Design Your Dream Home: Essential Plot Plans for Houses
Embarking on the journey of building a dream home requires meticulous planning and a clear understanding of the property's potential. A crucial element in this process is the development of a comprehensive plot plan. This document serves as a blueprint for the entire project, detailing the house's placement, landscaping, utilities, and other essential features within the property boundaries. Without a well-defined plot plan, the construction process can become chaotic, leading to costly errors and delays. This article explores the significance of plot plans in house design, highlighting the key components and considerations that contribute to a successful project.
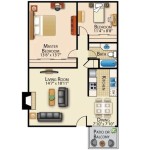
A plot plan, also known as a site plan, is a scaled drawing that illustrates the proposed and existing conditions of a specific piece of land. It provides a bird's-eye view of the property, showing the boundaries, the location of the house, driveways, sidewalks, utilities, landscaping, and other relevant features. This document is essential for obtaining building permits, ensuring compliance with local zoning regulations, and coordinating the work of various contractors involved in the construction process. The accuracy and completeness of the plot plan are paramount to the overall success of the project.
The creation of a plot plan typically involves a professional land surveyor who accurately measures the property and identifies existing features. Architects and designers then use this information to incorporate the proposed house design and other elements into the plan. The process often involves multiple iterations, as adjustments may be necessary to meet regulatory requirements, optimize the use of the land, and achieve the desired aesthetic appeal. Thorough communication between the homeowner, architect, and surveyor is critical to ensure that the plot plan accurately reflects the vision for the dream home.
Understanding the Key Components of a Plot Plan
A comprehensive plot plan includes several essential components that provide a complete picture of the property and the proposed construction. These components are not merely aesthetic additions but represent crucial elements influencing the functionality, safety, and regulatory compliance of the house.
Property Lines and Boundaries: The plot plan accurately depicts the property lines, demonstrating the legal boundaries of the land. This delineation is crucial for preventing encroachments on neighboring properties and ensuring compliance with setback requirements imposed by local zoning ordinances. Setbacks define the minimum distance a building must be from property lines, roads, and other structures. Violating these regulations can result in costly fines and delays.
Building Footprint and Placement: The plan showcases the exact location and dimensions of the proposed house on the property. This includes the orientation of the building, its distance from property lines, and its relationship to other structures on the site. Optimizing the building's placement considers factors such as sun exposure, prevailing winds, and views. This ensures a comfortable living environment and energy efficiency.
Topography and Grading: The plot plan illustrates the existing and proposed topography of the land, including contour lines that indicate elevation changes. This information is vital for managing stormwater runoff, preventing erosion, and ensuring proper drainage around the house. Grading involves reshaping the land to create a level building site and direct water away from the foundation. Proper grading is essential for preventing water damage and maintaining the structural integrity of the house.
Utilities and Easements: The plan identifies the location of existing and proposed utility lines, including water, sewer, gas, electricity, and telecommunications. It also indicates the presence of any easements on the property. Easements are legal rights granted to utility companies or other parties to access and maintain their infrastructure on the land. Understanding the location of utilities and easements is crucial for avoiding conflicts during construction and ensuring that the house is properly connected to essential services.
Access and Circulation: The plot plan outlines the location of driveways, sidewalks, parking areas, and other access routes on the property. This component ensures safe and convenient access to the house and considers factors such as traffic flow, pedestrian safety, and accessibility for people with disabilities. The location of driveways and sidewalks must comply with local regulations regarding curb cuts and sidewalk widths.
Landscaping and Site Features: The plan includes details about existing and proposed landscaping, including trees, shrubs, lawns, and other vegetation. It also identifies other site features such as fences, decks, patios, and swimming pools. Landscaping can enhance the aesthetic appeal of the property, provide shade and privacy, and improve stormwater management. The selection of appropriate plant species and the placement of site features should be carefully considered to create a functional and visually appealing outdoor space.
Navigating Zoning Regulations and Building Codes
Zoning regulations and building codes are essential considerations in the house design process, and the plot plan plays a key role in ensuring compliance. These regulations govern land use, building size, setbacks, and other aspects of construction to promote public health, safety, and welfare. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in costly delays, fines, and even the rejection of building permits. Therefore, a thorough understanding of local zoning regulations and building codes is crucial for a successful project.
Zoning Regulations: Zoning regulations dictate how land can be used within specific areas. They often specify minimum lot sizes, setbacks, height restrictions, and parking requirements. The plot plan must demonstrate that the proposed house complies with all applicable zoning regulations. This includes verifying that the building's footprint, height, and location adhere to the prescribed limits. Zoning regulations can also address issues such as landscaping, fencing, and signage.
Building Codes: Building codes establish minimum standards for the design, construction, and maintenance of buildings to ensure structural integrity, fire safety, and energy efficiency. The plot plan must demonstrate that the proposed house complies with relevant building codes. This includes requirements for foundation design, structural framing, electrical wiring, plumbing, and HVAC systems. Building codes also address accessibility for people with disabilities, requiring features such as ramps, accessible entrances, and accessible restrooms.
Permitting Process: The plot plan is a key document in the building permit application process. Local authorities use the plot plan to verify that the proposed construction complies with zoning regulations and building codes. The permitting process typically involves submitting the plot plan and other construction documents to the local building department for review. The building department may request revisions to the plot plan or other documents before issuing a permit. Obtaining the necessary building permits is essential before commencing construction.
Environmental Regulations: In some cases, environmental regulations may also apply to the project. These regulations may address issues such as stormwater management, erosion control, and the protection of wetlands and endangered species. The plot plan may need to include information about proposed environmental protection measures. Compliance with environmental regulations is crucial for protecting the environment and avoiding costly fines and penalties.
Optimizing Site Orientation and Design Considerations
The orientation of the house on the property and various design considerations play a significant role in creating a comfortable, energy-efficient, and visually appealing living environment. The plot plan serves as a valuable tool for analyzing these factors and making informed decisions about the house's placement and design.
Solar Orientation: The orientation of the house relative to the sun can significantly impact its energy efficiency and comfort. In general, orienting the long axis of the house along an east-west axis allows for optimal solar gain in the winter and minimizes solar heat gain in the summer. Utilizing passive solar design principles, such as strategic placement of windows and overhangs, can further enhance energy efficiency. The plot plan can be used to analyze the sun's path throughout the year and determine the optimal orientation for the house.
Wind Patterns: Analyzing prevailing wind patterns is crucial for designing a house that is comfortable and energy-efficient. Properly placed windows and ventilation systems can take advantage of natural breezes to cool the house in the summer. Windbreaks, such as trees and shrubs, can be used to protect the house from strong winds in the winter. The plot plan can be used to analyze prevailing wind patterns and design the house to optimize natural ventilation and minimize exposure to harsh weather.
Views and Privacy: The orientation of the house should also consider the views from the property and the need for privacy. Maximizing desirable views, such as mountain vistas or waterfronts, can enhance the enjoyment of the living space. Strategically placing windows and outdoor spaces can create a sense of connection to the surrounding environment. At the same time, it’s important to consider privacy from neighboring properties and public areas. Landscaping, fencing, and the placement of the house itself can be used to create a sense of privacy and seclusion.
Accessibility and Circulation: The plot plan should address accessibility and circulation both inside and outside the house. This includes providing accessible entrances, ramps, and walkways for people with disabilities. The plan should also consider the flow of traffic within the house and the ease of moving between different areas. An efficient and well-planned circulation pattern can enhance the functionality and livability of the house.
Outdoor Living Spaces: The plot plan should incorporate outdoor living spaces, such as decks, patios, and gardens. These spaces can extend the living area of the house and provide opportunities for recreation and relaxation. The design of outdoor living spaces should consider factors such as sun exposure, privacy, and access to utilities. Integrating outdoor living spaces into the overall design of the house can create a seamless transition between the indoor and outdoor environments.
The process of designing a dream home necessitates a comprehensive and well-executed plot plan. This crucial document is not merely a technical drawing but a roadmap for the entire project, ensuring regulatory compliance, optimizing site usage, and creating a harmonious living environment. By carefully considering the key components of a plot plan, navigating zoning regulations and building codes, and optimizing site orientation and design considerations, homeowners can transform their vision into a tangible reality.
How To Design A House From Sketch Reality
Free House Design Home And Plans
How To Draw A Floor Plan Live Home 3d
Stylish And Simple Inexpensive House Plans To Build Houseplans Blog Com
Where You Can House Plans Live Home 3d
How To Design A House From Sketch Reality
How To Design A House From Sketch Reality
How To Draw Blueprints For A House With Pictures Wikihow
Low Budget Simple House Design Plans For Builders Blog Builderhouseplans Com
Create And Visualize House Plans In Minutes Roomsketcher
Related Posts