Design Basics House Plans, often referred to as blueprint, is a detailed document that outlines the architectural design of a house, including its layout, dimensions, and materials. They serve as a crucial guide for builders and contractors during the construction process, ensuring the proper execution of the intended design.
These plans typically include floor plans, elevation drawings, cross-sections, and other technical specifications. By studying a Design Basics House Plan, professionals can visualize the final structure, plan its construction sequence, and estimate material requirements.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the various components of Design Basics House Plans, exploring their significance and providing practical guidance on how to read and interpret these essential documents.
Design Basics House Plans are essential guides for builders and contractors, providing a comprehensive overview of the architectural design of a house. Here are 9 important points to consider:
- Floor Plans
- Elevation Drawings
- Cross-Sections
- Dimensions
- Materials
- Construction Sequence
- Material Requirements
- Building Codes
- Energy Efficiency
These components work together to provide a clear and detailed blueprint for the construction of a house, ensuring its structural integrity, functionality, and aesthetic appeal.
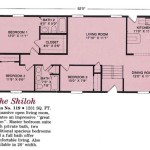
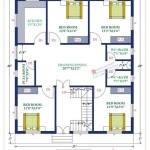
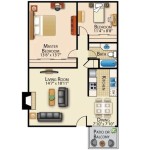
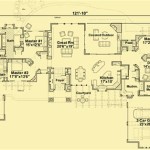
Floor Plans
Floor plans are one of the most important components of Design Basics House Plans. They provide a detailed layout of each floor of the house, showing the arrangement of rooms, walls, doors, and windows. Floor plans are essential for:
- Visualizing the flow and functionality of the house
- Determining the placement of furniture and fixtures
- Calculating the square footage of each room
Floor plans typically include the following information:
- The overall dimensions of the house
- The location of all exterior and interior walls
- The location of all doors and windows
- The location of all plumbing fixtures (sinks, toilets, showers, etc.)
- The location of all electrical outlets and switches
Floor plans can be drawn to scale or not to scale. Scaled floor plans show the exact dimensions of the house, while not-to-scale floor plans provide a general overview of the layout. Scaled floor plans are more useful for construction purposes, while not-to-scale floor plans are more helpful for visualization and planning.
In addition to the basic information listed above, floor plans may also include additional details, such as:
- The location of built-in furniture (such as cabinets and bookshelves)
- The location of appliances
- The location of fireplaces and chimneys
- The location of stairs and elevators
- The type of flooring and finishes used in each room
Floor plans are essential for communicating the design of a house to builders, contractors, and other professionals involved in the construction process. They are also helpful for homeowners who are planning renovations or additions to their homes.
Elevation Drawings
Elevation drawings are another important component of Design Basics House Plans. They show the exterior of the house from different sides, providing a clear understanding of its overall shape and appearance. Elevation drawings are essential for:
- Visualizing the overall massing and proportions of the house
- Determining the placement of windows and doors
- Selecting exterior finishes and materials
Elevation drawings typically include the following information:
- The overall height and width of the house
- The location of all exterior walls, windows, and doors
- The type of roofing material used
- The location of any decks, patios, or porches
Elevation drawings can be drawn to scale or not to scale. Scaled elevation drawings show the exact dimensions of the house, while not-to-scale elevation drawings provide a general overview of the exterior appearance. Scaled elevation drawings are more useful for construction purposes, while not-to-scale elevation drawings are more helpful for visualization and planning.
In addition to the basic information listed above, elevation drawings may also include additional details, such as:
- The location of chimneys and other exterior features
- The type of siding and trim used
- The color scheme of the house
- The landscaping around the house
Elevation drawings are essential for communicating the design of a house to builders, contractors, and other professionals involved in the construction process. They are also helpful for homeowners who are planning renovations or additions to their homes.
Here are some additional details about elevation drawings:
- Elevation drawings are typically drawn from the front, back, and sides of the house. However, they can also be drawn from other angles, such as the roof or the interior of the house.
- Elevation drawings can be used to create 3D models of the house. This can be helpful for visualizing the house from different perspectives and for making design decisions.
- Elevation drawings are often used in conjunction with floor plans to create a complete set of construction documents.
Cross-Sections
Cross-sections are another important component of Design Basics House Plans. They show a vertical slice through the house, revealing the interior structure and layout. Cross-sections are essential for:
- Understanding the structural system of the house
- Determining the placement of mechanical systems (such as HVAC and plumbing)
- Visualizing the relationship between different floors of the house
Cross-sections typically include the following information:
- The overall height of the house
- The location of all exterior and interior walls
- The location of all floors and ceilings
- The location of all windows and doors
- The location of all mechanical systems
Cross-sections can be drawn to scale or not to scale. Scaled cross-sections show the exact dimensions of the house, while not-to-scale cross-sections provide a general overview of the interior structure. Scaled cross-sections are more useful for construction purposes, while not-to-scale cross-sections are more helpful for visualization and planning.
In addition to the basic information listed above, cross-sections may also include additional details, such as:
- The type of framing used
- The location of insulation and other building materials
- The location of electrical wiring and plumbing pipes
- The location of built-in furniture (such as cabinets and bookshelves)
Cross-sections are essential for communicating the design of a house to builders, contractors, and other professionals involved in the construction process. They are also helpful for homeowners who are planning renovations or additions to their homes.
Here are some additional details about cross-sections:
- Cross-sections are typically drawn through the most important parts of the house, such as the living room, kitchen, and bedrooms.
- Cross-sections can be used to create 3D models of the house. This can be helpful for visualizing the house from different perspectives and for making design decisions.
- Cross-sections are often used in conjunction with floor plans and elevation drawings to create a complete set of construction documents.
Dimensions
Dimensions are one of the most important aspects of Design Basics House Plans. They provide the exact measurements of the house, ensuring that all of the components fit together properly and that the house is built to the correct size. Dimensions are essential for:
- Determining the overall size of the house
- Calculating the square footage of the house
- Determining the placement of walls, windows, and doors
- Ordering materials for construction
Dimensions are typically shown on floor plans, elevation drawings, and cross-sections. They are usually given in feet and inches, but they can also be given in meters or other units of measurement. The most important dimensions to include on Design Basics House Plans are:
- The overall length and width of the house
- The height of the house from the ground to the roof
- The thickness of the walls
- The size of the windows and doors
- The distance between the walls, windows, and doors
In addition to the basic dimensions listed above, Design Basics House Plans may also include additional dimensions, such as:
- The height of the ceilings
- The size of the rooms
- The size of the closets and other storage spaces
- The size of the garage and other outbuildings
Dimensions are essential for communicating the design of a house to builders, contractors, and other professionals involved in the construction process. They are also helpful for homeowners who are planning renovations or additions to their homes.
Here are some additional details about dimensions:
- Dimensions should be accurate and consistent throughout the Design Basics House Plans.
- Dimensions should be clearly labeled and easy to read.
- Dimensions should be checked carefully before construction begins to avoid any mistakes.
By providing accurate and detailed dimensions, Design Basics House Plans help to ensure that the house is built to the correct size and that all of the components fit together properly.
Materials
The materials used in the construction of a house have a significant impact on its overall appearance, durability, and energy efficiency. Design Basics House Plans typically specify the materials to be used for the following components:
- Exterior walls
The materials used for exterior walls include wood, brick, stone, stucco, and vinyl siding. Each material has its own advantages and disadvantages, so it is important to choose the right material for the climate and style of the house. - Roofing
The materials used for roofing include asphalt shingles, metal roofing, tile roofing, and wood shakes. Asphalt shingles are the most common type of roofing material, but metal roofing is becoming increasingly popular due to its durability and energy efficiency. - Windows and doors
The materials used for windows and doors include wood, vinyl, aluminum, and fiberglass. Wood windows and doors are the most traditional, but vinyl windows and doors are becoming increasingly popular due to their low maintenance and energy efficiency. - Flooring
The materials used for flooring include hardwood, carpet, tile, and laminate. Hardwood flooring is the most popular type of flooring, but carpet is a good choice for bedrooms and other areas where comfort is important. Tile is a good choice for kitchens and bathrooms, and laminate is a good choice for high-traffic areas.
In addition to the materials listed above, Design Basics House Plans may also specify the materials to be used for other components, such as:
- Framing
- Insulation
- Siding
- Trim
- Hardware
By specifying the materials to be used in the construction of the house, Design Basics House Plans help to ensure that the house is built to the correct specifications and that the materials are compatible with each other.
Construction Sequence
The construction sequence is a detailed plan that outlines the order in which the various tasks involved in building a house must be completed. It is an essential part of Design Basics House Plans, as it helps to ensure that the house is built safely and efficiently.
The construction sequence typically includes the following steps:
- Site preparation
This step involves clearing the land, excavating the foundation, and pouring the foundation. - Framing
This step involves erecting the frame of the house, which includes the walls, floors, and roof. - Exterior finishes
This step involves installing the siding, roofing, and windows. - Interior finishes
This step involves installing the drywall, flooring, and cabinetry. - Mechanical systems
This step involves installing the heating, cooling, plumbing, and electrical systems. - Final touches
This step involves painting the house, installing the appliances, and landscaping the yard.
The construction sequence may vary depending on the size and complexity of the house. However, the general steps listed above are typically followed for most houses.
By following the construction sequence, builders can ensure that the house is built in a safe and efficient manner. It also helps to avoid delays and cost overruns.
Here are some additional details about the construction sequence:
- The construction sequence should be developed by a qualified architect or engineer.
- The construction sequence should be reviewed and approved by the building department before construction begins.
- The construction sequence should be updated as necessary during the construction process.
By following these guidelines, builders can help to ensure that the house is built to the correct specifications and that the construction process is completed safely and efficiently.
Material Requirements
Material requirements are a detailed list of all the materials that are needed to build a house. This includes the quantity, size, and type of materials, as well as the cost of each item. Material requirements are an essential part of Design Basics House Plans, as they help to ensure that the house is built to the correct specifications and that the materials are available when needed.
- Lumber
Lumber is the most common material used in the construction of houses. It is used for framing, sheathing, roofing, and other purposes. The type of lumber used will depend on the climate and the style of the house. For example, pressure-treated lumber is often used for decks and other outdoor structures, while hardwood lumber is often used for flooring and cabinetry.
- Concrete
Concrete is another common material used in the construction of houses. It is used for foundations, slabs, and other structural elements. The type of concrete used will depend on the strength and durability requirements of the structure.
- Masonry
Masonry is a general term for building materials that are made from stone, brick, or concrete blocks. Masonry is often used for exterior walls, chimneys, and other structural elements. The type of masonry used will depend on the climate and the style of the house.
- Insulation
Insulation is a material that is used to reduce heat loss and gain in a house. Insulation is typically installed in the walls, ceiling, and attic. The type of insulation used will depend on the climate and the energy efficiency requirements of the house.
In addition to the materials listed above, Design Basics House Plans may also include material requirements for other items, such as:
- Windows and doors
- Hardware
- Fixtures
- Appliances
- Landscaping materials
By providing a detailed list of material requirements, Design Basics House Plans help to ensure that the house is built to the correct specifications and that all of the necessary materials are available when needed.
Building Codes
Building codes are a set of regulations that govern the construction of buildings. They are in place to ensure that buildings are safe and habitable, and to protect the public from health and safety hazards.
Building codes are typically developed and enforced by local governments. However, some states and countries have their own building codes. Building codes may vary from place to place, but they all share the same basic goal: to ensure that buildings are safe and habitable.
Design Basics House Plans must comply with all applicable building codes. This means that the plans must be designed in accordance with the building code requirements for the location where the house will be built.
Building codes typically address the following areas:
- Structural safety
This includes requirements for the design and construction of the building’s structural elements, such as the foundation, walls, and roof. - Fire safety
This includes requirements for the installation of smoke detectors and fire sprinklers, as well as the use of fire-resistant materials. - Electrical safety
This includes requirements for the installation and maintenance of electrical systems. - Plumbing safety
This includes requirements for the installation and maintenance of plumbing systems. - Energy efficiency
This includes requirements for the use of energy-efficient building materials and appliances.
By complying with building codes, Design Basics House Plans help to ensure that the house is safe and habitable, and that it meets the minimum standards for health and safety.
Here are some additional details about building codes:
- Building codes are typically updated on a regular basis to reflect changes in technology and construction practices.
- Building codes are enforced by building inspectors. Building inspectors review plans and inspect buildings to ensure that they comply with the building code.
- Failure to comply with building codes can result in fines or other penalties.
By following building codes, builders can help to ensure that the house is safe and habitable, and that it meets the minimum standards for health and safety.
Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is an important consideration in the design of any house. By incorporating energy-efficient features into the design, homeowners can save money on their energy bills and reduce their environmental impact.
Energy Basics House Plans include elements that can enhance the energy efficiency of the homes, such as:
- Proper Insulation
Insulation is one of the most important factors in determining the energy efficiency of a house. Insulation helps to keep the house warm in the winter and cool in the summer by preventing heat from escaping or entering the house. Design Basics House Plans should specify the type and thickness of insulation to be used in the walls, ceiling, and attic.
- Energy-Efficient Windows and Doors
Windows and doors are another important factor in determining the energy efficiency of a house. Heat can easily escape through windows and doors that are not properly insulated. Design Basics House Plans should specify the type of windows and doors to be used, as well as the type of glazing to be used in the windows.
- Energy-Efficient Appliances
Appliances can also contribute to the energy consumption of a house. Design Basics House Plans should specify the energy efficiency rating of the appliances to be used in the house. ENERGY STAR appliances are the most energy-efficient appliances on the market.
- Renewable Energy Sources
Renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and geothermal heat pumps, can be used to reduce the energy consumption of a house. Design Basics House Plans should consider the potential for incorporating renewable energy sources into the design of the house.
By incorporating these energy-efficient features into the design, homeowners can save money on their energy bills and reduce their environmental impact.










Related Posts