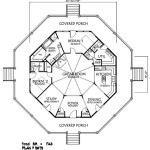
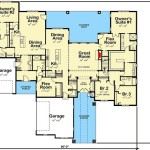
Elevated house design plans entail meticulously engineered architectural schemes that elevate a structure above ground level. These designs often employ stilts, columns, or other support systems to raise the home, typically for specific functional or aesthetic reasons. One notable example of elevated house design can be found in coastal areas, where homes are elevated to protect them from potential flooding and storm surges.
The reasons for elevating a house vary widely. Practical considerations, such as protection from environmental hazards or the creation of additional space beneath the structure, are common drivers. Moreover, elevated house designs can enhance views, improve natural ventilation, and even reduce the risk of pest infestations. Architects and designers leverage these advantages to create homes that are both practical and aesthetically pleasing.
As we delve deeper into this article, we will explore the various types of elevated house design plans, their advantages and disadvantages, and key factors to consider when designing and building an elevated home. We will also showcase inspiring case studies and provide practical guidance to help you make informed decisions about your own elevated house design project.
When considering elevated house design plans, several key points merit attention:
- Flood protection
- Enhanced views
- Improved ventilation
- Pest resistance
- Additional storage space
- Higher construction costs
- Structural complexity
- Maintenance considerations
- Local building codes
Understanding these factors will empower you to make informed decisions and design an elevated home that meets your specific needs and preferences.
Flood protection
Elevated house design plans offer a proactive approach to flood protection, safeguarding homes from the devastating effects of water damage. By raising the structure above the anticipated flood level, elevated homes minimize the risk of inundation and its associated hazards.
In flood-prone areas, elevated homes provide peace of mind and reduce the need for costly flood insurance. They protect not only the structural integrity of the home but also valuable possessions and personal belongings from the damaging effects of water. Additionally, elevating a home can improve indoor air quality by preventing mold and mildew growth caused by excessive moisture.
Building codes in flood-prone areas often mandate specific elevation requirements for new construction. These codes are based on historical flood data and projections of future flood risks. By adhering to these regulations, homeowners can ensure their properties meet the minimum safety standards and qualify for flood insurance.
When designing an elevated home for flood protection, careful consideration must be given to the height of the elevation, the type of foundation system, and the materials used in construction. Engineers and architects work together to determine the appropriate elevation level based on flood risk assessments and local building codes. The foundation system must be robust enough to withstand the forces exerted by floodwaters, and the materials used in construction should be resistant to water damage and mold growth.
Elevated house design plans offer a comprehensive solution for flood protection, providing homeowners with peace of mind, increased safety, and reduced financial risks.
Enhanced views
Elevated house design plans offer unparalleled opportunities to enhance the visual experience of a home. By elevating the structure, architects and designers can unlock panoramic vistas, expansive sightlines, and breathtaking views of the surrounding landscape.
- Unobstructed panoramas
Elevated homes provide unobstructed views of the surrounding landscape, allowing residents to enjoy sweeping vistas of mountains, forests, oceans, or city skylines. Large windows and expansive balconies or decks further enhance the visual connection to the outdoors, creating a sense of openness and tranquility.
- Natural light optimization
Elevated homes can be positioned to maximize natural light throughout the day. By carefully orienting the home and strategically placing windows, architects can design spaces that are filled with an abundance of sunlight, reducing the need for artificial lighting and creating a warm and inviting atmosphere.
- Privacy and seclusion
Elevation can provide a sense of privacy and seclusion, especially in densely populated areas. Elevated homes offer a unique vantage point that overlooks neighboring properties, creating a buffer zone that enhances the home’s privacy.
- Connection to nature
Elevated homes foster a stronger connection to nature by bringing residents closer to the surrounding environment. Elevated decks and balconies become outdoor sanctuaries, offering a place to relax, entertain, and immerse oneself in the beauty of the natural world.
Overall, elevated house design plans provide a unique opportunity to enhance the visual experience of a home, creating spaces that are both aesthetically pleasing and deeply connected to the surrounding environment.
Improved ventilation
Elevated house design plans offer significant advantages in terms of ventilation, creating healthier and more comfortable indoor environments.
- Enhanced natural ventilation
Elevated homes are positioned to take advantage of natural air currents. By strategically placing windows and vents at different heights, architects can create a stack effect that draws fresh air into the home and expels stale air. This continuous airflow helps to reduce indoor air pollution, remove excess moisture, and maintain a comfortable temperature throughout the home.
- Reduced reliance on air conditioning
Improved ventilation can significantly reduce the need for air conditioning, especially in warmer climates. The natural airflow created by elevated design helps to cool the home, reducing energy consumption and lowering utility bills.
- Improved indoor air quality
Elevated homes are less susceptible to moisture buildup and mold growth, which can lead to poor indoor air quality. The constant airflow helps to circulate fresh air throughout the home, diluting indoor pollutants and creating a healthier environment for occupants.
- Reduced humidity levels
In humid climates, elevated homes can help to reduce indoor humidity levels. The natural ventilation created by the elevated design helps to remove excess moisture from the air, reducing the risk of condensation and mold growth.
Overall, elevated house design plans offer a comprehensive solution for improved ventilation, creating healthier, more comfortable, and more energy-efficient indoor environments.
Pest resistance
Elevated house design plans offer inherent advantages in terms of pest resistance, creating homes that are less susceptible to infestation and damage from insects, rodents, and other pests.
- Reduced ground contact
Elevated homes have minimal contact with the ground, which eliminates direct pathways for pests to enter the home. This reduces the risk of infestation from ants, termites, and other ground-dwelling pests.
- Improved ventilation
As discussed earlier, elevated homes benefit from improved ventilation, which helps to reduce moisture and humidity levels. This creates an unfavorable environment for pests that thrive in moist conditions, such as cockroaches and mold mites.
- Limited access points
Elevated homes often have fewer access points at ground level, making it more difficult for pests to enter the home. Careful attention to sealing gaps and cracks around windows, doors, and pipes further minimizes the risk of pest intrusion.
- Discouragement of burrowing pests
The open and airy space beneath elevated homes discourages burrowing pests, such as rodents and moles, from nesting and causing damage to the structure or landscaping.
Overall, elevated house design plans offer a comprehensive approach to pest resistance, creating homes that are less susceptible to infestation and damage, and providing peace of mind for homeowners.
In addition to the inherent advantages mentioned above, there are specific design features and materials that can further enhance the pest resistance of elevated homes. For example, using pest-resistant building materials, such as treated lumber and metal flashing, can help to deter pests and prevent damage to the home’s structure. Additionally, incorporating features such as screened vents and crawl space access doors can provide additional protection against pest intrusion.
Additional storage space
Elevated house design plans offer a unique opportunity to create additional storage space beneath the elevated structure. This space can be utilized for a variety of purposes, providing homeowners with valuable storage solutions.
- Garage and workshop space
The space beneath an elevated home can be enclosed to create a garage or workshop area. This is particularly useful for homes with limited garage space or for those who need a dedicated space for hobbies and projects.
- Storage rooms
Additional storage rooms can be created beneath the elevated structure, providing ample space for seasonal items, bulky belongings, or anything that needs to be stored out of sight.
- Wine cellars and pantries
The consistent temperature and humidity levels beneath an elevated home make it an ideal location for storing wine or creating a pantry for food storage.
- Home gyms and recreation areas
The space beneath an elevated home can be transformed into a home gym or recreation area, providing a dedicated space for fitness, entertainment, or hobbies.
Overall, the additional storage space created by elevated house design plans provides homeowners with valuable and versatile options for storing belongings, pursuing hobbies, and enhancing their overall quality of life.
Higher construction costs
Elevated house design plans generally entail higher construction costs compared to traditional single-story homes. This is primarily due to the additional materials, engineering, and labor required to elevate the structure.
- Materials
Elevated homes require more materials, including additional framing, support beams, columns, and foundations. These materials can add significant costs to the overall construction budget.
- Engineering
The design and engineering of an elevated home are more complex than a traditional home. Engineers must carefully calculate the loads and stresses on the structure to ensure its stability and safety. This additional engineering work can increase the overall cost of the project.
- Labor
Building an elevated home requires specialized labor and techniques. Carpenters, masons, and other skilled tradespeople must work together to construct the elevated structure, which can lead to higher labor costs.
- Foundation
Elevated homes require specialized foundation systems, such as piers, columns, or stilts, to support the structure above ground level. These foundations are more complex and expensive to construct than traditional slab or crawlspace foundations.
Despite the higher construction costs, elevated house design plans offer unique advantages in terms of flood protection, enhanced views, improved ventilation, pest resistance, and additional storage space. Homeowners should carefully weigh these benefits against the additional costs when considering an elevated home design.
Structural complexity
Elevated house design plans introduce a unique set of structural complexities that require careful engineering and precise execution. Unlike traditional single-story homes, elevated homes must be designed to withstand the additional forces and stresses imposed by their elevated position.
One of the primary structural challenges in elevated house design is ensuring the stability and integrity of the support structure. The columns, piers, or stilts that elevate the home must be carefully engineered to the weight of the structure and resist lateral forces such as wind and seismic activity. Engineers must also consider the potential for differential settlement, which can occur when the soil beneath the support structure compresses unevenly over time.
Another structural complexity in elevated house design is the need to provide adequate lateral stability to prevent the structure from swaying or overturning. This is achieved through a combination of structural elements, including shear walls, moment frames, and bracing systems. The design of these elements must carefully consider the specific loads and forces that the elevated home will be subjected to.
Furthermore, elevated house design plans must address the potential for moisture and water damage to the support structure. This is particularly important in areas prone to flooding or high humidity. Engineers must specify materials and construction techniques that are resistant to moisture and rot to ensure the long-term durability of the elevated structure.
Overall, the structural complexity of elevated house design plans requires a high level of engineering expertise and careful attention to detail. Architects and engineers must work closely together to create a structurally sound and safe elevated home that meets the specific needs and requirements of the homeowner.
Maintenance considerations
Elevated house design plans require specific maintenance considerations to ensure the long-term integrity and safety of the structure. Homeowners should be aware of these considerations and plan for regular maintenance tasks to preserve the value and functionality of their elevated home.
- Regular inspection of support structure
The support structure of an elevated home, including columns, piers, or stilts, should be inspected regularly for signs of damage or deterioration. This includes checking for cracks, corrosion, or any other signs of structural compromise. Regular inspection and maintenance can help to identify and address potential issues before they become major problems.
- Moisture protection
Elevated homes are exposed to moisture and water from various sources, including rain, snow, and humidity. It is important to ensure that the support structure and other elements of the home are adequately protected from moisture damage. This may involve applying sealants or coatings to exposed surfaces, installing gutters and downspouts to direct water away from the structure, and maintaining proper ventilation to prevent moisture buildup.
- Termite and pest control
Elevated homes may be more susceptible to termite and pest infestations due to their proximity to the ground. Regular termite and pest inspections and treatments are recommended to prevent damage to the structure and ensure the health and safety of the occupants.
- Deck and balcony maintenance
Elevated homes often feature decks and balconies that require regular maintenance to ensure their safety and functionality. This includes cleaning, staining, or sealing the deck surface to protect it from moisture and UV damage, as well as inspecting and maintaining railings and other safety features.
By following these maintenance considerations, homeowners can help to ensure the longevity, safety, and enjoyment of their elevated home.
Local building codes
Local building codes play a crucial role in regulating the design and construction of elevated house design plans to ensure public safety and well-being. These codes establish minimum standards for structural integrity, fire safety, accessibility, and other aspects of building construction.
When it comes to elevated house design plans, local building codes typically address specific requirements related to:
- Foundation design
Building codes specify the minimum requirements for the design and construction of the foundation system for elevated homes. This includes for the type of foundation, depth, reinforcement, and soil bearing capacity. The codes aim to ensure that the foundation can adequately support the weight of the structure and resist lateral forces. - Structural design
Building codes provide guidelines for the structural design of elevated homes, including the design of columns, beams, and other structural elements. The codes specify the minimum strength and dimensions of structural members to ensure the stability and safety of the structure under various load conditions, such as dead loads, live loads, and wind loads. - Fire safety
Building codes include provisions for fire safety in elevated homes. These provisions address requirements for fire-rated materials, compartmentalization, means of egress, and fire protection systems. The codes aim to minimize the risk of fire and ensure the safe evacuation of occupants in the event of a fire. - Accessibility
Building codes often include accessibility requirements for elevated homes to ensure that they are accessible to individuals with disabilities. These requirements may include provisions for ramps, elevators, accessible entrances, and other features that facilitate access and mobility for all occupants.
It is important for architects, engineers, and homeowners to be familiar with the local building codes that apply to elevated house design plans. Adhering to these codes is not only a legal requirement but also essential for ensuring the safety, functionality, and habitability of elevated homes.










Related Posts