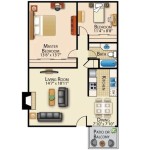
Concrete House Plans are detailed blueprints that outline the structural design and construction process of a concrete home. These plans provide essential instructions for the placement, reinforcement, and pouring of concrete, ensuring the stability and durability of the structure. For instance, a concrete house plan might specify the dimensions and spacing of concrete walls, the type and quantity of reinforcing steel, and the design of concrete footings and slabs.
Creating a concrete house plan requires meticulous consideration of factors such as the local climate, soil conditions, and building codes. Architects and engineers collaborate to develop plans that meet these criteria while optimizing the home’s energy efficiency, aesthetics, and functionality. Concrete House Plans serve as a crucial foundation for the construction phase, guiding contractors and builders in executing the design and ensuring the structural integrity of the home.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the key elements of Concrete House Plans, exploring the benefits, considerations, and best practices involved in their creation and implementation.
Here are eight important points about Concrete House Plans:
- Detailed structural blueprints
- Outline construction process
- Ensure stability and durability
- Consider local climate and soil
- Meet building codes
- Optimize energy efficiency
- Guide contractors and builders
- Foundation for construction phase
Concrete House Plans are essential for the successful construction of concrete homes, providing a roadmap for the entire process and ensuring the structural integrity of the final product.
Detailed structural blueprints
Concrete House Plans serve as detailed structural blueprints that outline every aspect of the concrete home’s construction, providing a comprehensive guide for architects, engineers, contractors, and builders. These plans include precise specifications for the placement, reinforcement, and pouring of concrete, ensuring the structural integrity and durability of the home.
The structural blueprints encompass the following key elements:
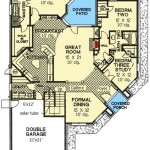
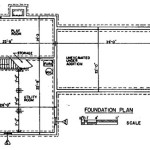
- Foundation plan: Outlines the design and dimensions of the concrete footings, slabs, and walls that will support the entire structure. It specifies the type of concrete mix, reinforcement requirements, and any special considerations for soil conditions or seismic activity.
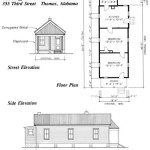
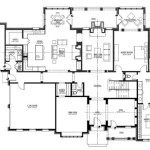
- Floor plans: Provide a detailed layout of each floor, including the location and dimensions of walls, windows, doors, and other structural elements. These plans also indicate the type and thickness of concrete slabs for each floor level.
- Roof plan: Specifies the design and construction of the roof structure, including the type of concrete (e.g., reinforced concrete, precast concrete), the slope and drainage system, and any special features such as skylights or solar panels.
- Elevation drawings: Offer multiple views of the home’s exterior, showcasing the overall shape, height, and architectural details. These drawings help visualize the home’s appearance and ensure that it meets aesthetic and functional requirements.
- Cross-sections: Provide detailed views of the home’s interior, displaying the relationship between different structural elements and the flow of space. They illustrate the thickness and arrangement of walls, floors, and roof components.
By providing such detailed structural blueprints, Concrete House Plans serve as a critical tool for ensuring the safety, stability, and durability of concrete homes.
Outline construction process
Concrete House Plans not only provide detailed structural blueprints but also outline the step-by-step construction process, ensuring a smooth and efficient build. The plans guide contractors and builders through each phase, from site preparation to the final finishes.
- Site preparation: This phase involves preparing the building site by clearing vegetation, leveling the ground, and establishing drainage systems. Concrete House Plans specify the excavation requirements for the foundation and any necessary soil amendments to ensure a stable base for the structure.
- Foundation construction: The foundation is the backbone of any concrete home, and Concrete House Plans provide precise instructions for its construction. This includes the layout and dimensions of footings, slabs, and walls, as well as the placement and reinforcement of concrete.
- Framing and walls: Once the foundation is complete, the framing and walls begin to take shape. Concrete House Plans outline the placement of concrete walls, the installation of windows and doors, and any structural reinforcements required to meet building codes and withstand environmental loads.
- Roof construction: The roof protects the home from the elements, and Concrete House Plans specify the design and materials to be used. This includes the type of concrete (e.g., reinforced concrete, precast concrete), the slope and drainage system, and the installation of roofing materials.
Concrete House Plans are essential for coordinating the various stages of construction, ensuring that each step is executed correctly and according to the overall design intent.
Ensure stability and durability
Concrete House Plans prioritize the stability and durability of the structure, ensuring a safe and long-lasting home for occupants. Several key factors contribute to the exceptional stability and durability of concrete homes:
- Structural integrity: Concrete is renowned for its strength and resilience, providing a robust framework for the entire home. Concrete House Plans carefully calculate the dimensions, reinforcement, and placement of concrete elements to withstand various loads, including dead loads (e.g., the weight of the structure), live loads (e.g., furniture and occupants), and environmental loads (e.g., wind, snow, earthquakes). By adhering to these plans, the structural integrity of the home is maintained, ensuring its ability to endure external forces and remain stable over time.
- Fire resistance: Concrete is a naturally fire-resistant material, offering superior protection against the spread of flames and heat. Concrete House Plans incorporate fire safety measures, such as specifying fire-rated concrete mixes and detailing fire-resistant construction techniques. This inherent fire resistance enhances the safety of the home’s occupants and minimizes the risk of structural damage in the event of a fire.
- Weather resistance: Concrete’s durability extends to its resistance against weathering elements. Concrete House Plans account for local climate conditions and specify concrete mixes and treatments that can withstand extreme temperatures, moisture, and UV radiation. This ensures that the home’s exterior remains intact, protecting the interior from the elements and maintaining its aesthetic appeal.
- Pest resistance: Concrete is not susceptible to damage from pests, such as termites or insects, making it an ideal choice for areas prone to these infestations. Concrete House Plans consider pest resistance by specifying concrete mixes and detailing construction methods that prevent pests from entering or nesting within the structure, ensuring the home’s longevity and integrity.
By incorporating these factors into the design, Concrete House Plans provide a solid foundation for stable and durable concrete homes that can withstand the test of time.
Consider local climate and soil
When designing a concrete house, it is crucial to consider the local climate and soil conditions. These factors can significantly impact the structural design, material selection, and construction techniques employed in the Concrete House Plans.
Local climate
The local climate plays a vital role in determining the specific requirements for a concrete house. Factors such as temperature fluctuations, precipitation levels, and wind loads must be taken into account to ensure the home’s durability and energy efficiency.
- Temperature fluctuations: Extreme temperature variations can cause concrete to expand and contract, leading to cracks and structural damage. Concrete House Plans must specify concrete mixes and reinforcement strategies that can withstand these temperature changes without compromising the integrity of the structure.
- Precipitation levels: High rainfall or snowfall can increase the moisture content in the soil, affecting the stability of the foundation. Concrete House Plans should include measures to prevent water accumulation and ensure proper drainage around the home.
- Wind loads: Strong winds can exert significant pressure on a building’s exterior. Concrete House Plans must incorporate structural reinforcements and design features to resist wind loads and prevent damage to the roof, walls, and windows.
Soil conditions
The soil conditions at the building site can also impact the design of a concrete house. Factors such as soil type, bearing capacity, and drainage characteristics must be carefully assessed to ensure a stable foundation and prevent structural issues.
- Soil type: Different soil types have varying load-bearing capacities. Concrete House Plans must specify foundation designs that are appropriate for the soil conditions at the building site, ensuring the foundation can adequately support the weight of the structure.
- Bearing capacity: The bearing capacity of the soil determines the amount of weight it can support without settling or collapsing. Concrete House Plans must ensure that the foundation design distributes the load of the structure evenly across the soil, preventing excessive settlement and structural damage.
- Drainage characteristics: Poor drainage can lead to water accumulation around the foundation, weakening the soil and compromising the stability of the structure. Concrete House Plans should include drainage systems to effectively channel water away from the foundation, preventing moisture-related issues.
By carefully considering the local climate and soil conditions, Concrete House Plans can be tailored to meet the specific requirements of the building site, ensuring the durability, stability, and energy efficiency of the concrete home.
Meet building codes
Concrete House Plans must adhere to the established building codes and regulations set forth by local authorities. These codes ensure that buildings are constructed safely and meet minimum standards for structural integrity, energy efficiency, and accessibility.
- Structural safety: Building codes specify requirements for the design and construction of concrete structures to withstand various loads and forces, including dead loads (the weight of the structure), live loads (occupants and furniture), and environmental loads (wind, snow, earthquakes). Concrete House Plans must comply with these structural safety codes to ensure the stability and integrity of the home.
- Fire safety: Building codes also include fire safety regulations to minimize the risk of fire and protect occupants in the event of a fire. Concrete House Plans must incorporate fire-resistant materials and construction methods that meet these codes, such as specifying fire-rated concrete mixes and detailing fire-resistant assemblies for walls, floors, and roofs.
- Energy efficiency: Many building codes now include energy efficiency requirements to reduce the environmental impact of buildings and lower energy costs for occupants. Concrete House Plans must consider energy-efficient design strategies, such as incorporating insulation, using energy-efficient appliances and lighting, and designing for passive solar heat gain, to meet these codes.
- Accessibility: Building codes often include accessibility requirements to ensure that buildings are accessible to individuals with disabilities. Concrete House Plans must incorporate design features that comply with these codes, such as providing ramps or elevators for wheelchair access, widening doorways, and installing accessible fixtures and amenities.
By adhering to building codes, Concrete House Plans ensure that the resulting concrete home is safe, structurally sound, energy-efficient, and accessible, meeting the minimum standards established by local authorities.
Optimize energy efficiency
Concrete House Plans can significantly contribute to optimizing energy efficiency, reducing energy consumption, and minimizing the environmental impact of the home. Several key strategies are employed to achieve energy efficiency in concrete homes:
Insulation: Concrete has a relatively low thermal resistance compared to other building materials. However, Concrete House Plans can specify the incorporation of insulation materials into the walls, roof, and floor assemblies to improve the home’s thermal performance. Insulation materials, such as fiberglass, cellulose, or spray foam, create a barrier that reduces heat transfer, keeping the home cooler in summer and warmer in winter.
Thermal mass: Concrete has a high thermal mass, meaning it can absorb and store heat energy. Concrete House Plans can utilize this property to design homes that take advantage of passive solar heating. By orienting the home to maximize sunlight exposure and incorporating large concrete walls and floors, the home can absorb heat during the day and release it slowly at night, reducing the need for artificial heating.
Airtightness: Air leakage can account for significant energy loss in a home. Concrete House Plans can specify construction techniques and materials that minimize air leakage, such as sealing gaps around windows and doors, using weatherstripping and caulking, and installing a continuous air barrier around the home’s envelope. By reducing air leakage, the home’s heating and cooling systems can operate more efficiently.
Energy-efficient appliances and lighting: Concrete House Plans can also include specifications for energy-efficient appliances and lighting systems. By incorporating ENERGY STAR-rated appliances, LED lighting, and smart home technologies that optimize energy usage, the home’s overall energy consumption can be further reduced.
By implementing these energy-efficiency strategies, Concrete House Plans can create homes that are more comfortable, sustainable, and cost-effective to operate, reducing the environmental impact and providing long-term savings for homeowners.
Guide contractors and builders
Concrete House Plans serve as essential guides for contractors and builders throughout the construction process, providing detailed instructions and specifications to ensure the accurate and efficient execution of the design.
- Foundation construction: Concrete House Plans provide precise guidance for the construction of the foundation, which is the critical base of the concrete home. The plans specify the dimensions, reinforcement requirements, and concrete mix design for the footings, slabs, and walls, ensuring a stable and durable foundation that can withstand the weight of the structure and various environmental loads.
- Structural framework: The plans outline the layout and reinforcement details for the concrete structural framework, including walls, columns, beams, and slabs. These elements work together to provide the home’s structural integrity and stability, resisting forces such as gravity, wind, and seismic activity. Concrete House Plans ensure that the structural framework is designed and constructed according to code requirements and industry best practices.
- Exterior finishes: Concrete House Plans specify the materials and techniques for the exterior finishes, such as concrete siding, stucco, or stone veneer. These finishes not only enhance the aesthetic appeal of the home but also provide protection against the elements and contribute to the overall durability of the structure.
- Interior layout and MEP systems: The plans include detailed layouts for the interior spaces, including room dimensions, window and door placements, and the integration of mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) systems. Contractors and builders use these plans to coordinate the installation of electrical wiring, plumbing pipes, HVAC systems, and other essential utilities, ensuring a functional and comfortable living environment.
By providing comprehensive guidance and technical specifications, Concrete House Plans enable contractors and builders to execute the construction process efficiently and accurately, resulting in a concrete home that meets the design intent, building codes, and the expectations of the homeowners.
Foundation for construction phase
Concrete House Plans serve as the foundation for the construction phase of a concrete home, providing a comprehensive roadmap for contractors and builders to follow. The plans outline every aspect of the foundation’s design and construction, ensuring a stable and durable base for the entire structure.
- Precise dimensions and reinforcement details:
Concrete House Plans specify the exact dimensions of the foundation, including the depth and width of footings, the thickness of slabs, and the height of walls. Additionally, the plans provide detailed reinforcement requirements, indicating the type, size, and spacing of steel reinforcing bars or mesh to ensure the foundation’s structural integrity.
- Concrete mix design and quality control:
The plans stipulate the specific concrete mix design to be used for the foundation, taking into account factors such as the strength requirements, exposure to environmental conditions, and local building codes. The plans may also include quality control measures to ensure that the concrete mix meets the specified strength and durability requirements before it is poured.
- Excavation and site preparation:
Concrete House Plans provide guidance on the excavation and site preparation required for the foundation. This includes the depth of excavation, the removal of existing structures or vegetation, and the establishment of proper drainage systems to prevent water accumulation around the foundation.
- Inspection and documentation:
The plans emphasize the importance of regular inspections during the foundation construction phase to ensure that the work is carried out according to the plans and specifications. The plans may also require documentation of inspections and tests to verify the quality and integrity of the foundation.
By providing a comprehensive foundation for the construction phase, Concrete House Plans empower contractors and builders to construct a solid and reliable foundation for the concrete home, setting the stage for a structurally sound and durable building.










Related Posts