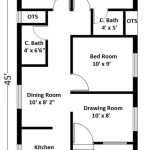
An Energy Efficient House Floor Plan is a thoughtfully designed blueprint that prioritizes the efficient use of energy in a residential building. By optimizing the placement of rooms, windows, and insulation, these floor plans aim to reduce energy consumption and create a more sustainable living environment. For instance, a well-conceived energy-efficient floor plan might situate living spaces in areas with ample natural light, reducing the need for artificial lighting during the day.
Adopting energy-efficient floor plans offers numerous advantages. Not only do they contribute to environmental conservation, but they also translate into significant cost savings for homeowners. By reducing energy consumption, these floor plans lower utility bills and promote long-term financial sustainability. Additionally, they enhance the overall comfort and well-being of occupants by creating a more stable and energy-efficient indoor climate.
Energy-efficient house floor plans incorporate key design elements to minimize energy consumption and create a more sustainable living environment.
- Optimized window placement
- Strategic insulation
- Efficient room layout
- Passive solar design
- Energy-efficient appliances
- LED lighting
- Smart home technology
- Renewable energy sources
- Sustainable building materials
By considering these factors during the design process, homeowners can create energy-efficient houses that reduce their environmental impact and lower their utility bills.
Optimized window placement
The placement of windows in a house has a significant impact on its energy efficiency. Windows allow natural light to enter the home, reducing the need for artificial lighting during the day. However, windows can also be a source of heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer, so it is important to carefully consider their placement.
- South-facing windows: South-facing windows allow the most sunlight to enter the home, which can help to reduce heating costs in the winter. However, it is important to shade these windows in the summer to prevent overheating.
- North-facing windows: North-facing windows receive less sunlight than south-facing windows, but they can still provide natural light without causing overheating. North-facing windows are a good choice for rooms that are used less frequently, such as bedrooms and bathrooms.
- East-facing windows: East-facing windows receive morning sunlight, which can help to warm up the home in the morning. However, it is important to shade these windows in the afternoon to prevent overheating.
- West-facing windows: West-facing windows receive afternoon sunlight, which can cause the home to overheat in the summer. It is important to carefully consider the placement of west-facing windows and to shade them adequately.
In addition to the orientation of the windows, the size and shape of the windows also affect the home’s energy efficiency. Larger windows allow more sunlight to enter the home, but they can also be a source of heat loss. Smaller windows are less efficient at providing natural light, but they can help to reduce heat loss.
Strategic insulation
Insulation is one of the most important factors to consider when designing an energy-efficient house. Insulation helps to keep the home warm in the winter and cool in the summer, reducing the need for heating and cooling. There are many different types of insulation available, so it is important to choose the right type for your home and climate.
- Attic insulation: Attic insulation is one of the most important types of insulation, as it helps to prevent heat from escaping through the roof. Attic insulation should be installed in all homes, regardless of climate.
- Wall insulation: Wall insulation helps to keep the home warm in the winter and cool in the summer. Wall insulation should be installed in all exterior walls, including the walls of the basement and garage.
- Floor insulation: Floor insulation helps to keep the home warm in the winter and cool in the summer. Floor insulation should be installed in all floors, including the floors of the basement and garage.
- Window and door insulation: Window and door insulation helps to prevent heat from escaping through windows and doors. Window and door insulation should be installed in all windows and doors, including the windows and doors of the basement and garage.
In addition to the type of insulation, it is also important to consider the thickness of the insulation. The thicker the insulation, the better it will insulate the home. However, thicker insulation can also be more expensive. It is important to find a balance between the cost of the insulation and the energy savings that it will provide.
Efficient room layout
The layout of a house can have a significant impact on its energy efficiency. A well-designed floor plan can help to reduce heat loss and heat gain, and can also make it easier to take advantage of natural light and ventilation. When designing an energy-efficient house, it is important to consider the following factors:
- Orientation of the house: The orientation of the house on the lot can have a significant impact on its energy efficiency. A house that is oriented to the south will receive more sunlight than a house that is oriented to the north. This can help to reduce heating costs in the winter. However, it is important to shade the south-facing windows in the summer to prevent overheating.
- Placement of rooms: The placement of rooms within the house can also affect its energy efficiency. Rooms that are used more frequently, such as the living room and kitchen, should be placed on the south side of the house. This will help to take advantage of natural light and heat. Rooms that are used less frequently, such as bedrooms and bathrooms, can be placed on the north side of the house.
- Size and shape of rooms: The size and shape of rooms can also affect the energy efficiency of the house. Smaller rooms are more energy-efficient than larger rooms, and rooms with a square or rectangular shape are more energy-efficient than rooms with an irregular shape.
- Use of natural light: Natural light can help to reduce the need for artificial lighting, which can save energy. When designing a house, it is important to place windows in areas where they will provide the most natural light. Skylights can also be used to provide natural light to interior rooms.
- Use of ventilation: Ventilation is important for maintaining a healthy indoor environment and for reducing the risk of moisture problems. Natural ventilation can be used to cool the house in the summer and to ventilate the house year-round. When designing a house, it is important to provide for adequate ventilation.
By considering these factors, it is possible to design an energy-efficient house that is comfortable and healthy to live in.
Passive solar design
Passive solar design is a building design approach that takes advantage of the sun’s energy to heat and cool a building. This can be done through a variety of design elements, such as:
- Orientation of the building: The orientation of the building on the lot can have a significant impact on its passive solar performance. A building that is oriented to the south will receive more sunlight than a building that is oriented to the north. This can help to reduce heating costs in the winter. However, it is important to shade the south-facing windows in the summer to prevent overheating.
- Window placement: The placement of windows can also affect the building’s passive solar performance. Windows that are placed on the south side of the building will allow more sunlight to enter the building than windows that are placed on the north side of the building. This can help to reduce heating costs in the winter. However, it is important to shade these windows in the summer to prevent overheating.
- Thermal mass: Thermal mass is a material that can absorb and store heat. Thermal mass can be used to help regulate the temperature of a building. In the winter, thermal mass can help to store heat from the sun and release it at night. In the summer, thermal mass can help to absorb heat from the building and release it at night.
- Insulation: Insulation is important for any energy-efficient building, but it is especially important for passive solar buildings. Insulation helps to keep the heat in the building in the winter and out of the building in the summer.
Passive solar design can be used to create energy-efficient buildings that are comfortable and healthy to live in. By using the sun’s energy to heat and cool a building, passive solar design can help to reduce energy costs and create a more sustainable building.
Here are some specific examples of passive solar design in action:
- The Trombe wall: A Trombe wall is a wall that is made of concrete or masonry and has a glass cover on the south side. The sun’s energy heats the wall during the day, and the wall releases the heat into the building at night.
- The solar greenhouse: A solar greenhouse is a greenhouse that is attached to the south side of a building. The greenhouse collects heat from the sun and transfers it to the building through the wall.
- The earth-sheltered house: An earth-sheltered house is a house that is built into the ground. The earth provides insulation for the house, which helps to reduce heating and cooling costs.
Passive solar design is a powerful tool that can be used to create energy-efficient buildings. By using the sun’s energy to heat and cool a building, passive solar design can help to reduce energy costs and create a more sustainable building.
Energy-efficient appliances
Energy-efficient appliances are an important part of any energy-efficient house floor plan. Appliances account for a significant portion of a home’s energy consumption, so choosing energy-efficient models can make a big difference in your energy bills. When choosing appliances, look for the Energy Star label. Energy Star appliances meet strict energy efficiency standards set by the US Environmental Protection Agency and the US Department of Energy.
Here are some tips for choosing energy-efficient appliances:
- Look for the Energy Star label: The Energy Star label is a quick and easy way to identify energy-efficient appliances. Energy Star appliances meet strict energy efficiency standards set by the US Environmental Protection Agency and the US Department of Energy.
- Compare the energy consumption of different models: When choosing appliances, be sure to compare the energy consumption of different models. The energy consumption of an appliance is measured in kilowatt-hours per year (kWh/year). The lower the kWh/year, the more energy-efficient the appliance.
- Consider the size of the appliance: The size of an appliance can also affect its energy consumption. In general, larger appliances use more energy than smaller appliances. However, there are some exceptions to this rule. For example, a smaller refrigerator may use more energy than a larger refrigerator if it is not energy-efficient.
- Consider your lifestyle: When choosing appliances, it is important to consider your lifestyle. If you are a large family, you may need a larger refrigerator or dishwasher. If you are a single person, you may be able to get by with a smaller appliance.
By following these tips, you can choose energy-efficient appliances that will help you save money on your energy bills and reduce your environmental impact.
Here are some specific examples of energy-efficient appliances:
- Energy-efficient refrigerators: Energy-efficient refrigerators use up to 40% less energy than conventional refrigerators. Look for refrigerators with the Energy Star label and a low kWh/year rating.
- Energy-efficient dishwashers: Energy-efficient dishwashers use up to 50% less energy than conventional dishwashers. Look for dishwashers with the Energy Star label and a low kWh/year rating.
- Energy-efficient clothes washers: Energy-efficient clothes washers use up to 50% less energy than conventional clothes washers. Look for clothes washers with the Energy Star label and a low kWh/year rating.
- Energy-efficient dryers: Energy-efficient dryers use up to 20% less energy than conventional dryers. Look for dryers with the Energy Star label and a low kWh/year rating.
By choosing energy-efficient appliances, you can make a significant impact on your home’s energy consumption and your environmental impact.
LED lighting
LED lighting is a type of lighting that uses light-emitting diodes (LEDs) as the source of light. LEDs are much more energy-efficient than traditional incandescent bulbs, and they also last much longer. As a result, LED lighting can help to reduce energy costs and maintenance costs.
- Energy efficiency: LEDs are much more energy-efficient than traditional incandescent bulbs. In fact, LEDs can use up to 80% less energy than incandescent bulbs. This can lead to significant savings on energy bills.
- Long lifespan: LEDs also have a much longer lifespan than traditional incandescent bulbs. LEDs can last for up to 50,000 hours, while incandescent bulbs typically last for only 1,000 hours. This means that LEDs can last for decades without needing to be replaced.
- Durability: LEDs are also more durable than traditional incandescent bulbs. LEDs are not as susceptible to damage from vibration or shock, which makes them ideal for use in areas where traditional bulbs may be more likely to break.
- Compact size: LEDs are also much smaller than traditional incandescent bulbs. This makes them ideal for use in tight spaces or in applications where space is limited.
LED lighting is a great way to improve the energy efficiency of your home. LEDs can help to reduce energy costs, maintenance costs, and environmental impact. When choosing LED lighting, be sure to look for the Energy Star label. Energy Star LEDs meet strict energy efficiency standards set by the US Environmental Protection Agency and the US Department of Energy.
Smart home technology
Smart home technology can help to make your home more energy-efficient and comfortable. Smart home devices can be controlled remotely using a smartphone or tablet, which gives you the ability to manage your home’s energy consumption even when you’re away.
One of the most popular types of smart home devices is the smart thermostat. Smart thermostats can be programmed to learn your heating and cooling preferences, and they can automatically adjust the temperature of your home to save energy. Some smart thermostats can also be controlled remotely, which allows you to adjust the temperature of your home from anywhere.
Another type of smart home device that can help to save energy is the smart lighting system. Smart lighting systems can be controlled remotely, and they can be programmed to turn lights on and off automatically. This can help to reduce energy consumption by ensuring that lights are only turned on when they are needed.
Smart home technology can also be used to monitor your home’s energy consumption. Some smart home devices can track your energy usage in real time, and they can provide you with detailed reports on your energy consumption patterns. This information can help you to identify areas where you can save energy.
Renewable energy sources
Renewable energy sources can be used to power energy-efficient homes, further reducing their environmental impact. Some common renewable energy sources for homes include solar energy, wind energy, and geothermal energy.
- Solar energy
Solar energy is the most abundant source of energy on Earth. Solar panels can be installed on the roof of a home to convert sunlight into electricity. Solar energy is a clean and renewable source of energy that can help to reduce energy costs.
- Wind energy
Wind energy is another clean and renewable source of energy. Wind turbines can be installed on a property to generate electricity from the wind. Wind energy is a cost-effective way to generate electricity, and it can help to reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
- Geothermal energy
Geothermal energy is the heat from the Earth’s interior. Geothermal heat pumps can be installed to extract heat from the ground and use it to heat and cool a home. Geothermal energy is a reliable and renewable source of energy that can help to reduce energy costs.
In addition to these renewable energy sources, energy-efficient homes can also be designed to take advantage of passive solar energy. Passive solar energy is the heat from the sun that is absorbed by a building and used to warm the interior. Passive solar design can help to reduce energy costs and create a more comfortable living environment.
Sustainable building materials
Sustainable building materials are materials that are produced and used in a way that minimizes their environmental impact. These materials are often made from recycled or renewable resources, and they are designed to be durable and energy-efficient. Using sustainable building materials can help to reduce the environmental impact of a home, and it can also help to improve the indoor air quality.
There are many different types of sustainable building materials available, including:
- Recycled materials: Recycled materials are materials that have been used in one form and then processed to be used again. Recycled materials can include things like recycled glass, metal, and plastic. Using recycled materials can help to reduce the amount of waste that is sent to landfills, and it can also help to conserve natural resources.
- Renewable resources: Renewable resources are materials that can be replenished naturally. Renewable resources include things like wood, bamboo, and cork. Using renewable resources can help to reduce the reliance on fossil fuels, and it can also help to promote sustainable forestry practices.
- Energy-efficient materials: Energy-efficient materials are materials that help to reduce energy consumption. Energy-efficient materials include things like insulation, energy-efficient windows, and solar panels. Using energy-efficient materials can help to reduce energy costs, and it can also help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Low-VOC materials: Low-VOC materials are materials that emit low levels of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). VOCs are chemicals that can be harmful to human health and the environment. Using low-VOC materials can help to improve the indoor air quality of a home.
Choosing sustainable building materials is an important part of creating an energy-efficient home. Sustainable building materials can help to reduce the environmental impact of a home, improve the indoor air quality, and save money on energy costs.










Related Posts