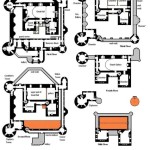
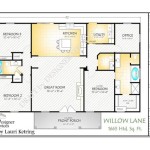
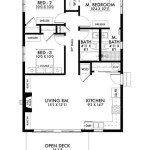
Designing a house floor plan involves creating a blueprint that outlines the layout and arrangement of rooms, spaces, and other features within a home. It’s a crucial step in the home construction process, as it determines the functionality, livability, and overall aesthetic of the dwelling.
Floor plans serve as a guide for architects, builders, and contractors, ensuring that the construction process aligns with the intended design. They specify the dimensions, placement, and interconnections of various rooms, including bedrooms, bathrooms, kitchens, living rooms, and hallways. Floor plans also include details such as window and door locations, electrical and plumbing fixtures, and any special features or amenities.
The design of a house floor plan requires careful consideration of factors such as the occupants’ needs and preferences, the available space, budget constraints, and building codes. It’s essential to strike a balance between functionality, aesthetics, and efficient use of space to create a harmonious and livable home.
When designing a house floor plan, consider these eight important points:
- Functionality
- Flow and circulation
- Natural light and ventilation
- Privacy
- Space utilization
- Building codes
- Personal preferences
- Budget
By carefully considering these factors, you can create a floor plan that meets your needs and creates a comfortable and livable home.
Functionality
Functionality is a crucial aspect of designing a house floor plan. It refers to the efficiency and practicality of the layout, ensuring that the home meets the needs and requirements of its occupants.
To achieve functionality, consider the following factors:
- Traffic flow: The floor plan should allow for smooth and efficient movement throughout the home. Avoid creating bottlenecks or awkward transitions between rooms.
- Room adjacencies: The placement of rooms should make sense in terms of their function and relationship to each other. For example, the kitchen should be adjacent to the dining room, and bedrooms should be near bathrooms.
- Furniture placement: Consider how furniture will be arranged in each room. Ensure there is ample space for essential pieces and that the layout allows for comfortable movement.
- Storage: Plan for adequate storage throughout the home, including closets, pantries, and built-in shelving. This helps keep the house organized and clutter-free.
- Accessibility: If the home will be occupied by individuals with disabilities, consider accessibility features such as wide doorways, ramps, and grab bars.
By prioritizing functionality, you can create a floor plan that is not only aesthetically pleasing but also highly livable and convenient for everyday use.
Flow and circulation
Flow and circulation refer to the seamless movement and transition between spaces within a house. A well-designed floor plan ensures that occupants can move around the home comfortably and efficiently, without encountering obstacles or bottlenecks.
To achieve good flow and circulation, consider the following:
- Traffic patterns: Observe and analyze how people will naturally move through the home. Create a floor plan that accommodates these patterns and minimizes unnecessary steps or detours.
- Room connections: Pay attention to how rooms connect to each other. Avoid creating dead-end spaces or awkward transitions. Instead, aim for a layout that allows for smooth flow between different areas of the home.
- Door placement: The placement of doors can significantly impact flow and circulation. Position doors strategically to avoid creating obstacles or blocking traffic.
- Hallways and corridors: Hallways and corridors should be wide enough to allow for comfortable movement, even when carrying items. Avoid narrow or cramped passageways.
By carefully considering flow and circulation, you can create a floor plan that is not only visually appealing but also highly functional and easy to navigate.
In addition to the points mentioned above, here are some specific design strategies to improve flow and circulation:
- Use open floor plans: Open floor plans eliminate walls and partitions between certain areas, creating a more spacious and interconnected living space.
- Incorporate hallways with multiple access points: Avoid long, narrow hallways that only lead to a single room. Instead, create hallways with multiple entry and exit points, allowing for more flexibility and movement.
- Utilize pocket doors: Pocket doors slide into the wall when opened, saving space and creating a more seamless transition between rooms.
- Consider circular or loop layouts: Circular or loop layouts allow for continuous movement throughout the home, reducing the need for backtracking or dead-ends.
By implementing these strategies, you can optimize flow and circulation within your house floor plan, creating a home that is both comfortable and enjoyable to live in.
Natural light and ventilation
Natural light and ventilation are essential elements of a healthy and comfortable home. A well-designed floor plan takes advantage of natural light to create a bright and inviting atmosphere, while also incorporating strategies to promote proper ventilation and air circulation.
- Maximize window placement: Position windows strategically to allow ample natural light to penetrate the home. Consider the orientation of the house and the path of the sun to ensure that rooms receive sunlight throughout the day.
- Utilize skylights and solar tubes: Skylights and solar tubes can bring natural light into areas of the home that lack windows, such as hallways, bathrooms, and closets.
- Incorporate cross-ventilation: Cross-ventilation occurs when air can flow freely through a space from one side to the other. Design the floor plan to include windows and doors on opposite sides of rooms to promote natural ventilation and reduce reliance on artificial lighting and air conditioning.
- Consider passive solar design: Passive solar design techniques can help regulate the temperature of the home by memanfaatkan natural heat from the sun. For example, incorporating south-facing windows and thermal mass materials can help absorb and store heat during the day and release it at night.
By incorporating these strategies into the floor plan, you can create a home that is not only energy-efficient but also provides a healthy and comfortable living environment.
Privacy
Privacy is an important consideration when designing a house floor plan. It refers to the ability of occupants to maintain their personal space and control who has access to different areas of the home.
To achieve privacy, consider the following factors:
- Separate public and private areas: The floor plan should clearly define public areas, such as the living room and dining room, and private areas, such as bedrooms and bathrooms. Public areas should be easily accessible to guests, while private areas should be secluded and offer a sense of retreat.
- Create buffer zones: Buffer zones, such as hallways, foyers, or mudrooms, can help to create a transition between public and private spaces. They provide a sense of privacy and prevent direct access to sensitive areas of the home.
- Consider room placement: The placement of rooms can impact privacy. For example, situating the master bedroom away from the main entrance and other high-traffic areas can provide a greater sense of seclusion.
- Utilize privacy screens and dividers: Privacy screens and dividers can be used to create temporary or semi-permanent barriers between different areas of the home. This can be particularly useful in open floor plans or shared spaces.
By incorporating these strategies into the floor plan, you can create a home that provides a balance between privacy and accessibility, ensuring that occupants feel comfortable and secure within their own space.
Space utilization
Space utilization refers to the efficient and effective use of the available space within a house. A well-designed floor plan maximizes space utilization to create a home that is both functional and comfortable.
- Minimize wasted space: Wasted space refers to areas that are not used or utilized effectively. When designing the floor plan, pay attention to how each room and space is being used and eliminate any unnecessary or underutilized areas.
- Utilize multi-purpose spaces: Multi-purpose spaces can serve multiple functions, maximizing the use of available space. For example, a guest room can also be used as a home office or a playroom.
- Consider built-in storage: Built-in storage, such as closets, shelves, and drawers, can help to keep the home organized and clutter-free. By incorporating storage solutions into the floor plan, you can maximize space utilization and reduce the need for bulky furniture or freestanding storage units.
- Use vertical space: Vertical space is often overlooked when designing a floor plan. By utilizing vertical space through the use of loft areas, built-in shelves, and mezzanines, you can create additional storage and living space without increasing the footprint of the home.
By incorporating these strategies into the floor plan, you can optimize space utilization and create a home that is both spacious and functional.
Building codes
Building codes are a set of regulations that govern the design, construction, and alteration of buildings. They are established to ensure the safety, health, and welfare of building occupants and the general public. When designing a house floor plan, it is essential to comply with applicable building codes to ensure that the home meets the minimum standards for safety and habitability.
- Structural integrity: Building codes specify requirements for the structural integrity of a home, including the foundation, framing, and roofing. These requirements are designed to ensure that the home can withstand various loads and forces, such as wind, snow, and earthquakes.
- Fire safety: Building codes also include provisions for fire safety, such as the use of fire-resistant materials, the installation of smoke detectors and fire sprinklers, and the provision of adequate means of escape in case of a fire.
- Accessibility: Building codes often include accessibility requirements to ensure that homes are accessible to individuals with disabilities. These requirements may include the provision of ramps, elevators, and accessible bathrooms.
- Energy efficiency: Building codes may also include energy efficiency requirements, such as insulation standards and the use of energy-efficient appliances and lighting. These requirements are designed to reduce the energy consumption of the home and lower utility costs.
By complying with building codes, you can ensure that your house floor plan meets the minimum standards for safety, health, and welfare. It is important to consult with local building officials to obtain the specific building codes that apply to your area.
Personal preferences
Personal preferences play a significant role in designing a house floor plan that meets the unique needs and desires of the occupants. Here are some key considerations:
- Lifestyle: Consider your lifestyle and how you use your home. Do you entertain frequently? Do you need a home office or dedicated space for hobbies? Understanding your lifestyle will help you determine the types of spaces and amenities you need in your home.
- Family composition: The size and composition of your family will impact the design of your house floor plan. Consider the number of bedrooms and bathrooms needed, as well as the need for dedicated spaces for children, guests, or elderly family members.
- Personal style: Your personal style and preferences should be reflected in the design of your home. Choose a floor plan that complements your taste and creates a space that feels like your own. Consider factors such as the overall aesthetic, color scheme, and choice of materials.
- Future needs: Think about your future needs and how your home may need to adapt over time. Consider the potential for expanding your family, changing your lifestyle, or accommodating aging-in-place needs.
By carefully considering your personal preferences, you can create a house floor plan that not only meets your current needs but also provides a comfortable and enjoyable living space for years to come.
Budget
Budget is a crucial factor to consider when designing a house floor plan. The cost of building a home can vary significantly depending on the size, complexity, and materials used. Here are some key considerations related to budget:
Determine your budget: Before you start designing your floor plan, it is essential to determine your budget. This will help you make informed decisions about the size, features, and materials used in your home.
Prioritize your needs: Once you have a budget, prioritize your needs and wants. Determine which features are most important to you and allocate your budget accordingly. For example, you may choose to prioritize a larger living space over a formal dining room.
Choose cost-effective materials: The materials you choose for your home will have a significant impact on the overall cost. Consider using cost-effective materials, such as vinyl flooring instead of hardwood, or laminate countertops instead of granite, to save money without sacrificing style or functionality.
Design a compact and efficient floor plan: A compact and efficient floor plan can help you save money on construction costs. Avoid unnecessary square footage and design a layout that minimizes wasted space. Consider using multi-purpose spaces and built-in storage solutions to maximize space utilization.
By carefully considering your budget and implementing these strategies, you can design a house floor plan that meets your needs and financial constraints.









Related Posts