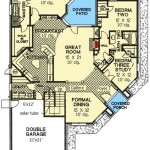
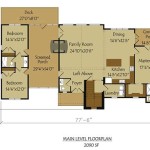
Flood Zone House Plans are blueprints specifically designed to withstand the potential impact of flooding. They incorporate structural components and design features aimed at minimizing the risk of water damage and ensuring the safety of occupants in flood-prone areas.
For instance, houses built in accordance with flood zone regulations often employ elevated foundations, raised porches, and waterproof exterior materials. These measures help to protect the structural integrity and habitable areas of the house during flood events, preventing costly damage and ensuring the well-being of residents.
As we delve into the main body of this article, we will explore the essential elements of flood zone house plans, their advantages and considerations, and how they contribute to the safety and resilience of homes in flood-prone communities.
Flood Zone House Plans incorporate crucial elements to ensure the safety and resilience of homes in flood-prone areas. Here are 8 important points to consider:
- Elevated foundations
- Raised porches
- Waterproof materials
- Flood vents
- Breakaway walls
- Wet floodproofing
- Dry floodproofing
- Flood insurance
By adhering to these guidelines, flood zone house plans help minimize the risk of water damage, protect structural integrity, and ensure the well-being of occupants during flood events.
Elevated foundations
Elevated foundations are a crucial component of flood zone house plans, designed to raise the living space of a home above the anticipated flood level. This elevation helps mitigate the risk of water damage during flooding events, protecting both the structural integrity of the house and the belongings of its occupants.
Building codes in flood-prone areas typically specify minimum elevation requirements for new construction. These requirements vary depending on the flood risk level of the specific location, which is determined by factors such as historical flood data, rainfall patterns, and proximity to bodies of water. By adhering to these regulations, builders ensure that homes are constructed at a height that minimizes the potential for floodwater to enter the habitable areas.
There are various methods for elevating a foundation, including the use of piers, columns, or a raised concrete slab. Piers and columns are typically made of concrete or steel and are used to support the weight of the house above the ground level. A raised concrete slab, on the other hand, is a single piece of concrete that is poured on top of a layer of compacted fill material.
Elevated foundations offer several advantages in flood-prone areas. Firstly, they reduce the risk of structural damage by keeping the main living areas of the house out of reach of floodwaters. Secondly, they allow for easier access during flood events, enabling occupants to evacuate safely and quickly. Additionally, elevated foundations can improve ventilation and airflow beneath the house, reducing the likelihood of moisture-related issues such as mold and mildew.
Raised porches
Raised porches are exterior platforms that are elevated above the ground level, typically supported by columns or piers. In the context of Flood Zone House Plans, raised porches serve multiple important functions:
Protection from floodwaters: During flood events, raised porches provide a safe and dry space for occupants to evacuate and take shelter. They elevate people and belongings above the floodwaters, reducing the risk of injury or damage. Additionally, raised porches can help to prevent floodwaters from entering the main living areas of the house, protecting the interior from water damage and mold growth.
Access during flooding: Raised porches provide a means of access to and from the house during flood events. When roads and sidewalks are inundated, raised porches allow occupants to enter and exit the house safely and conveniently. This is particularly important for emergency responders who may need to access the house to provide assistance.
Improved ventilation: Raised porches can improve ventilation and airflow beneath the house, reducing the likelihood of moisture-related issues such as mold and mildew. This is especially beneficial in flood-prone areas where high humidity and moisture levels can be a problem.
Additional living space: Raised porches can also serve as additional living space, providing a sheltered and comfortable area for relaxation, dining, or entertaining. They can be screened in to protect against insects and can be furnished with weather-resistant furniture to create an outdoor living room or dining area.
Waterproof materials
The use of waterproof materials is essential in Flood Zone House Plans to minimize the risk of water damage and ensure the structural integrity of the house during flood events.
- Exterior cladding
Exterior cladding materials, such as vinyl siding, fiber cement siding, or metal siding, should be waterproof to prevent water penetration into the walls of the house. These materials are designed to withstand exposure to moisture and humidity, protecting the underlying structure from rot, mold, and other water-related damage.
- Roofing materials
Roofing materials, such as asphalt shingles, metal roofing, or tile roofing, should also be waterproof to prevent water leakage into the attic and living areas of the house. These materials are designed to shed water effectively and resist moisture penetration, ensuring the integrity of the roof and protecting the interior from water damage.
- Windows and doors
Windows and doors should be constructed with waterproof materials and installed properly to prevent water seepage into the house. This includes using weatherstripping, caulking, and other sealing methods to create a watertight seal around the openings. Waterproof windows and doors help to keep floodwaters out and protect the interior from moisture damage.
- Foundation materials
Foundation materials, such as concrete or treated lumber, should be waterproof to prevent water penetration into the basement or crawlspace of the house. Concrete foundations can be sealed with waterproofing membranes or coatings, while treated lumber is resistant to moisture and decay.
By incorporating waterproof materials into Flood Zone House Plans, builders can minimize the risk of water damage, protect the structural integrity of the house, and ensure the health and safety of the occupants.
Flood vents
Flood vents are openings installed in the foundation walls of a house located in a flood zone. They are designed to allow floodwaters to enter and exit the house during a flood event, equalizing the water pressure inside and outside the house. This helps to prevent the buildup of hydrostatic pressure against the foundation walls, which can cause the walls to collapse or crack.
Flood vents are typically made of durable materials such as plastic or metal and are equipped with flappers or dampers that open when the water level rises. The flappers or dampers are designed to close automatically once the floodwaters recede, preventing water from entering the house through the vents.
The size and number of flood vents required for a particular house depend on the size of the house, the flood risk level of the area, and the local building codes. Building codes typically specify the minimum size and spacing of flood vents based on the square footage of the enclosed area below the lowest floor.
Flood vents play a crucial role in protecting flood zone houses from structural damage during flood events. By allowing floodwaters to enter and exit the house, flood vents equalize the water pressure and reduce the risk of foundation failure. This helps to protect the structural integrity of the house and prevents costly repairs.
Breakaway walls
Breakaway walls are structural components designed to collapse or break away under the force of floodwaters, reducing the hydrostatic pressure against the foundation walls and preventing structural damage to the house.
Breakaway walls are typically constructed using lightweight materials such as plywood or foam panels and are designed to be weaker than the foundation walls. They are typically located in the lower portion of the house, below the elevation of the lowest habitable floor.
When floodwaters rise and exert pressure against the breakaway walls, the walls are designed to collapse or break away, allowing the floodwaters to enter the enclosed space. This equalizes the water pressure inside and outside the house, reducing the risk of foundation failure and structural damage.
Once the floodwaters recede, the breakaway walls can be easily repaired or replaced. This is typically less costly and time-consuming than repairing or replacing damaged foundation walls.
Building codes in flood-prone areas often require the use of breakaway walls in new construction. The specific requirements for breakaway walls, such as the materials used, the height of the walls, and the location of the walls, vary depending on the flood risk level of the area and the local building codes.
Wet floodproofing
Wet floodproofing involves allowing floodwaters to enter a designated area of the house, typically the lowest level, such as a basement or crawlspace. This approach is suitable for houses located in areas with a high risk of flooding, where floodwaters are expected to rise above the lowest habitable floor.
Floodable space
A floodable space is a designated area of the house that is designed to flood during a flood event. This space is typically located in the lowest level of the house, such as a basement or crawlspace. The floodable space is designed to accommodate the expected floodwaters and is constructed using materials that are resistant to water damage, such as concrete or tile.
Flood openings
Flood openings are openings in the foundation walls or exterior walls of the house that allow floodwaters to enter the floodable space. These openings are typically fitted with flood gates or vents that automatically open when the water level rises, allowing floodwaters to enter the space. Once the floodwaters recede, the flood gates or vents close automatically to prevent water from flowing back into the house.
Waterproofing and drainage
The floodable space is waterproofed using materials such as concrete sealant or epoxy coatings to prevent water from seeping into the rest of the house. Additionally, a drainage system is installed to remove floodwaters from the space once the flood event has passed. The drainage system typically consists of sump pumps or floor drains that pump or drain the water out of the floodable space.
Advantages of wet floodproofing
Wet floodproofing offers several advantages, including:
– It allows floodwaters to enter a designated area of the house, reducing the risk of structural damage to the rest of the house.
– It is a relatively cost-effective floodproofing method compared to other methods, such as dry floodproofing.
– It is suitable for houses located in areas with a high risk of flooding, where floodwaters are expected to rise above the lowest habitable floor.
Dry floodproofing
Dry floodproofing involves preventing floodwaters from entering the habitable areas of a house during a flood event. This approach is suitable for houses located in areas with a moderate risk of flooding, where floodwaters are not expected to rise above the lowest habitable floor.
Watertight construction
Dry floodproofing involves sealing all openings in the foundation walls and exterior walls of the house to prevent water from entering. This includes sealing cracks and gaps around windows, doors, pipes, and other penetrations. Additionally, the house is constructed using waterproof materials, such as concrete, brick, or vinyl siding, and all seams and joints are sealed to prevent water penetration.
Elevated utilities
All utilities, including electrical panels, HVAC systems, and water heaters, are elevated above the anticipated flood level. This ensures that these essential systems remain operational during a flood event and prevents damage from floodwaters.
Flood barriers
Temporary or permanent flood barriers, such as sandbags, inflatable dams, or flood gates, can be installed around the perimeter of the house to prevent floodwaters from entering. These barriers are typically deployed when a flood warning is issued and can be removed once the floodwaters recede.
Flood insurance
Flood insurance is a type of insurance that provides financial protection against losses caused by flooding. It is an essential consideration for homeowners in flood-prone areas, including those living in houses built according to Flood Zone House Plans.
- Coverage for flood-related damage
Flood insurance covers the costs of repairing or replacing damaged property, including the structure of the house, its contents, and any attached structures, such as garages or decks. It also provides coverage for additional living expenses, such as temporary housing and meals, if the house becomes uninhabitable due to flood damage.
- Peace of mind and financial protection
Flood insurance provides peace of mind and financial protection in the event of a flood. It ensures that homeowners have the resources they need to recover from flood-related losses and rebuild their lives.
- Requirement for federally backed mortgages
In many flood-prone areas, federally backed mortgages, such as FHA loans and VA loans, require homeowners to purchase flood insurance. This requirement ensures that lenders are protected against the financial risks associated with flooding.
- Discounts and benefits
Some insurance companies offer discounts on flood insurance premiums for homes that are built in accordance with Flood Zone House Plans. These discounts recognize the reduced risk of flood damage associated with these homes.
Overall, flood insurance is an essential consideration for homeowners in flood-prone areas. It provides financial protection against flood-related losses, peace of mind, and may be required for federally backed mortgages. Homeowners should carefully consider the benefits of flood insurance and consult with an insurance professional to determine the appropriate coverage for their needs.










Related Posts