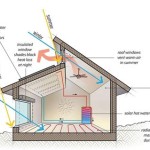
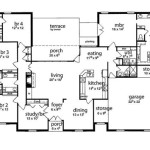
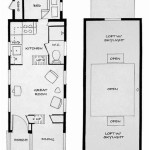
Elevated house plans refer to architectural designs for homes that are raised above the ground level, often supported by pillars or columns. This type of construction elevates the living spaces, providing protection from flooding, pests, and other ground-related hazards. An example of an elevated house plan is a stilt house, which is commonly found in coastal and flood-prone areas.
Elevating a house offers several advantages. It minimizes the risk of water damage during floods or storms, especially in areas with high water tables. By raising the home above the ground, it creates a barrier against moisture and pests that can cause structural damage and health issues. Additionally, elevated house plans can improve ventilation and airflow, promoting a healthier indoor environment.
In the following sections, we will explore the various aspects of elevated house plans, including their benefits, design considerations, and construction techniques. We will also provide specific examples and case studies to illustrate how elevated homes can adapt to different terrains and climatic conditions.
Important Considerations for Elevated House Plans:
- Flood protection
- Pest resistance
- Improved ventilation
- Enhanced views
- Terrain adaptability
- Structural stability
- Construction complexity
- Cost implications
When considering an elevated house plan, it is essential to carefully evaluate these factors to ensure a successful and satisfactory outcome.
Flood protection
Elevated house plans offer significant protection against flooding, making them an ideal choice for areas prone to heavy rainfall or coastal storm surges. By raising the living spaces above the ground level, elevated homes minimize the risk of water damage and structural compromise during flood events.**1. Reduced Water Damage:**When floodwaters rise, they can quickly inundate homes built at ground level, causing extensive damage to walls, floors, furniture, and appliances. Elevated homes, on the other hand, are situated well above the flood level, preventing water from entering the living spaces. This reduces the risk of costly repairs and the potential loss of personal belongings.**2. Structural Integrity:**Floodwaters can exert immense pressure on the walls and foundations of homes, leading to structural damage and even collapse. Elevated homes are designed to withstand these forces by distributing the weight of the building over a larger area. The pillars or columns supporting the elevated structure act as a barrier against floodwaters, preventing them from directly impacting the home’s foundation.**3. Health and Safety:**Floodwaters can carry contaminants, such as sewage and bacteria, which pose health risks to occupants. Elevated homes keep living spaces away from these contaminated waters, reducing the risk of waterborne diseases and infections. Additionally, elevating the home provides a safe haven during floods, allowing occupants to shelter above the rising waters.**4. Insurance Benefits:**In flood-prone areas, elevated homes may qualify for lower insurance premiums. Insurance companies recognize the reduced risk of flood damage associated with elevated homes and offer incentives to homeowners who invest in this type of construction.Elevated house plans are not only effective in flood protection but also offer other advantages, such as improved ventilation, enhanced views, and adaptability to various terrains. However, it is important to carefully consider the design, construction, and cost implications of elevated homes to ensure a successful and satisfactory outcome.
Pest resistance
Elevated house plans offer inherent resistance to pests, which can be a significant problem for homes built at ground level. By elevating the living spaces, elevated homes create a physical barrier that makes it more difficult for pests to access the home.**1. Reduced Ground Contact:**Pests often enter homes through cracks and openings in the foundation or walls that are close to the ground. Elevated homes minimize these entry points by reducing the amount of ground contact. The pillars or columns supporting the elevated structure create a gap between the home and the ground, making it more challenging for pests to crawl or burrow into the living spaces.**2. Limited Access Points:**Elevated homes have fewer access points for pests compared to homes built at ground level. The elevated structure reduces the number of potential entry points, such as crawl spaces, vents, and windows that are close to the ground. This makes it more difficult for pests to find a way into the home.**3. Improved Ventilation:**Elevated homes promote better ventilation and airflow, which helps to deter pests. Pests thrive in moist, humid environments, and elevated homes allow for increased air circulation, reducing the likelihood of creating a favorable habitat for pests. The open space beneath the elevated structure allows for cross-ventilation, which helps to keep the home dry and less attractive to pests.**4. Reduced Moisture:**Elevated homes are less prone to moisture issues, which can attract pests. By raising the living spaces above the ground, elevated homes reduce the risk of water accumulation and dampness, creating a less hospitable environment for pests.In addition to these pest-resistant features, elevated house plans can also incorporate specific design elements to further enhance pest control. For example, using pest-resistant materials in construction, such as treated lumber and metal flashing, can provide additional protection against pests. Additionally, installing screens on windows and vents can prevent pests from entering the home through these openings.
Improved ventilation
Elevated house plans promote improved ventilation and airflow, which offers several benefits for occupants and the home’s overall health.
- Reduced Moisture and Humidity: Elevated homes allow for increased air circulation beneath the structure, which helps to reduce moisture and humidity levels within the living spaces. This is particularly beneficial in humid climates or areas prone to flooding, as it helps to prevent the buildup of mold and mildew, which can cause respiratory problems and damage to the home’s structure.
- Improved Air Quality: The increased airflow in elevated homes helps to improve air quality by diluting indoor pollutants. Pollutants, such as dust, pollen, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), can accumulate in homes built at ground level, especially in areas with poor ventilation. Elevated homes allow for better air exchange, reducing the concentration of these pollutants and creating a healthier indoor environment.
- Reduced Energy Costs: Improved ventilation can help to reduce energy costs, particularly in warm climates. The increased airflow beneath the elevated structure creates a cooling effect, reducing the need for air conditioning. Additionally, the natural ventilation helps to regulate indoor temperatures, minimizing the reliance on heating and cooling systems.
- Enhanced Comfort: Improved ventilation contributes to the overall comfort of occupants by providing a more pleasant and refreshing living environment. The increased airflow helps to circulate fresh air throughout the home, reducing stuffiness and creating a more comfortable and inviting atmosphere.
In addition to these benefits, improved ventilation in elevated house plans can also help to extend the lifespan of the home’s structure by reducing moisture-related damage and promoting the longevity of building materials.
Enhanced views
Elevated house plans offer enhanced views of the surrounding landscape, providing occupants with breathtaking vistas and a greater connection to the outdoors.
- Unobstructed Views: Elevated homes are positioned above the ground, allowing for unobstructed views of the surrounding area. This is particularly advantageous in scenic locations, such as overlooking a lake, mountain range, or cityscape. The elevated perspective provides a panoramic view that would not be possible from a home built at ground level.
- Natural Light: The elevated position of these homes allows for larger windows and openings, maximizing natural light intake. The increased window space provides ample sunlight, creating brighter and more inviting living spaces. Natural light has been shown to improve mood, boost energy levels, and reduce stress.
- Connection to Nature: Elevated homes offer a stronger connection to the natural surroundings. The elevated perspective allows occupants to enjoy views of trees, plants, and wildlife from the comfort of their own home. This connection to nature can promote relaxation, reduce stress, and enhance overall well-being.
- Increased Privacy: The elevated position of these homes provides increased privacy, as they are less visible from the street and neighboring properties. This added privacy allows occupants to enjoy their outdoor spaces without feeling overlooked or exposed.
The enhanced views offered by elevated house plans contribute to the overall quality of life for occupants, providing a sense of spaciousness, tranquility, and connection to the natural environment.
Terrain adaptability
Elevated house plans offer exceptional terrain adaptability, allowing them to be constructed on a wide range of land types and slopes.
- Sloping Sites: Elevated homes are ideal for sloping sites, as they can be constructed to conform to the natural contours of the land. The pillars or columns supporting the elevated structure can be adjusted in height to accommodate the slope, creating a level living space while minimizing the need for extensive excavation or grading.
- Uneven Ground: Elevated homes can be adapted to uneven ground conditions, such as rocky terrain or areas with significant changes in elevation. The flexible design of elevated structures allows for the incorporation of different column heights and foundation systems to accommodate uneven surfaces, ensuring stability and structural integrity.
- Flood-Prone Areas: Elevated house plans are particularly well-suited for flood-prone areas, as they can be raised above the anticipated flood level. By elevating the living spaces, elevated homes provide protection against floodwaters, minimizing the risk of damage to the home and its contents.
- Coastal Locations: Elevated homes are often found in coastal locations, where they offer protection against storm surges and high winds. The elevated structure creates a barrier between the living spaces and the harsh coastal environment, reducing the risk of damage from storms and erosion.
The terrain adaptability of elevated house plans makes them a versatile and practical choice for a variety of building sites and challenging terrains, providing homeowners with greater flexibility in choosing their desired location.
Structural stability
Elevated house plans require careful attention to structural stability to ensure the safety and integrity of the home. Here are key considerations for structural stability in elevated house plans:
- Foundation Design: The foundation of an elevated home is crucial for its stability. Depending on the soil conditions and the height of the elevation, different foundation systems may be employed, such as concrete piers, steel columns, or reinforced concrete slabs. The foundation must be designed to distribute the weight of the structure evenly and resist lateral forces, such as high winds or seismic activity.
- Column Strength and Spacing: The columns or pillars supporting the elevated structure play a vital role in maintaining stability. They must be strong enough to bear the weight of the home and withstand lateral forces. The spacing of the columns should be carefully calculated to ensure adequate support and prevent excessive deflection.
- Lateral Bracing: Elevated homes require proper lateral bracing to resist wind and seismic forces. This can be achieved through the use of shear walls, diagonal braces, or moment-resisting frames. Lateral bracing helps to distribute lateral forces throughout the structure, preventing it from swaying or collapsing.
- Connections and Joints: The connections between the columns, beams, and other structural components must be carefully designed and constructed to ensure the stability of the elevated structure. Strong and durable connections are essential to maintain the integrity of the home under various loading conditions.
By addressing these structural stability considerations, elevated house plans can be engineered to withstand various forces and ensure the safety and longevity of the home.
Construction complexity
Elevated house plans involve more complex construction techniques compared to traditional ground-level homes. Here are key considerations that contribute to the construction complexity of elevated house plans:
- Foundation and Substructure: Elevated homes require specialized foundation systems, such as piers, columns, or reinforced concrete slabs, to support the structure above the ground. The design and construction of these foundations must carefully consider soil conditions, elevation height, and lateral forces.
- Structural Framing: The framing of elevated homes is more complex than ground-level homes due to the need to create a stable and load-bearing structure at a height. This involves the use of stronger beams, joists, and connections to ensure the integrity of the elevated structure.
- Access and Elevation: Constructing elevated homes requires specialized equipment and techniques to safely access and work at elevated heights. This can include the use of scaffolding, cranes, or lifts to transport materials and workers during the construction process.
- Utility and Service Connections: Running utilities, such as plumbing, electrical, and HVAC systems, to elevated homes can be more complex than in ground-level homes. This requires careful planning and coordination to ensure proper installation and maintenance of these systems.
While elevated house plans offer unique advantages, the increased construction complexity requires specialized expertise and careful execution to ensure the safety and structural integrity of the home.
Despite the construction challenges, elevated house plans have become increasingly popular due to their ability to adapt to challenging terrains, provide protection from flooding and pests, and offer enhanced views and ventilation. With proper planning, engineering, and skilled construction practices, elevated homes can be built to withstand various forces and provide safe and comfortable living spaces.
Cost implications
Elevated house plans generally have higher construction costs compared to traditional ground-level homes. Here are several factors that contribute to the increased costs associated with elevated house plans:
- Foundation and Substructure: Elevated homes require specialized foundation systems, such as piers, columns, or reinforced concrete slabs, to support the structure above the ground. These foundation systems are more complex to design and construct compared to traditional foundations for ground-level homes, resulting in higher material and labor costs.
- Structural Framing: The framing of elevated homes is more complex than ground-level homes due to the need to create a stable and load-bearing structure at a height. This involves the use of stronger beams, joists, and connections to ensure the integrity of the elevated structure, leading to increased material and labor costs.
- Access and Elevation: Constructing elevated homes requires specialized equipment and techniques to safely access and work at elevated heights. This can include the use of scaffolding, cranes, or lifts to transport materials and workers during the construction process, resulting in additional rental or purchase costs for this equipment.
- Utility and Service Connections: Running utilities, such as plumbing, electrical, and HVAC systems, to elevated homes can be more complex than in ground-level homes. This requires careful planning and coordination to ensure proper installation and maintenance of these systems, potentially leading to higher material and labor costs.
Despite the higher construction costs, elevated house plans can offer long-term benefits that may offset the initial investment. These benefits include reduced risk of flood damage, improved durability against pests and moisture, enhanced ventilation and natural lighting, and increased property value in certain markets. Carefully weighing the cost implications against the potential benefits is essential when considering an elevated house plan.










Related Posts