, thereby minimizing energy consumption for heating and cooling. House design plans should specify the type and thickness of insulation materials to be used in walls, ceilings, and floors. Proper insulation helps maintain a comfortable indoor temperature, reduces drafts, and improves overall energy efficiency.
- Natural lighting:
Natural lighting can significantly reduce the need for artificial lighting during daytime hours, leading to energy savings. House design plans should maximize the use of windows, skylights, and other openings to allow ample natural light to enter the building. Proper placement and orientation of windows can optimize daylighting while minimizing heat gain or loss.
- Sustainable features:
Sustainable features, such as solar panels, rainwater harvesting systems, and energy-efficient appliances, can further enhance the energy efficiency of a house. House design plans should consider the incorporation of these features to reduce reliance on non-renewable energy sources and promote environmental sustainability. Solar panels can generate electricity, rainwater harvesting systems can supplement water supply, and energy-efficient appliances can minimize energy consumption.
- Building envelope:
The building envelope, which includes the roof, walls, and windows, plays a vital role in energy efficiency. House design plans should specify materials and construction methods that enhance the thermal performance of the building envelope. This can include the use of high-performance windows, proper air sealing, and thermal bridging mitigation to minimize heat loss and gain.
By incorporating these energy-efficient strategies into house design plans, architects and homeowners can create buildings that are not only comfortable and aesthetically pleasing but also environmentally responsible and cost-effective to operate.
Cost estimation: Determine the financial implications of the plan’s materials and construction.
Cost estimation is a critical aspect of house design planning, as it helps homeowners and builders determine the financial implications of the chosen design. Accurate cost estimates are essential for budgeting, securing financing, and making informed decisions throughout the construction process.
The cost of building a house can vary significantly depending on a range of factors, including the size and complexity of the design, the materials used, and the local construction costs. House design plans should provide a detailed breakdown of the estimated costs for each major component of the house, including materials, labor, permits, and professional fees.
Material costs represent a significant portion of the overall construction budget. House design plans should specify the types and quantities of materials required for the foundation, framing, roofing, exterior cladding, interior finishes, and fixtures. The cost of materials can vary depending on factors such as quality, availability, and transportation costs.
Labor costs are another major expense to consider. House design plans should provide an estimate of the labor hours required for each phase of construction, including site preparation, foundation work, framing, electrical and plumbing installation, and finishing work. Labor costs can vary depending on the skill level of the workers, union contracts, and local labor market conditions.
In addition to materials and labor, other costs to consider include permits, inspections, and professional fees. Permits are required for most construction projects and can vary in cost depending on the size and complexity of the project. Inspections are also required to ensure compliance with building codes and can add to the overall cost. Professional fees for architects, engineers, and other consultants should also be factored into the cost estimation.
Zoning compliance: Verify that the plan aligns with local building regulations.
Zoning compliance is a crucial aspect of house design planning, as it ensures that the proposed design adheres to the zoning regulations and building codes established by local authorities. Zoning laws are regulations that govern the use, height, and density of buildings within specific geographic areas.
Before finalizing house design plans, it is essential to conduct thorough research on the zoning regulations applicable to the property. This involves checking with the local planning department or building authority to obtain information about the zoning district in which the property is located and the specific requirements that apply to that district. These requirements may include restrictions on building height, setbacks from property lines, lot coverage, and permitted uses.
Verifying zoning compliance helps avoid potential conflicts and delays during the construction process. It ensures that the proposed design meets the minimum requirements for the zoning district and does not violate any height, setback, or density limitations. Compliance with zoning regulations also helps protect the character and integrity of the neighborhood and ensures that new developments are compatible with the surrounding area.
To ensure zoning compliance, house design plans should clearly indicate the building’s height, setbacks, and lot coverage. The plans should also demonstrate how the proposed use of the building complies with the permitted uses for the zoning district. By carefully considering zoning regulations and incorporating them into the design process, architects and homeowners can increase the likelihood of obtaining building permits and avoid costly revisions or legal challenges.
In addition to zoning compliance, house design plans should also adhere to building codes. Building codes are technical regulations that set minimum standards for the construction of buildings to ensure their safety, structural integrity, and habitability. Building codes cover various aspects of construction, including structural design, fire safety, plumbing, electrical systems, and energy efficiency.
Flexibility: Consider future modifications or expansions.
Flexibility is a key consideration in house design planning, as it allows homeowners to adapt their homes to changing needs and circumstances over time. By incorporating flexibility into the design, homeowners can create spaces that can be easily modified or expanded in the future without major renovations or structural changes.
- Modular design:
Modular design involves dividing the house into smaller, self-contained units or modules. These modules can be easily added, removed, or reconfigured to create new spaces or expand existing ones. This approach provides flexibility for future changes in family size, lifestyle, or functional requirements.
- Multi-purpose spaces:
Designing spaces that can serve multiple functions allows for greater flexibility. For example, a guest room can be designed to double as a home office or a playroom. Convertible spaces can be created using movable walls, partitions, or built-in furniture that can be reconfigured to suit different needs.
- Future expansion potential:
House design plans should consider the potential for future expansions, such as adding a new room, extending the existing footprint, or creating an additional story. This can be achieved by incorporating structural elements that can support future additions, such as reinforced foundations or pre-planned electrical and plumbing connections.
- Universal design principles:
Universal design principles aim to create spaces that are accessible and adaptable to people of all ages and abilities. By incorporating features such as wider doorways, accessible bathrooms, and adaptable kitchens, homeowners can ensure that their homes can accommodate changing needs over time.
By considering flexibility in house design plans, homeowners can create homes that are not only beautiful and functional but also adaptable to their evolving needs and aspirations. This foresight can save time, money, and disruption in the future, ensuring that the home remains a comfortable and enjoyable living space for years to come.
Personalization: Tailor the plan to suit individual needs and preferences.
Personalization is at the heart of house design planning, as it allows homeowners to create a living space that truly reflects their unique style, needs, and aspirations. By tailoring the design to their individual preferences, homeowners can ensure that their home is not only aesthetically pleasing but also functional and comfortable for their daily lives.
One important aspect of personalization is understanding the specific lifestyle and routines of the homeowners. This includes considering the number of occupants, their ages, and their daily activities. For example, a family with young children may require a more open floor plan to facilitate supervision and interaction, while a couple of empty nesters may prefer a more formal layout with separate living and dining areas.
Personalization also extends to the choice of materials, finishes, and fixtures. Homeowners can select colors, textures, and patterns that align with their personal tastes and create a cohesive and inviting atmosphere. The kitchen, for instance, can be designed with custom cabinetry, unique countertops, and high-end appliances that cater to the homeowner’s culinary preferences and cooking style.
Furthermore, personalization involves incorporating features that enhance the homeowners’ comfort and well-being. This can include designing spaces for specific hobbies or interests, such as a dedicated home office, a music room, or a home gym. Smart home technology can also be integrated to provide convenience, security, and energy efficiency, tailored to the homeowners’ daily routines and preferences.
By prioritizing personalization, house design plans empower homeowners to create homes that are not just structures but extensions of their personalities and lifestyles. A well-personalized home fosters a sense of belonging, comfort, and joy, making it a truly special and cherished space.
Professional expertise: Seek guidance from qualified architects and engineers.
Engaging the services of qualified architects and engineers is crucial for successful house design planning and construction. These professionals possess the knowledge, skills, and experience necessary to create safe, functional, and aesthetically pleasing living spaces that meet the specific needs and preferences of homeowners.
- Architectural design expertise:
Architects are trained professionals who specialize in the art and science of building design. They possess a comprehensive understanding of architectural styles, space planning, structural systems, and building codes. Architects work closely with homeowners to translate their vision and requirements into functional and visually appealing design solutions.
- Engineering expertise:
Engineers, particularly structural engineers, play a vital role in ensuring the structural integrity and safety of buildings. They analyze loads, design structural elements, and specify materials to withstand various forces and environmental conditions. Engineers also work closely with architects to ensure that the design is structurally feasible and complies with building codes.
- Project management and coordination:
Architects and engineers often serve as project managers, overseeing the entire design and construction process. They coordinate with contractors, subcontractors, and other professionals to ensure that the project is completed on time, within budget, and to the required standards.
- Building code compliance:
Architects and engineers are well-versed in building codes and regulations. They ensure that the design plans adhere to these codes, ensuring the safety and habitability of the building. They also provide guidance on obtaining necessary permits and inspections.
By seeking the guidance of qualified architects and engineers, homeowners can benefit from their expertise, experience, and professionalism. This collaboration leads to well-conceived house design plans that meet the homeowners’ needs, comply with building codes, and result in safe, functional, and aesthetically pleasing living spaces.






Related Posts