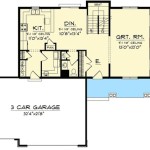
Floor Plans Of A House constitute the arrangement of rooms, spaces, and other physical features on each level of a house or building. It depicts essential elements such as walls, doors, windows, stairs, furniture, and fixtures, enabling visualization of the layout and flow of the living space. Like blueprints for a construction project, floor plans provide a detailed representation of the house’s design and functionality, ensuring that all aspects of the building are thoroughly planned and coordinated.
Understanding floor plans is crucial for various stakeholders involved in the building process. Architects, builders, and engineers use them to design and construct the house, ensuring structural integrity and functionality. For homeowners, floor plans serve as a roadmap for their living space, allowing them to visualize the placement of rooms, furniture, and appliances. These plans also play a vital role in real estate transactions, as they help potential buyers envision the layout and flow of the house.
In the following sections, we will delve into the various elements of a floor plan and explore its significance in the design and construction of houses. We will also discuss different types of floor plans and their advantages, providing insights into creating functional and aesthetically pleasing living spaces.
Floor plans encompass various elements essential for understanding the layout and functionality of a house. Here are nine key points to consider:
- Room arrangement
- Space allocation
- Wall placement
- Door and window locations
- Staircase design
- Furniture layout
- Fixture placement
- Scale and dimensions
- Building codes
These elements collectively contribute to the overall design, functionality, and safety of the house.
Room arrangement
Room arrangement refers to the layout and placement of rooms within a house. It involves determining the purpose, size, and relationship of each room to create a functional and comfortable living space.
- Purpose of rooms: The first step in room arrangement is to identify the intended use of each room. This includes categorizing rooms into public spaces (e.g., living room, dining room) and private spaces (e.g., bedrooms, bathrooms). Assigning specific functions to rooms helps establish a clear hierarchy and flow within the house.
- Size of rooms: The size of each room should be carefully considered based on its intended use and the number of occupants. Public spaces, such as living rooms, typically require more space to accommodate furniture and movement, while bedrooms and bathrooms can be smaller and more private.
- Relationship of rooms: Room arrangement also involves considering the relationship between different rooms. Frequently used rooms, such as the kitchen and living room, should be easily accessible from each other. Private areas, like bedrooms, should be located in quieter parts of the house to ensure privacy.
- Flow of movement: The arrangement of rooms should promote a smooth flow of movement throughout the house. Avoid creating unnecessary obstacles or bottlenecks, and ensure that there is a clear path between different areas.
Thoughtful room arrangement is essential for creating a house that is both functional and comfortable. By carefully considering the purpose, size, and relationship of each room, architects and homeowners can design living spaces that meet their specific needs and preferences.
Space allocation
Space allocation refers to the efficient distribution of available space within a house to accommodate various functions and activities. It involves dividing the total area into different rooms and spaces, ensuring that each area is appropriately sized and meets the needs of the occupants.
Effective space allocation considers several key factors:
- Number of occupants: The number of people living in the house influences the amount of space required. A larger family will need more bedrooms, bathrooms, and living areas than a single person or a couple.
- Lifestyle and needs: The lifestyle and daily routines of the occupants also impact space allocation. For instance, a family that enjoys cooking and entertaining may require a larger kitchen and dining area, while a family with young children may need more play space and storage.
- Building codes and regulations: Local building codes and regulations often specify minimum sizes for different rooms, such as bedrooms, bathrooms, and kitchens. These regulations ensure that houses meet certain safety and habitability standards.
Architects and homeowners can use various techniques to optimize space allocation:
Open floor plans: Open floor plans combine multiple areas, such as the living room, dining room, and kitchen, into one large space. This approach creates a sense of spaciousness and allows for multiple activities to occur simultaneously.Multi-purpose rooms: Multi-purpose rooms can serve multiple functions, such as a guest room that doubles as a home office or a playroom that can also be used as a study area.Built-in storage: Built-in storage solutions, such as closets, cabinets, and shelves, can maximize space utilization and keep the house organized.
Thoughtful space allocation is essential for creating a house that is both comfortable and functional. By carefully considering the needs of the occupants, architects and homeowners can design living spaces that optimize available space and enhance the overall quality of life.
Wall placement
Wall placement is a crucial aspect of floor plan design, as it determines the shape, size, and layout of rooms and spaces within a house. Walls serve several important functions:
- Structural support: Walls provide structural support to the house, bearing the weight of the roof, floors, and other components.
- Space division: Walls divide the house into different rooms and spaces, creating separate areas for various activities and functions.
- Privacy and noise control: Walls provide privacy and noise control between different rooms, ensuring that occupants can enjoy peace and quiet in their own spaces.
- Thermal insulation: Walls act as thermal insulators, helping to regulate the temperature inside the house and reduce energy consumption.
When placing walls, architects and homeowners consider various factors:
- Room size and shape: The placement of walls determines the size and shape of each room. Careful consideration is given to ensure that rooms are appropriately sized and have a functional shape.
- Load-bearing capacity: Load-bearing walls are structural walls that support the weight of the house. Their placement is critical to ensure the stability and safety of the building.
- Traffic flow: Walls should be placed in a way that promotes smooth traffic flow throughout the house. Avoid creating unnecessary obstacles or bottlenecks, and ensure that there is a clear path between different areas.
- Natural lighting: The placement of walls should allow for natural light to enter the house. Windows and doors should be strategically positioned to maximize daylighting and reduce the need for artificial lighting.
- Building codes: Local building codes often specify minimum wall heights, thicknesses, and fire ratings. These regulations ensure that houses meet certain safety and habitability standards.
Thoughtful wall placement is essential for creating a house that is both functional and comfortable. By carefully considering the various factors involved, architects and homeowners can design living spaces that meet their specific needs and preferences.
Door and window locations
The placement of doors and windows in a floor plan is crucial for both functionality and aesthetics. Doors provide access to different rooms and spaces, while windows allow for natural light and ventilation. Careful consideration of their locations ensures a comfortable and inviting living environment.
- Entry and exit points: Doors should be strategically placed to provide convenient entry and exit points to the house. The main entrance should be easily accessible from the outside, while secondary entrances can be located in areas such as the garage or backyard.
- Flow of movement: Door placement should promote a smooth flow of movement throughout the house. Avoid creating unnecessary obstacles or bottlenecks, and ensure that there is a clear path between different areas.
- Privacy and security: The location of windows and doors should consider privacy and security concerns. Windows in private areas, such as bedrooms and bathrooms, should be placed to minimize visibility from outside. Doors should be equipped with appropriate locks and security features.
- Natural lighting: Windows should be strategically positioned to maximize natural daylighting. Larger windows in south-facing rooms can bring in ample sunlight, reducing the need for artificial lighting and creating a brighter, more inviting atmosphere.
Thoughtful placement of doors and windows enhances the functionality, comfort, and aesthetics of a house. By carefully considering the various factors involved, architects and homeowners can design living spaces that meet their specific needs and preferences.
Staircase design
Staircase design is a crucial aspect of floor plan layout, as it provides vertical circulation between different levels of a house. Thoughtful planning of staircases ensures safe, convenient, and aesthetically pleasing movement throughout the house.
- Location: The location of the staircase should consider traffic flow and accessibility. It should be easily accessible from main living areas, avoiding awkward or inconvenient placement.
- Type: The type of staircase chosen depends on factors such as space constraints, style preferences, and building codes. Common types include straight stairs, L-shaped stairs, and spiral stairs.
- Dimensions: Staircase dimensions, including tread width, riser height, and overall length, should comply with building codes and ergonomic principles to ensure safety and comfort.
- Materials: The materials used for stairs, such as wood, metal, or concrete, should complement the overall design style of the house and provide durability and functionality.
Well-designed staircases enhance the functionality and aesthetics of a house. By carefully considering the various factors involved, architects and homeowners can create staircases that are both practical and beautiful.
Furniture layout
Furniture layout refers to the arrangement and placement of furniture within a room or space. It plays a crucial role in creating a functional, comfortable, and aesthetically pleasing living environment. Careful consideration of furniture layout can enhance the overall design and functionality of a house.
When planning furniture layout, several key factors should be considered:
- Functionality: The primary goal of furniture layout is to create a functional space that meets the needs of the occupants. Furniture should be arranged to facilitate movement, access to amenities, and various activities.
- Flow of movement: Furniture should be placed in a way that promotes a smooth flow of movement throughout the room. Avoid creating unnecessary obstacles or bottlenecks, and ensure that there is enough space to move around comfortably.
- Focal point: Identifying a focal point, such as a fireplace, window, or artwork, can help guide the furniture layout. Arrange furniture to draw attention to the focal point and create a visually appealing arrangement.
In addition to these key factors, personal preferences and style also play a role in furniture layout. Different furniture arrangements can create distinct ambiences and cater to varying tastes:
- Formal arrangements: Formal furniture layouts are characterized by symmetry and balance. Furniture is typically arranged in pairs or sets, creating a sense of order and sophistication.
- Informal arrangements: Informal furniture layouts are more relaxed and comfortable. Furniture is often arranged in groups or clusters, encouraging conversation and interaction.
- Eclectic arrangements: Eclectic furniture layouts combine elements from different styles and periods. This approach creates a unique and personalized living space that reflects the tastes and interests of the occupants.
Thoughtful furniture layout is essential for creating a house that is both functional and stylish. By carefully considering the factors discussed above, homeowners can design living spaces that meet their specific needs and preferences.
Fixture placement
Fixture placement refers to the strategic arrangement of fixed elements and appliances within a house. Fixtures are typically connected to utilities such as plumbing, electrical, and gas lines and include items like sinks, toilets, showers, light fixtures, and kitchen appliances. Careful planning of fixture placement is essential for creating a functional, comfortable, and aesthetically pleasing living environment.
- Functionality: The primary consideration for fixture placement is functionality. Fixtures should be placed in locations that maximize their usability and convenience. For example, sinks should be positioned near countertops for easy access to water, and light fixtures should be placed to provide adequate illumination for various activities.
- Ergonomics: Fixture placement should also consider ergonomic principles to ensure comfort and ease of use. Fixtures should be placed at heights and distances that are appropriate for the average user. For instance, kitchen countertops should be at a height that allows for comfortable food preparation, and bathroom sinks should be at a height that minimizes strain on the back.
- Aesthetics: Fixture placement can also contribute to the overall aesthetics of a space. Fixtures can be chosen to complement the design style of the house and to create a visually appealing arrangement. For example, a modern bathroom may feature sleek, minimalist fixtures, while a traditional bathroom may incorporate more ornate and decorative fixtures.
- Building codes and regulations: Fixture placement must adhere to local building codes and regulations. These codes specify minimum distances and clearances for fixtures to ensure safety and proper functioning. For example, building codes may require a certain distance between a toilet and a shower to prevent water splashing.
Thoughtful fixture placement is essential for creating a house that is both functional and aesthetically pleasing. By carefully considering the factors discussed above, architects and homeowners can design living spaces that meet their specific needs and preferences.
Scale and dimensions
Scale and dimensions play a crucial role in floor plans, as they accurately represent the size and proportions of the house. The scale refers to the ratio between the size of the drawing and the actual size of the house. Common scales used in floor plans include 1/4 inch = 1 foot, 1/8 inch = 1 foot, and 1/16 inch = 1 foot.
Accurate dimensions are essential for ensuring that the floor plan is a true representation of the house. Dimensions should be carefully measured and recorded to ensure that the layout is correct and that all components, such as walls, doors, and windows, are properly sized and positioned.
Dimensions also help in calculating the square footage of each room and the overall house. This information is important for various purposes, such as estimating construction costs, determining property taxes, and comparing the size of different houses.
In addition to the overall dimensions of the house, floor plans also include detailed dimensions for individual components, such as the width and height of doors and windows, the length and depth of countertops, and the size and placement of appliances. These detailed dimensions ensure that all elements of the house fit together properly and that the space is efficiently utilized.
Accurate scale and dimensions are essential for creating floor plans that are both informative and reliable. By carefully following these principles, architects and homeowners can ensure that their floor plans are accurate representations of their houses, allowing for successful construction and a well-designed living space.
Building codes
Building codes are essential regulations that govern the design and construction of houses to ensure safety, structural integrity, and habitability. Floor plans must adhere to these codes to obtain building permits and ensure compliance with local regulations.
- Zoning codes: Zoning codes regulate the use of land and buildings in specific areas. They determine the types of buildings allowed in a particular zone, such as residential, commercial, or industrial, and specify requirements such as setbacks from property lines and height restrictions.
- Building codes: Building codes address the structural safety and habitability of buildings. They establish minimum standards for materials, construction methods, and design criteria. These codes cover aspects such as foundation design, fire safety, electrical systems, plumbing systems, and accessibility features.
- Energy codes: Energy codes promote energy efficiency and sustainability in buildings. They set requirements for insulation, windows, lighting, and appliances to reduce energy consumption and minimize environmental impact.
- Plumbing codes: Plumbing codes regulate the design and installation of plumbing systems to ensure proper water supply and drainage. They specify requirements for pipe sizes, fixture types, and ventilation systems to prevent leaks, contamination, and backflow.
Compliance with building codes is not only a legal requirement but also essential for creating safe and healthy living environments. By adhering to these codes, architects and homeowners can ensure that their floor plans meet the necessary standards for structural integrity, functionality, and safety.










Related Posts