Draw Your Dream Home: A Step-by-Step Guide to Creating House Plans
Creating house plans is a crucial initial stage in any home construction or renovation project. These plans serve as a visual blueprint, outlining the dimensions, layout, and overall design of the dwelling. Developing these plans, even in a rudimentary form, enables homeowners to articulate their vision clearly, facilitate communication with architects and builders, and ultimately ensure the project aligns with their needs and aspirations. This article provides a structured guide for individuals seeking to create their own house plans, covering essential steps from conceptualization to preliminary drafting.
Establishing Needs and Requirements
The first phase in creating house plans involves a thorough assessment of current and future needs. This entails considering lifestyle considerations, anticipated family growth, and specific accessibility requirements. Carefully evaluating these factors will ensure the eventual house plan reflects a comfortable and functional living space for all inhabitants.
Begin by listing the number of bedrooms and bathrooms required. Account for potential future occupants, such as children or aging parents. Consider the size and type of living spaces needed. Will a formal living room suffice, or is a more casual family room preferred? What about a home office, a library, or a recreational space? Think about the required storage space, closets, and pantry areas needed to comfortably store belongings.
Accessibility is another crucial consideration. Incorporate features such as wider doorways, ramps, or grab bars into the design to accommodate individuals using wheelchairs, walkers, or who may have other mobility limitations. This proactive approach ensures the home is accessible and adaptable for years to come.
Beyond functional needs, consider aesthetic preferences. Note styles of architecture, interior décor themes, and landscape preferences which will allow later steps to incorporate these elements into a cohesive plan.
Measuring and Assessing the Building Site
Accurate assessment of the building site is essential for generating realistic and compliant house plans. This involves measuring the lot's dimensions, noting any existing structures or utilities, and understanding zoning regulations. These factors directly impact the permissible size, shape, and placement of the house.
Begin by obtaining a site survey, if available. A site survey is a detailed map of the property that shows property lines, easements, utility locations, and any existing structures. If a site survey is unavailable, accurate measurements must be taken manually. Use a measuring tape or laser distance measurer to determine the length and width of the property's boundaries. Note the location of any existing structures, such as garages, sheds, or fences.
Identify the location of utility lines, including water, sewer, gas, and electricity. This information is crucial for planning the placement of the house and avoiding conflicts during construction. Contact local utility companies for assistance in locating underground lines.
Understanding zoning regulations is paramount. Zoning ordinances dictate the permissible uses of land, building setbacks, height restrictions, and other development standards. Contact the local planning department to obtain zoning maps and regulations for the property. Ensure the proposed house plan complies with all applicable zoning requirements.
Finally, consider the topography of the site. Note the slopes and elevations, as these can impact the design and construction process. Steep slopes may require retaining walls or specialized foundation systems. Consult with a soil engineer to assess the soil conditions and determine the suitability of the site for building.
Developing Preliminary Sketches and Floor Plans
Once the needs assessment and site analysis are complete, the next step involves creating preliminary sketches and floor plans. This is where the initial concepts are translated into visual representations. These sketches serve as a starting point for refining the design and developing more detailed plans.
Begin by creating bubble diagrams. These simple diagrams illustrate the relationships between different rooms or areas of the house. For example, the kitchen might be adjacent to the dining room, or the master bedroom might be located away from the other bedrooms for privacy. Bubble diagrams help to visualize the overall layout and flow of the house.
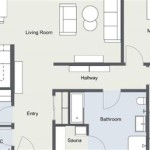
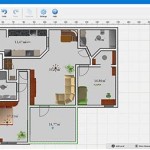
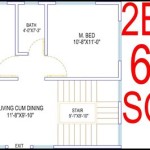
Based on the bubble diagrams, develop rough floor plans. These plans show the approximate dimensions of each room, the location of walls, doors, and windows, and the placement of fixtures such as sinks, toilets, and appliances. Use graph paper or a computer-aided design (CAD) program to create these plans.
Experiment with different layouts to find the most functional and aesthetically pleasing design. Consider the flow of traffic through the house, the orientation of rooms to maximize natural light and views, and the placement of stairs and hallways. It is preferable to generate multiple layout options, comparing and contrasting the benefits of each before moving to a finalized layout.
Consider drawing elevations, or exterior views, of the house. These elevations illustrate the roofline, the placement of windows and doors, and the overall architectural style. Elevations provide a visual representation of how the house will look from the outside.
As the floor plans and elevations are developed, consider the structural components of the house. Note the location of load-bearing walls, beams, and columns. These elements are essential for supporting the weight of the house and ensuring its structural integrity. Consult with a structural engineer to ensure the design is structurally sound.
Incorporating Detail and Refinement
After developing preliminary sketches and floor plans, the next phase involves incorporating detail and refining the design. This includes specifying materials, adding dimensions and annotations, and ensuring compliance with building codes. This step transforms the rough sketches into more accurate and comprehensive house plans.
Add dimensions to the floor plans. These dimensions specify the length and width of each room, the thickness of the walls, and the spacing between windows and doors. Accurate dimensions are essential for builders to construct the house according to the plans.
Specify the materials to be used for the construction of the house. This includes the type of foundation, the framing materials, the roofing materials, the siding materials, and the interior finishes. Consider the cost, durability, and aesthetics of each material.
Add annotations to the plans. These annotations provide additional information about the design, such as the type of windows and doors, the location of electrical outlets and switches, and the placement of plumbing fixtures. Clear and concise annotations ensure that the plans are easily understood by builders and contractors.
Ensure compliance with building codes. Building codes are a set of regulations that govern the design and construction of buildings. These codes are designed to ensure the safety and health of building occupants. Consult with a building inspector or a structural engineer to ensure the house plans comply with all applicable building codes.
Review the plans with family members and other stakeholders. Gather feedback and make revisions as needed. The goal is to create a set of house plans that meet everyone's needs and expectations.
Consider energy efficiency. Incorporate energy-efficient features into the design, such as insulation, energy-efficient windows and doors, and solar panels. These features can save money on energy bills and reduce the environmental impact of the house.
Finalizing and Presenting the Plans
The final stage in creating house plans involves finalizing the design, preparing presentation-quality drawings, and obtaining necessary permits. This ensures the plans are suitable for construction and comply with all applicable regulations.
Create a detailed set of construction drawings. These drawings include floor plans, elevations, sections, and details. Each drawing should be clearly labeled and dimensioned. The construction drawings serve as the primary reference for builders and contractors during construction.
Prepare a site plan. The site plan shows the location of the house on the property, the location of utilities, and the landscaping. The site plan is required for obtaining building permits.
Obtain building permits. Building permits are required for most construction projects. The permit process ensures that the house plans comply with building codes and zoning regulations. Submit the construction drawings and site plan to the local building department for review and approval.
Present the plans to builders and contractors. Obtain bids for the construction of the house. Review the bids carefully and select a qualified contractor. Ensure the contractor understands the plans and has experience building similar houses.
Consider hiring an architect or a draftsperson to review the plans and provide professional guidance. An architect or a draftsperson can identify potential problems with the design and offer solutions. They can also help to ensure that the plans comply with building codes and zoning regulations.
Digitize the plans for easy sharing and modification. Using CAD software allows for easy modification as the project progresses.

How To Design A House From Sketch Reality

How To Read The Blueprint Of Your Dream Home

How To Draw Blueprints For A House With Pictures Wikihow

How To Draw A Floor Plan By Hand Step Guide

How To Read The Blueprint Of Your Dream Home

How To Draw Blueprints For A House With Pictures Wikihow

Floor Plans Learn How To Design And Plan

How To Draw A Floor Plan Live Home 3d

A Guide To Building Your Dream Home In Minnesota

Simple House Design A Step By Visual Guide
Related Posts