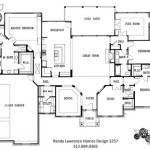
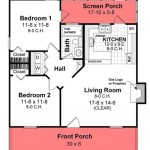
English Tudor house plans are blueprints or designs that provide a detailed outline for the construction of a Tudor-style home. These plans typically include specifications for the exterior and interior of the house, including dimensions, materials, and architectural features.
Tudor house plans are popular among homeowners who appreciate the historical charm and architectural details of the Tudor era. These homes are characterized by their steeply pitched roofs, decorative chimneys, and half-timbered exteriors. Many Tudor house plans also include modern amenities and conveniences, making them a comfortable choice for contemporary living.
In this article, we will discuss the key elements of English Tudor house plans and explore the different types of plans available. We will also provide tips on how to choose the right plan for your needs.
English Tudor house plans are a popular choice for homeowners who appreciate the historical charm and architectural details of the Tudor era.
- Steeply pitched roofs
- Decorative chimneys
- Half-timbered exteriors
- Arched doorways
- Leaded glass windows
- Grand fireplaces
- Elaborate moldings
- Multiple gables
These homes are characterized by their steeply pitched roofs, decorative chimneys, and half-timbered exteriors. Many Tudor house plans also include modern amenities and conveniences, making them a comfortable choice for contemporary living.
Steeply pitched roofs
One of the most distinctive features of English Tudor houses is their steeply pitched roofs. These roofs were designed to shed water and snow quickly and efficiently, which was important in a climate with frequent rainfall. The steep pitch also helped to create a sense of height and grandeur, which was desirable in a large house.
Tudor roofs were typically made of thatch, which was a readily available and inexpensive material. Thatch is a good insulator, which helped to keep homes warm in the winter and cool in the summer. However, thatch is also flammable, so it was important to keep it well-maintained.
In the 16th century, tiles began to replace thatch as the roofing material of choice for Tudor homes. Tiles were more durable and fire-resistant than thatch, and they also gave roofs a more finished appearance. However, tiles were also more expensive than thatch, so they were typically used on the roofs of larger and more important houses.
The steeply pitched roofs of English Tudor houses are a key part of their overall design. These roofs not only provide protection from the elements, but they also add to the home’s visual appeal.
Decorative chimneys
Chimneys were an essential part of English Tudor houses, as they provided a way to vent smoke and heat from the fireplace. However, Tudor chimneys were not just functional; they were also highly decorative.
Tudor chimneys were typically made of brick or stone, and they were often elaborately ornamented with moldings, carvings, and other decorative elements. Some chimneys were even topped with finials or other decorative features.
The shape of Tudor chimneys varied greatly. Some chimneys were tall and slender, while others were short and squat. Some chimneys were square or rectangular, while others were octagonal or even round.
The decoration of Tudor chimneys also varied greatly. Some chimneys were decorated with simple moldings, while others were covered in intricate carvings. Some chimneys were even painted with bright colors or gilded with gold leaf.
The decorative chimneys of English Tudor houses are a key part of their overall design. These chimneys not only provided a way to vent smoke and heat, but they also added to the home’s visual appeal.
Half-timbered exteriors
Half-timbered exteriors are a defining feature of English Tudor houses. These exteriors are characterized by a framework of wooden beams that are infilled with plaster or brick.
- Structural support
The timber frame of a half-timbered exterior provides structural support for the house. The beams are typically made of oak, which is a strong and durable wood. The beams are joined together with mortise and tenon joints, which are very strong and can withstand centuries of use.
- Weather protection
The infill panels of a half-timbered exterior help to protect the house from the elements. The plaster or brick infill is weather-resistant and helps to keep the house warm and dry.
- Decorative appeal
Half-timbered exteriors are also highly decorative. The exposed timber beams add visual interest to the house and create a sense of charm and character. The infill panels can be painted or decorated in a variety of ways, which allows for a great deal of customization.
- Historical significance
Half-timbered exteriors are a reminder of the rich history of English Tudor architecture. These exteriors have been used for centuries and have become a defining feature of English homes.
Half-timbered exteriors are a beautiful and distinctive feature of English Tudor houses. These exteriors are not only structurally sound and weather-resistant, but they are also highly decorative. Half-timbered exteriors are a reminder of the rich history of English architecture and continue to be popular today.
Arched doorways
Arched doorways are a common feature of English Tudor houses. These doorways are characterized by their curved tops, which can be either pointed or rounded. Arched doorways are often used in conjunction with other Tudor architectural elements, such as half-timbered exteriors and decorative chimneys.
There are several reasons why arched doorways were popular in Tudor architecture. First, arches are structurally strong and can span large openings without the need for additional support. This made them ideal for use in doorways, which are often one of the largest openings in a house. Second, arches are visually appealing and can add a touch of elegance to a home. The curved shape of an arch can also create a sense of movement and flow, which can be desirable in a doorway.
Tudor arched doorways were typically made of wood or stone. Wooden doorways were more common, as they were less expensive and easier to work with. Stone doorways were more durable and weather-resistant, but they were also more expensive and difficult to construct. The choice of material for a doorway would often depend on the budget and the desired level of durability.
Tudor arched doorways were often decorated with moldings, carvings, and other decorative elements. The decoration of a doorway would often reflect the overall style of the house. For example, a house with a half-timbered exterior might have an arched doorway with exposed timber beams. A house with a stone exterior might have an arched doorway with carved stone moldings.
Arched doorways are a beautiful and distinctive feature of English Tudor houses. These doorways are not only structurally sound and visually appealing, but they also add a touch of historical charm to a home.
Leaded glass windows
Leaded glass windows are a defining feature of English Tudor houses. These windows are made up of small pieces of glass that are held together by lead strips. The lead strips are typically arranged in a geometric pattern, which creates a distinctive and visually appealing look.
Leaded glass windows were first developed in the Middle Ages. At that time, glass was a very expensive material, so leaded glass windows were only used in the homes of the wealthy. Over time, leaded glass windows became more affordable and they began to be used in a wider range of homes.
There are several reasons why leaded glass windows were popular in Tudor architecture. First, leaded glass windows are very durable and can withstand centuries of use. The lead strips help to protect the glass from damage, and they also make the windows more resistant to wind and rain.
Second, leaded glass windows are very energy-efficient. The small pieces of glass help to trap heat inside the house, which can reduce energy costs. Leaded glass windows also help to block out noise, which can make a home more peaceful and quiet.
Leaded glass windows are a beautiful and distinctive feature of English Tudor houses. These windows are not only durable and energy-efficient, but they also add a touch of historical charm to a home.
Grand fireplaces
Grand fireplaces were a central feature of English Tudor homes. These fireplaces were not only a source of heat, but they were also a gathering place for family and friends. Tudor fireplaces were typically large and elaborate, with intricate carvings and decorative details.
- Heat source
Tudor fireplaces were the primary source of heat for the home. The large size of the fireplaces allowed them to generate a lot of heat, which was essential for keeping the home warm during the cold winter months.
- Cooking
Tudor fireplaces were also used for cooking. A large iron crane was suspended over the fire, and pots and pans could be hung from the crane to cook food.
- Social gathering
Tudor fireplaces were a gathering place for family and friends. The large hearth provided a comfortable place to sit and talk, and the fire provided a warm and inviting atmosphere.
- Decorative element
Tudor fireplaces were also a decorative element. The elaborate carvings and decorative details added a touch of beauty and elegance to the home.
Grand fireplaces were an essential part of English Tudor homes. These fireplaces provided heat, a place to cook, a gathering place for family and friends, and a decorative element. Tudor fireplaces are a reminder of the rich history of English architecture and continue to be popular today.
Elaborate moldings
Elaborate moldings are a defining feature of English Tudor houses. These moldings are typically made of wood or plaster, and they are used to decorate the walls, ceilings, and doorways of a home. Tudor moldings are often very intricate and detailed, and they can add a touch of elegance and sophistication to a home.
There are many different types of Tudor moldings. Some of the most common types include:
- Cornice moldings: These moldings are used to decorate the top of a wall or ceiling. They can be simple or elaborate, and they often feature dentils, egg-and-dart motifs, and other decorative elements.
- Cove moldings: These moldings are used to create a curved transition between a wall and a ceiling. They can be simple or elaborate, and they often feature gadroons, rosettes, and other decorative elements.
- Panel moldings: These moldings are used to frame panels on walls or ceilings. They can be simple or elaborate, and they often feature reeding, beading, and other decorative elements.
- Doorway moldings: These moldings are used to decorate the doorways of a home. They can be simple or elaborate, and they often feature architraves, friezes, and other decorative elements.
Tudor moldings are a beautiful and distinctive feature of English Tudor houses. These moldings add a touch of elegance and sophistication to a home, and they can help to create a sense of historical charm.
Tudor moldings can be used in a variety of ways to decorate a home. For example, they can be used to:
- Frame doorways and windows
- Create decorative panels on walls and ceilings
- Add a touch of elegance to furniture
- Create a sense of historical charm in a new home
If you are interested in adding Tudor moldings to your home, there are a few things to keep in mind. First, it is important to choose moldings that are appropriate for the style of your home. Second, it is important to have the moldings installed by a professional. This will ensure that the moldings are installed correctly and that they will last for many years to come.
Multiple gables
Multiple gables are a defining feature of English Tudor houses. Gables are triangular sections of a wall that are created by the intersection of two sloping rooflines. Tudor houses often have multiple gables, which adds visual interest and complexity to the exterior of the home.
- Ornamentation
Gables were often used as a way to add ornamentation to a home. Tudor gables were often decorated with elaborate moldings, carvings, and other decorative elements. This decoration helped to create a sense of grandeur and opulence.
- Light
Gables can also be used to add light to a home. The windows in a gable can provide natural light to the rooms below. This was especially important in Tudor times, when artificial light was limited.
- Ventilation
Gables can also be used to ventilate a home. The windows in a gable can allow air to circulate, which can help to keep the home cool and comfortable in the summer months.
- Structural support
Gables can also provide structural support to a home. The sloping rooflines of a gable help to distribute the weight of the roof, which can help to prevent the walls of the home from collapsing.
Multiple gables are a beautiful and distinctive feature of English Tudor houses. These gables add visual interest, light, ventilation, and structural support to a home. Tudor gables are a reminder of the rich history of English architecture and continue to be popular today.










Related Posts