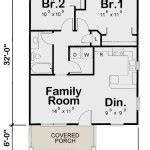
Colonial House Floor Plans are blueprints or diagrams that outline the layout, room arrangement, and dimensions of houses built during the colonial era. These plans serve as a historical record of the architectural styles and living arrangements that were prevalent during that time.
During the colonial period, houses were typically designed with a central chimney and a rectangular or square footprint. The first floor usually consisted of a large living room, a kitchen, and a dining room. The second floor featured bedrooms and storage spaces. Social status also played a role in floor plan design, with more elaborate and spacious homes being built for the wealthy.
In the following sections, we will explore various aspects of Colonial House Floor Plans, including their regional variations, the influence of architectural styles, and their significance in understanding the history of colonial architecture.
Colonial House Floor Plans offer valuable insights into the architectural styles and living arrangements of the colonial era. Here are eight important points to consider:
- Central chimney
- Rectangular or square footprint
- Large living room
- Kitchen and dining room on first floor
- Bedrooms and storage on second floor
- Regional variations
- Influence of architectural styles
- Historical significance
Understanding these points helps us appreciate the diversity and evolution of colonial architecture.
Central chimney
The central chimney was a defining feature of Colonial House Floor Plans. It served several important functions:
- Structural support: The central chimney provided structural support to the house, helping to hold up the roof and walls.
- Heat distribution: The chimney acted as a natural heating system, distributing heat from the fireplace throughout the house.
- Smoke and ventilation: The chimney allowed smoke from the fireplace to escape, and it also helped to ventilate the house.
- Cooking and food preservation: The fireplace was often used for cooking, and the chimney provided a convenient place to hang food for smoking and preservation.
The central chimney was a versatile and essential element of Colonial House Floor Plans, playing a crucial role in the structure, heating, ventilation, and daily life of colonial homes.
Rectangular or square footprint
Colonial House Floor Plans typically featured a rectangular or square footprint. This shape was favored for several reasons:
- Structural stability: Rectangular and square shapes are inherently more stable than other shapes, making them well-suited for load-bearing structures.
- Efficient use of space: Rectangular and square footprints allow for efficient use of space, maximizing the amount of livable area within the house.
- Ease of construction: Rectangular and square houses are relatively easy to build, using simple framing techniques that were commonly available during the colonial period.
- Symmetry and aesthetics: Rectangular and square shapes were considered aesthetically pleasing and symmetrical, which was a desirable quality in colonial architecture.
While rectangular and square footprints were the most common, some colonial houses also featured more complex shapes, such as L-shaped or T-shaped footprints. These variations were often used to accommodate specific site conditions or to create more interesting and visually appealing designs.
The rectangular or square footprint was a fundamental characteristic of Colonial House Floor Plans, influencing the overall layout, room arrangement, and structural integrity of these historic homes.
Large living room
The large living room was a prominent feature of Colonial House Floor Plans. It served as the central gathering space for the family and was often used for a variety of activities, including:
- Family gatherings: The living room was a place for family members to spend time together, engage in conversation, and share meals.
- Entertaining guests: The living room was also used to entertain guests, providing a comfortable and welcoming space for social gatherings.
- Formal occasions: The living room was often used for formal occasions, such as weddings, funerals, and religious services.
- Everyday activities: In addition to these special occasions, the living room was also used for everyday activities, such as reading, writing, and playing games.
The large living room was typically located at the front of the house, facing the street. This placement gave it a prominent position within the home and allowed for ample natural light to enter the space. The room was often the largest room in the house, and it was often used to make a statement about the family’s status and wealth.
Kitchen and dining room on first floor
In Colonial House Floor Plans, the kitchen and dining room were typically located on the first floor. This arrangement had several advantages:
- Convenience: Having the kitchen and dining room on the first floor made it easy for families to prepare and serve meals. It also allowed for easy access to the outdoors, making it convenient to bring in food and supplies.
- Heat efficiency: The kitchen was often the warmest room in the house due to the heat generated by the fireplace and cooking activities. By locating the dining room adjacent to the kitchen, families could take advantage of this warmth during meals.
- Socialization: The close proximity of the kitchen and dining room encouraged socialization and interaction between family members and guests. While meals were being prepared, family members could gather in the kitchen to or chat, and after meals, they could linger in the dining room for conversation and relaxation.
- Multi-purpose space: The dining room could also be used for other purposes, such as entertaining guests, holding meetings, or engaging in crafts and other activities. This flexibility made the dining room a valuable and versatile space within the home.
The location of the kitchen and dining room on the first floor was a practical and efficient arrangement that met the needs of colonial families. It facilitated convenience, heat efficiency, socialization, and multi-purpose use of space.
Bedrooms and storage on second floor
Colonial House Floor Plans typically featured bedrooms and storage spaces on the second floor. This arrangement had several advantages:
- Privacy: The second floor provided a more private space for bedrooms, away from the hustle and bustle of the first floor. This was especially important for families with older children or guests who needed a quiet and secluded space to sleep.
- Warmth: The second floor was typically warmer than the first floor, as heat rises from the lower levels of the house. This made the second floor an ideal location for bedrooms, ensuring a comfortable sleeping environment.
- Storage: The second floor also provided ample space for storage. Attics and other storage areas could be used to store seasonal items, extra bedding, and other belongings that were not needed on a regular basis.
- Multi-purpose space: In some cases, the second floor could also be used for other purposes, such as a playroom, a study, or a guest room. This flexibility made the second floor a valuable and versatile space within the home.
The location of bedrooms and storage spaces on the second floor was a practical and efficient arrangement that met the needs of colonial families. It provided privacy, warmth, storage, and multi-purpose use of space.
Regional variations
Colonial House Floor Plans exhibited regional variations due to factors such as climate, available building materials, and cultural influences. These variations can be seen in the size, shape, and layout of colonial homes across different regions of the American colonies.
- New England: Colonial houses in New England were typically compact and rectangular, with a central chimney and a steeply pitched roof to shed snow. They often featured a large living room, a kitchen, and a dining room on the first floor, with bedrooms and storage spaces on the second floor.
- Mid-Atlantic: Colonial houses in the Mid-Atlantic region were often larger and more elaborate than those in New England. They typically featured a central hall with rooms on either side, and they often had two or more stories. The use of brick and stone was more common in the Mid-Atlantic region, giving the houses a more substantial appearance.
- South: Colonial houses in the South were designed to accommodate the warmer climate. They were typically larger and more open, with wide porches and balconies. The use of wood was more common in the South, and the houses often featured unique architectural details, such as intricate moldings and carved woodwork.
- West: Colonial houses in the West were influenced by a variety of architectural styles, including Spanish, French, and Native American. They were often built using adobe or logs, and they typically featured a large central room with a fireplace and a sleeping loft.
These regional variations in Colonial House Floor Plans reflect the diverse cultural and environmental conditions that existed in the American colonies. They provide valuable insights into the lives and lifestyles of the people who lived in these homes.
Influence of architectural styles
Colonial House Floor Plans were influenced by a variety of architectural styles, including English, French, Spanish, and Dutch. These styles were brought to the American colonies by European settlers, and they were adapted to suit the local climate and building materials. The resultingof styles created a unique and distinctive American colonial architecture.
One of the most influential architectural styles was the English style. English settlers brought with them the traditional English house plan, which featured a central chimney, a rectangular footprint, and a symmetrical facade. This style was widely adopted in the New England colonies, and it can still be seen in many colonial homes today.
Another influential style was the French style. French settlers introduced the concept of the open-plan house, which featured a large central room that served as a living room, dining room, and kitchen. This style was popular in the Mississippi River Valley and the Great Lakes region. French colonial homes often had steep roofs and dormer windows, and they were often built using logs or stone.
Spanish and Dutch architectural styles also had an influence on Colonial House Floor Plans. Spanish settlers introduced the use of courtyards and patios, while Dutch settlers introduced the gambrel roof. These elements can be seen in many colonial homes in the Southwest and Mid-Atlantic regions respectively.
The influence of architectural styles on Colonial House Floor Plans is evident in the diversity of designs found in colonial homes across the United States. These homes reflect the cultural and historical influences that shaped the American colonies, and they continue to be admired for their beauty and functionality today.
Historical significance
Colonial House Floor Plans provide valuable insights into the lives and lifestyles of the people who lived in the American colonies. They offer a glimpse into the social, economic, and cultural factors that shaped the development of American architecture.
One of the most important aspects of Colonial House Floor Plans is their reflection of the social hierarchy of the time. Larger and more elaborate homes were typically owned by wealthy landowners and merchants, while smaller and more modest homes were occupied by farmers, artisans, and laborers. The size and layout of a home could also indicate the family’s status within the community.
Colonial House Floor Plans also reveal the importance of family life in colonial society. Homes were typically designed to accommodate large families, with multiple bedrooms and common areas. The central chimney was a focal point of the home, providing a gathering place for family members to cook, eat, and socialize.
Finally, Colonial House Floor Plans provide valuable information about the technological and economic conditions of the time. The use of local materials and construction techniques reflects the availability of resources and the level of craftsmanship in each region. The presence of certain features, such as indoor plumbing or fireplaces, can also indicate the wealth and status of the family.
In conclusion, Colonial House Floor Plans are an invaluable resource for understanding the history and culture of the American colonies. They offer insights into the lives of the people who lived in these homes, the social and economic factors that shaped their design, and the technological and economic conditions of the time. By studying these floor plans, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the rich architectural heritage of the United States.










Related Posts