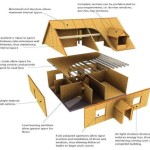
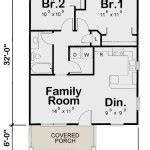
A “Free Tiny House Plan” refers to a detailed blueprint and set of instructions that guide individuals in constructing a compact and economical dwelling without incurring design fees. These plans provide step-by-step guidance, including material lists, floor layouts, and detailed diagrams, allowing anyone with basic DIY skills to build a functional and comfortable home on a smaller scale.
The increasing popularity of tiny houses is attributed to their affordability, environmental friendliness, and adaptability to various lifestyles. Building a tiny house from scratch offers several benefits, including cost savings, customization options, and the satisfaction of creating a space that truly meets one’s specific needs. Free tiny house plans empower individuals to embark on this journey without the added financial burden of professional designs.
In the following sections, we will explore the advantages and considerations associated with utilizing free tiny house plans, provide a curated selection of reputable sources offering these plans, and delve into specific examples of these plans to inspire and guide your tiny home building aspirations.
To help you make the most of your free tiny house plan, here are ten important points to keep in mind:
- Clear Design: Opt for plans with simple and straightforward designs.
- Detailed Instructions: Ensure the plans provide thorough step-by-step instructions.
- Material Lists: Verify that the plans include comprehensive material lists.
- Measurements: Pay attention to precise measurements to avoid costly errors.
- Foundation: Choose plans that align with your desired foundation type.
- Adaptability: Consider plans that allow for customization and future expansion.
- Local Building Codes: Ensure the plans comply with local building regulations.
- Realistic Timeline: Allow ample time for construction based on the plan’s complexity.
- DIY Skills: Assess your DIY capabilities and select plans that match your skill level.
- Cost Estimation: Factor in the cost of materials and labor before starting construction.
By following these key points, you can successfully navigate the process of building your dream tiny home using a free tiny house plan.
Clear Design: Opt for plans with simple and straightforward designs.
When selecting a free tiny house plan, clarity of design is paramount. Simple and straightforward plans are easier to follow, reducing the likelihood of errors and costly mistakes during construction. Look for plans that provide clear and concise instructions, avoiding complex architectural details or intricate designs. Simpler designs typically require fewer materials and less specialized skills, making them more suitable for first-time builders or those with limited experience.
Plans with straightforward designs often feature rectangular or square shapes, which optimize space utilization and simplify the construction process. Avoid plans with excessive angles, curves, or intricate rooflines, as these elements can increase complexity and require more advanced building techniques. Stick to basic layouts with well-defined spaces for sleeping, cooking, and living. By choosing a plan with a clear and simple design, you set yourself up for a smoother and more manageable building experience.
Furthermore, simple designs allow for greater flexibility and customization down the road. If you decide to expand or modify your tiny house in the future, a straightforward design provides a solid foundation upon which to build. You can easily add rooms or features without compromising the structural integrity or overall aesthetic of your home. In contrast, complex designs may limit your options for future modifications.
Remember, the goal of a free tiny house plan is to provide a cost-effective and accessible way to build a compact and comfortable dwelling. Opting for a plan with a clear and simple design aligns with this objective, ensuring a straightforward and enjoyable building experience.
By prioritizing clarity of design in your free tiny house plan, you lay the groundwork for a successful and rewarding construction project.
Detailed Instructions: Ensure the plans provide thorough step-by-step instructions.
When selecting a free tiny house plan, the level of detail in the instructions is crucial. Thorough and comprehensive instructions guide you through each stage of construction, minimizing uncertainties and preventing costly mistakes. Look for plans that provide step-by-step directions, detailed diagrams, and clear explanations.
Well-written instructions break down complex tasks into manageable steps, ensuring that even novice builders can follow along. Each step should be accompanied by clear diagrams or illustrations that visually demonstrate the process. Plans with detailed instructions empower you to tackle the construction process with confidence, knowing that you have a reliable guide to follow.
Furthermore, thorough instructions anticipate potential challenges and provide solutions or alternative approaches. They address common pitfalls and offer troubleshooting tips, helping you navigate unforeseen circumstances. By providing detailed guidance, the plans empower you to make informed decisions and adapt to site-specific conditions or personal preferences.
Plans with comprehensive instructions not only simplify the construction process but also promote safety. Clear instructions ensure that you perform each step correctly, minimizing the risk of accidents or structural issues. By following well-documented plans, you can build a tiny house that is not only beautiful but also safe and durable.
Remember, detailed instructions are the cornerstone of a successful tiny house building project. By choosing a plan that provides thorough step-by-step guidance, you set yourself up for a smooth and rewarding experience.
Material Lists: Verify that the plans include comprehensive material lists.
When selecting a free tiny house plan, the inclusion of comprehensive material lists is essential. Detailed material lists provide a complete inventory of all the materials required for construction, ensuring that you have everything you need before starting the project. This eliminates the hassle of guesswork and potential delays due to missing or incorrect materials.
- Accurate Quantities: Comprehensive material lists specify the exact quantities of each material needed, minimizing waste and ensuring that you don’t run short during construction.
- Material Specifications: The lists should include detailed specifications for each material, including size, grade, and type. This ensures that you purchase the correct materials for the intended purpose.
- Cost Estimation: Material lists allow you to estimate the total cost of your tiny house project. By knowing the quantities and specifications of the required materials, you can accurately budget for the construction.
- Procurement Planning: Comprehensive material lists assist in procurement planning. You can easily identify the materials that need to be ordered in advance and those that can be purchased locally.
By using a free tiny house plan that includes a comprehensive material list, you gain several advantages. You can confidently purchase the necessary materials without worrying about shortages or errors. This streamlines the construction process, saves you time and money, and reduces the risk of delays.
Measurements: Pay attention to precise measurements to avoid costly errors.
When working with a free tiny house plan, precise measurements are of utmost importance. Even minor errors in measurements can lead to costly mistakes and structural issues down the road. Careful attention to measurements ensures that your tiny house is built to last and meets your specific requirements.
- Foundation and Framing: Accurate measurements are crucial for laying a solid foundation and framing the structure of your tiny house. Errors in these initial stages can compromise the overall stability and integrity of the building.
- Window and Door Openings: Precise measurements are essential for ensuring that windows and doors fit properly. Incorrect measurements can result in gaps, drafts, and security issues.
- Interior Layout: Careful measurements are necessary to optimize the interior layout of your tiny house. This includes determining the placement of walls, furniture, and appliances to maximize space utilization and functionality.
- Material Cutting: Precise measurements are vital when cutting materials such as, metal, and insulation. Errors in cutting can lead to wasted materials, increased costs, and potential safety hazards.
By paying meticulous attention to measurements throughout the construction process, you can avoid costly errors and ensure the structural integrity, functionality, and aesthetic appeal of your tiny house. Remember, precision is key when it comes to building a safe and durable home.
Foundation: Choose plans that align with your desired foundation type.
When selecting a free tiny house plan, careful consideration should be given to the type of foundation that best suits your needs and site conditions. The foundation is the base of your tiny house and plays a crucial role in its stability, durability, and overall performance. Choosing a plan that aligns with your desired foundation type is essential to ensure a solid and secure structure.
There are several types of foundations commonly used for tiny houses, each with its own advantages and considerations. Here are some of the most popular options:
- Skid Foundation: A skid foundation consists of treated wooden beams or metal skids that support the tiny house. It is a simple and cost-effective option, making it a popular choice for DIY builders. However, skid foundations are not suitable for all soil conditions and may require additional support in areas with frost or expansive soils.
- Concrete Slab Foundation: A concrete slab foundation is a solid and durable option that provides a level and stable base for your tiny house. It is relatively easy to install and can be poured directly on the ground or on a prepared gravel bed. However, concrete slab foundations require a significant amount of concrete and may be more expensive than other types of foundations.
- Pier and Beam Foundation: A pier and beam foundation consists of concrete piers that support wooden beams, which in turn support the tiny house. This type of foundation is well-suited for uneven or sloping sites and provides good ventilation for the underside of the house. However, pier and beam foundations can be more complex to install and may require additional materials and labor.
By carefully considering your desired foundation type and site conditions, you can choose a free tiny house plan that aligns with your specific needs. A properly designed and installed foundation will provide a solid and stable base for your tiny house, ensuring its longevity and structural integrity.
Adaptability: Consider plans that allow for customization and future expansion.
When selecting a free tiny house plan, adaptability should be a key consideration. Choosing a plan that allows for customization and future expansion provides the flexibility to tailor your tiny house to your unique needs and lifestyle. It also ensures that your tiny house can grow and adapt as your needs change over time.
- Customization: Adaptable plans allow you to customize the design and layout of your tiny house to suit your specific preferences and requirements. This includes the ability to modify room sizes, add or remove features, and choose finishes that reflect your personal style. By selecting a plan that supports customization, you can create a tiny house that truly feels like your own.
- Future Expansion: Life circumstances can change, and your tiny house should be able to adapt to those changes. Adaptable plans often include provisions for future expansion, such as adding a loft or extending the living space. This flexibility ensures that your tiny house can grow with you, whether you need more room for a growing family, a dedicated workspace, or simply more storage.
- Multi-Purpose Spaces: Adaptable plans often incorporate multi-purpose spaces that can serve various functions. For example, a loft area can be used for sleeping, storage, or as a guest room. A living area can be easily converted into a dining space or a home office. By choosing a plan with multi-purpose spaces, you maximize the functionality and versatility of your tiny house.
- Removable Walls: Some adaptable plans feature removable walls or partitions that allow you to reconfigure the interior layout of your tiny house as needed. This flexibility is ideal for those who may want to change the layout in the future or accommodate different uses for the space.
By choosing a free tiny house plan that prioritizes adaptability, you gain the freedom to customize your home and adapt it to your evolving needs. This ensures that your tiny house remains a comfortable and functional space that grows with you over time.
Local Building Codes: Ensure the plans comply with local building regulations.
Before embarking on your tiny house building project, it is crucial to ensure that your plans comply with local building codes and regulations. Building codes are established to protect the health, safety, and welfare of occupants and the general public. They set minimum standards for the design, construction, and maintenance of buildings, including tiny houses.
Failure to adhere to local building codes can lead to serious consequences, including fines, construction delays, and even the potential for legal action. In some cases, non-compliant structures may be deemed unsafe and uninhabitable. By ensuring that your tiny house plans meet local building codes, you safeguard your investment and protect the well-being of those who will occupy the space.
To determine the specific building codes applicable to your project, contact the local building department or planning office. They can provide you with detailed information about the requirements in your area. Building codes typically cover a wide range of aspects, including:
- Structural integrity: Codes ensure that the tiny house is structurally sound and can withstand the local climate and environmental conditions.
- Fire safety: Codes specify requirements for fire-resistant materials, smoke detectors, and emergency exits.
- Electrical and plumbing systems: Codes regulate the installation and maintenance of electrical wiring, plumbing fixtures, and appliances.
- Energy efficiency: Codes may include standards for insulation, windows, and heating and cooling systems to promote energy conservation.
- Accessibility: Codes ensure that tiny houses are accessible to individuals with disabilities, including wheelchair ramps and wider doorways.
By carefully reviewing and adhering to local building codes, you can ensure that your tiny house is safe, compliant, and meets the required standards for habitation in your area.
Realistic Timeline: Allow ample time for construction based on the plan’s complexity.
When embarking on a tiny house building project, it is essential to establish a realistic timeline that aligns with the complexity of the chosen plan. Underestimating the time required can lead to stress, financial strain, and potential safety hazards. Conversely, overestimating the timeline can result in unnecessary delays and increased costs.
To determine an appropriate timeline, carefully assess the complexity of the tiny house plan. Consider the following factors:
- Structural Design: Complex structural designs, such as multiple stories, unusual rooflines, or large open spaces, require more time to frame and construct.
- Material Selection: The type of materials used can impact the construction timeline. Natural materials like wood and stone may require more time to work with compared to manufactured materials.
- Finishes and Fixtures: The level of detail and customization in the finishes and fixtures, such as cabinetry, countertops, and lighting, can significantly extend the timeline.
- Site Conditions: The location and conditions of the building site can influence the timeline. Factors like uneven terrain, lack of infrastructure, or inclement weather can add delays.
- Skill Level: The experience and skill level of the builders involved will impact the construction speed. Inexperienced builders may require more time to complete tasks.
By thoroughly considering these factors, you can establish a realistic timeline that accounts for the complexities of your chosen plan. Remember, rushing the construction process can compromise the quality and safety of your tiny house.
DIY Skills: Assess your DIY capabilities and select plans that match your skill level.
When selecting a free tiny house plan, it is crucial to assess your DIY skills and choose a plan that aligns with your capabilities. Building a tiny house requires a combination of practical skills, knowledge, and experience. By selecting a plan that matches your skill level, you can avoid potential frustrations, costly mistakes, and safety hazards.
- Basic Skills: If you are a beginner with limited DIY experience, it is advisable to choose a plan that focuses on simplicity and functionality. Plans designed for beginners typically provide clear instructions, avoid complex techniques, and utilize common materials that are easy to work with.
- Intermediate Skills: For those with some prior experience in construction or woodworking, intermediate plans offer a good balance of complexity and achievability. These plans may incorporate more intricate designs, require the use of specialized tools, and involve more advanced construction techniques.
- Advanced Skills: Experienced builders and craftspeople may opt for advanced plans that push the boundaries of tiny house design and construction. These plans often feature unique architectural elements, custom details, and the use of specialized materials. Advanced skills are necessary to execute these plans safely and effectively.
- Skill Development: It is important to note that your DIY skills can improve over time with practice and experience. If you are determined to build a tiny house but lack the necessary skills, consider starting with a simpler plan and gradually taking on more complex projects as your skills develop.
By realistically assessing your DIY capabilities and selecting a plan that matches your skill level, you can set yourself up for a successful and rewarding tiny house building experience.
Cost Estimation: Factor in the cost of materials and labor before starting construction.
Before embarking on your tiny house building project, it is crucial to conduct a thorough cost estimation to determine the financial resources required. This involves factoring in the cost of materials, labor, and other expenses associated with construction. Accurate cost estimation helps ensure that you have a realistic understanding of the financial commitment involved and can avoid unexpected expenses.
- Material Costs: The cost of materials accounts for a significant portion of the overall project budget. Research and compare prices from different suppliers to secure the best deals. Consider the type and quality of materials used, as well as the quantity required based on your chosen plan.
- Labor Costs: If you plan to hire contractors for specific tasks or the entire construction process, it is essential to obtain quotes and factor in labor costs. The cost of labor will vary depending on the complexity of the project, the skill level of the contractors, and your location.
- Permits and Inspections: Building permits and inspections are often required by local authorities. These costs can vary depending on the size and location of your tiny house. Factor in the expenses associated with obtaining necessary permits and scheduling inspections throughout the construction process.
- Tools and Equipment: Building a tiny house requires a range of tools and equipment. If you do not own all the necessary tools, you may need to purchase or rent them. Consider the cost of essential tools, safety gear, and any specialized equipment required for your specific plan.
By conducting a comprehensive cost estimation and allocating sufficient funds, you can avoid financial surprises and ensure that your tiny house project stays within your budget. Remember, underestimating costs can lead to project delays, additional expenses, and potential financial strain.










Related Posts