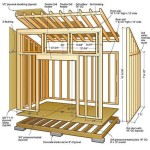
Economical house plans designs are blueprints that prioritize cost-effectiveness while ensuring functionality and aesthetic appeal. These designs employ innovative strategies to minimize construction costs without compromising quality or style. For instance, a typical economical house plan might incorporate open floor plans to reduce the need for interior walls, utilize energy-efficient materials to lower operating costs, and optimize space utilization to maximize living areas while minimizing the overall footprint.
The demand for economical house plans designs has surged in recent times due to rising housing costs and a growing awareness of sustainability. These designs empower homeowners with the ability to build affordable, comfortable, and eco-friendly homes that meet their specific needs and budgets.
Let’s explore the key elements and advantages of economical house plans designs in the following sections:
Economical house plans designs prioritize cost-effectiveness while ensuring livability and style. Here are 10 important points to consider:
- Simple and efficient layouts: Minimize unnecessary walls and hallways.
- Energy-efficient materials: Reduce heating and cooling costs.
- Smart space utilization: Maximize living areas while minimizing footprint.
- Optimized material usage: Reduce waste and construction costs.
- Local and sustainable materials: Lower transportation and environmental impact.
- DIY-friendly designs: Empower homeowners to save on labor costs.
- Prefabricated components: Fast and cost-effective construction.
- Passive solar design: Utilize natural heating and cooling.
- Low-maintenance materials: Reduce ongoing expenses.
- Multi-purpose spaces: Combine functions to save space and costs.
By incorporating these principles, economical house plans designs offer affordable, comfortable, and sustainable living spaces that meet the needs of homeowners on a budget.
Simple and efficient layouts: Minimize unnecessary walls and hallways.
In economical house plans, simplicity and efficiency are key. Unnecessary walls and hallways not only add to construction costs but also waste valuable space and make the home feel cluttered and cramped. By minimizing these elements, designers can create more open and spacious living areas while reducing overall square footage and construction expenses.
One way to achieve a simple and efficient layout is to incorporate open floor plans. Open floor plans eliminate walls between common areas such as the living room, dining room, and kitchen, creating a more cohesive and expansive space. This approach not only reduces the need for walls and hallways but also improves natural light flow and fosters a sense of spaciousness.
Another strategy is to utilize multi-purpose spaces. By combining functions into a single room, homeowners can save space and reduce the need for additional rooms. For example, a guest room can double as a home office, or a breakfast nook can be incorporated into the kitchen area. These versatile spaces not only enhance functionality but also contribute to a more efficient and cost-effective layout.
Furthermore, designers can optimize space utilization by employing creative storage solutions. Built-in shelves, cabinets, and closets can be strategically placed throughout the home to maximize storage capacity without taking up valuable floor space. By eliminating the need for bulky furniture and clutter, homeowners can maintain a clean and organized living environment while maximizing space efficiency.
By adopting these principles of simplicity and efficiency, economical house plans can provide homeowners with comfortable and functional living spaces without sacrificing affordability or style.
Energy-efficient materials: Reduce heating and cooling costs.
In the pursuit of economical house plans, energy efficiency plays a crucial role in reducing long-term operating costs and promoting sustainable living. By incorporating energy-efficient materials and construction practices, homeowners can significantly lower their heating and cooling expenses while enhancing the overall comfort and value of their homes.
One of the most important aspects of energy-efficient design is the selection of appropriate building materials. Materials with high thermal resistance, such as insulated concrete forms (ICFs), structural insulated panels (SIPs), and cellulose insulation, can effectively minimize heat transfer through walls, ceilings, and floors. By reducing thermal bridging and air infiltration, these materials help maintain a consistent and comfortable indoor temperature, reducing the reliance on heating and cooling systems.
Windows and doors are another key area for energy efficiency. ENERGY STAR-certified windows and doors are designed to meet strict energy performance standards, reducing heat loss and gain through glazed areas. By choosing high-performance windows and doors, homeowners can significantly improve the thermal envelope of their homes, leading to lower energy consumption and utility bills.
In addition to insulation and windows, the building envelope can be further enhanced by incorporating passive solar design principles. By strategically positioning windows and utilizing natural shading, homeowners can harness the sun’s energy for heating during the winter months and minimize heat gain during the summer. This approach not only reduces the demand on HVAC systems but also creates a more comfortable and naturally lit living environment.
By carefully selecting energy-efficient materials and implementing passive solar design strategies, economical house plans can provide homeowners with substantial savings on energy costs while promoting environmental sustainability and enhancing overall living comfort.
Smart space utilization: Maximize living areas while minimizing footprint.
In economical house plans, smart space utilization is essential for creating comfortable and functional living areas without exceeding budget constraints or increasing the overall footprint of the home. This involves maximizing the efficiency of every square foot and employing creative design techniques to achieve a spacious and inviting living environment.
One key strategy is to incorporate open floor plans. By eliminating unnecessary walls and hallways, open floor plans create a more cohesive and expansive space. This approach not only reduces construction costs but also improves natural light flow and fosters a sense of spaciousness. Open floor plans are particularly well-suited for common areas such as the living room, dining room, and kitchen, where families and guests can interact and socialize freely.
Another way to maximize space utilization is to utilize multi-purpose spaces. By combining functions into a single room, homeowners can save space and reduce the need for additional rooms. For example, a guest room can double as a home office, or a breakfast nook can be incorporated into the kitchen area. These versatile spaces not only enhance functionality but also contribute to a more efficient and cost-effective layout.
Built-in storage solutions are another effective way to optimize space utilization. Custom-designed cabinets, shelves, and closets can be strategically placed throughout the home to maximize storage capacity without taking up valuable floor space. By eliminating the need for bulky furniture and clutter, homeowners can maintain a clean and organized living environment while maximizing space efficiency. Built-in storage can be particularly useful in areas such as the kitchen, bathroom, and laundry room, where space is often limited.
By employing these smart space utilization techniques, economical house plans can provide homeowners with comfortable and functional living spaces without sacrificing affordability or style. By maximizing the efficiency of every square foot, homeowners can enjoy a spacious and inviting living environment within a compact footprint.
Optimized material usage: Reduce waste and construction costs.
In economical house plan designs, optimizing material usage is crucial for minimizing waste and reducing construction costs. By carefully selecting materials and employing efficient construction techniques, homeowners can significantly lower their building expenses without compromising the quality or durability of their homes.
One of the key strategies for optimized material usage is to minimize waste. This can be achieved by employing precise cutting techniques, using prefabricated components, and implementing modular construction methods. Prefabricated components, such as wall panels and roof trusses, are manufactured off-site under controlled conditions, reducing waste and ensuring dimensional accuracy. Modular construction involves assembling prefabricated modules into a complete structure, further minimizing waste and construction time.
Another important aspect of optimized material usage is the selection of appropriate materials. Sustainable and durable materials, such as recycled steel, reclaimed wood, and low-VOC paints, not only reduce environmental impact but can also contribute to cost savings. By choosing materials that are locally sourced and readily available, transportation costs can be minimized.
Furthermore, efficient framing techniques can significantly reduce material usage and construction costs. Proper spacing of studs, joists, and rafters ensures structural integrity without overusing materials. Utilizing advanced framing techniques, such as metal connectors and engineered lumber, can further optimize material usage and enhance structural performance.
By adopting these principles of optimized material usage, economical house plans can effectively reduce waste and construction costs, allowing homeowners to build affordable and environmentally friendly homes without sacrificing quality or durability.
Local and sustainable materials: Lower transportation and environmental impact.
Incorporating local and sustainable materials into economical house plans offers significant advantages in terms of both cost and environmental impact. By sourcing materials from local suppliers and prioritizing sustainability, homeowners can reduce transportation costs, minimize carbon emissions, and contribute to the well-being of their communities.
- Reduced transportation costs:
Utilizing local materials significantly reduces transportation distances, leading to lower fuel consumption and associated costs. This not only benefits homeowners financially but also contributes to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions.
- Lowered carbon footprint:
Local materials often have a lower carbon footprint compared to materials transported from distant locations. By reducing the distance materials travel, the embodied energy and associated emissions are minimized, contributing to a more sustainable building process.
- Support for local businesses:
Sourcing materials locally supports the local economy and fosters relationships with businesses in the community. This not only benefits the local economy but also helps preserve traditional skills and industries.
- Enhanced durability and resilience:
Local materials are often well-suited to the specific climate and environmental conditions of the region. By using local materials, homeowners can enhance the durability and resilience of their homes, reducing the need for costly repairs and replacements in the future.
In addition to these benefits, sustainable materials offer further advantages. For example, using recycled materials reduces waste and promotes a circular economy, while low-VOC (volatile organic compound) materials contribute to a healthier indoor environment. By incorporating local and sustainable materials into economical house plans, homeowners can create affordable, environmentally friendly, and resilient homes that support both their families and their communities.
DIY-friendly designs: Empower homeowners to save on labor costs.
DIY-friendly designs are an integral aspect of economical house plans, empowering homeowners to take an active role in the construction process and save on labor costs. By incorporating user-friendly features and providing clear instructions, these designs enable homeowners with varying skill levels to complete tasks that would otherwise require professional contractors.
- Simplified construction methods:
DIY-friendly house plans utilize simplified construction methods that are easy to understand and execute. These methods often involve step-by-step guides, detailed diagrams, and pre-cut materials, reducing the need for specialized knowledge or intricate techniques.
- Modular components:
Modular components, such as prefabricated wall panels and roof trusses, are commonly used in DIY-friendly designs. These components are manufactured off-site under controlled conditions, ensuring precision and ease of assembly. By eliminating the need for complex framing and joinery, modular components simplify the construction process and minimize the need for skilled labor.
- Accessible materials:
DIY-friendly house plans prioritize the use of materials that are readily available and easy to work with. This includes materials like plywood, OSB (oriented strand board), and pressure-treated lumber, which are commonly found at local home improvement stores and can be handled without specialized equipment.
- Online resources and support:
Homeowners embarking on DIY projects have access to a wealth of online resources and support. Numerous websites, forums, and instructional videos provide guidance and troubleshooting tips, empowering homeowners to confidently complete tasks and overcome challenges.
By embracing DIY-friendly designs, homeowners can actively participate in the construction of their homes, gaining valuable skills and saving on labor costs. This not only reduces the overall project expenses but also fosters a sense of accomplishment and pride in creating a personalized living space.
Prefabricated components: Fast and cost-effective construction.
Prefabricated components offer a multitude of advantages in economical house plan designs, contributing to faster construction times and reduced costs. By utilizing prefabricated components, homeowners can streamline the building process, minimize labor requirements, and achieve significant savings.
- Reduced construction time:
Prefabricated components are manufactured off-site in controlled factory environments, allowing for precise assembly and quality control. This streamlined production process significantly reduces construction time compared to traditional site-built methods. Prefabricated components can be delivered to the construction site ready for assembly, eliminating the need for extensive on-site framing and finishing work.
- Lower labor costs:
Prefabricated components minimize the need for skilled labor on-site, reducing labor costs. The precision engineering and pre-assembly of components allow for faster and more efficient installation, requiring fewer workers and less time to complete the construction process. This reduction in labor requirements translates into substantial cost savings for homeowners.
- Enhanced quality control:
Factory-controlled production environments ensure consistent quality and precision in the manufacturing of prefabricated components. Prefabricated components are subject to rigorous quality inspections and testing before being delivered to the construction site, minimizing the risk of defects and errors. This high level of quality control contributes to the durability and longevity of the home.
- Improved energy efficiency:
Prefabricated components can be designed and manufactured with high levels of energy efficiency. Advanced insulation techniques and airtight construction methods utilized in factory settings minimize energy loss and improve the overall thermal performance of the home. This results in lower energy consumption and reduced utility costs for homeowners.
By incorporating prefabricated components into economical house plan designs, homeowners can benefit from faster construction times, lower labor costs, enhanced quality control, and improved energy efficiency. These advantages contribute to significant cost savings and a more streamlined, efficient building process.
Passive solar design: Utilize natural heating and cooling.
Passive solar design is a cost-effective and environmentally friendly approach to heating and cooling homes, reducing reliance on conventional HVAC systems and lowering energy consumption. By strategically positioning windows, utilizing thermal mass, and incorporating natural ventilation, passive solar design harnesses the power of the sun to create comfortable indoor temperatures throughout the year.
- Window placement:
Windows are strategically placed to maximize solar heat gain during the winter months and minimize heat gain during the summer months. South-facing windows allow sunlight to penetrate deep into the home, warming the interior spaces. Overhangs or awnings can be used to shade windows during the summer, preventing excessive heat gain.
- Thermal mass:
Thermal mass materials, such as concrete, brick, and tile, absorb and store heat from the sun during the day and release it slowly at night, helping to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature. These materials are often used in floors, walls, and ceilings to enhance the thermal performance of the home.
- Natural ventilation:
Natural ventilation utilizes airflow to cool homes during the summer months. Windows and vents are strategically placed to create cross-ventilation, allowing cool air to enter the home and warm air to escape. Attic fans or solar chimneys can also be used to enhance natural ventilation and remove hot air from the attic.
- Building orientation:
The orientation of the home on the building site is crucial for passive solar design. In the Northern Hemisphere, homes should be oriented with the majority of windows facing south to maximize solar heat gain. In the Southern Hemisphere, homes should be oriented with the majority of windows facing north.
By incorporating passive solar design principles into economical house plans, homeowners can create comfortable and energy-efficient homes that reduce their reliance on fossil fuels and lower their utility bills. Passive solar design not only contributes to cost savings but also promotes environmental sustainability and enhances the overall quality of living.
Low-maintenance materials: Reduce ongoing expenses.
In economical house plan designs, selecting low-maintenance materials is crucial for reducing ongoing expenses and preserving the aesthetic appeal of the home. By choosing materials that require minimal upkeep and withstand the elements, homeowners can save time, effort, and money in the long run.
Exterior materials play a significant role in determining the maintenance requirements of a home. Durable siding materials, such as fiber cement, vinyl, or metal, resist fading, warping, and insect damage, eliminating the need for frequent painting or repairs. Composite decking and railings offer similar advantages, providing a low-maintenance alternative to traditional wood.
Windows and doors should also be carefully considered for their low-maintenance properties. Vinyl or aluminum windows and doors are resistant to rot, rust, and fading, requiring minimal upkeep compared to wood counterparts. Energy-efficient windows with double or triple glazing can further reduce energy costs and enhance comfort.
Interior materials can also contribute to low maintenance. Durable flooring options, such as tile, laminate, or luxury vinyl plank, are easy to clean and maintain, withstanding daily wear and tear. Quartz or solid surface countertops are non-porous and resistant to stains and scratches, making them ideal for kitchens and bathrooms.
By incorporating low-maintenance materials into economical house plans, homeowners can minimize the time and expense associated with ongoing upkeep, ensuring a beautiful and comfortable home for years to come.
Multi-purpose spaces: Combine functions to save space and costs.
Multi-purpose spaces are a cornerstone of economical house plan designs, offering a clever and cost-effective way to maximize space utilization and reduce construction costs. By combining multiple functions into a single room, homeowners can eliminate the need for additional rooms, saving valuable square footage and construction expenses.
One common example of a multi-purpose space is the great room, which combines the functions of a living room, dining room, and kitchen into a single expansive area. This open floor plan design creates a sense of spaciousness and flow, while eliminating the need for separate rooms for each function. The great room is particularly well-suited for families and those who love to entertain, as it provides ample space for gathering, dining, and relaxing.
Another example of a multi-purpose space is the guest room/home office. This versatile room can serve as a spare bedroom for guests when needed, and as a dedicated home office or study space during the rest of the year. By combining these functions, homeowners can save the space and cost of having two separate rooms.
Multi-purpose spaces can also be incorporated into smaller homes to maximize space utilization. For example, a breakfast nook can be incorporated into the kitchen area, providing a casual dining space without the need for a separate dining room. Similarly, a mudroom can be combined with a laundry room, creating a functional space for both storing outdoor gear and doing laundry.
By embracing multi-purpose spaces in economical house plan designs, homeowners can create functional and space-efficient homes that meet their needs without exceeding their budget. These versatile spaces offer a cost-effective and creative approach to maximizing space utilization and enhancing the overall functionality of the home.










Related Posts