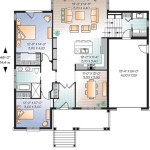
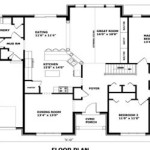
Building plans for a tiny house are a set of detailed instructions that guide the construction of a small, typically under 400 square feet, dwelling. These plans include specifications for the foundation, framing, electrical, plumbing, and other aspects of the house. By following these plans, individuals can build their own tiny house, saving on construction costs compared to traditional methods.
Tiny houses have gained popularity in recent years due to their affordability, sustainability, and mobility. They offer a simplified lifestyle, reducing energy consumption and waste. Whether you’re looking to downsize, embrace a more environmentally friendly living space, or embark on a nomadic adventure, building plans for a tiny house provide a comprehensive guide for creating your dream home.
Building plans for a tiny house are essential for ensuring a safe and successful construction process. Here are 10 important points to consider:
- Accurate dimensions
- Structural integrity
- Electrical and plumbing systems
- Window and door placement
- Material specifications
- Foundation and framing details
- Roofing and siding options
- Interior layout options
- Code compliance
- Permit requirements
By carefully considering these points, you can ensure that your tiny house is well-designed, durable, and meets all necessary building codes and safety standards.
Accurate dimensions
Accurate dimensions are crucial for ensuring that your tiny house is structurally sound and meets building codes. The plans should specify the exact measurements for every aspect of the house, including the foundation, framing, walls, roof, and windows and doors. This ensures that all the components fit together properly and that the house is safe and habitable.
- Foundation: The foundation is the base of the house and must be able to support the weight of the structure. The plans should specify the type of foundation (e.g., concrete slab, piers, etc.), its dimensions, and the depth at which it should be installed.
- Framing: The framing is the skeleton of the house and provides structural support. The plans should specify the size and spacing of the framing members (e.g., studs, joists, rafters, etc.) and how they should be connected.
- Walls: The walls enclose the house and protect it from the elements. The plans should specify the materials to be used for the walls (e.g., wood, metal, etc.), their thickness, and how they should be assembled.
- Roof: The roof protects the house from the elements and provides structural support. The plans should specify the type of roof (e.g., gable, hip, etc.), its pitch, and the materials to be used for the roofing.
By following the plans carefully and ensuring that all dimensions are accurate, you can build a tiny house that is safe, durable, and meets all building codes.
Structural integrity
Structural integrity refers to the ability of a building to withstand external forces and maintain its structural stability. In the context of tiny houses, ensuring structural integrity is crucial for the safety and durability of the dwelling.
Building plans for a tiny house should include detailed specifications for structural elements such as the foundation, framing, and roof. These elements work together to distribute loads and resist forces that may act on the house, such as wind, snow, and earthquakes.
The foundation is the base of the house and must be designed to support the weight of the structure and transfer loads to the ground. Common foundation types for tiny houses include concrete slabs, piers, and helical piles. The plans should specify the dimensions, materials, and reinforcement requirements for the foundation.
The framing is the skeleton of the house and provides structural support for the walls, roof, and other components. The plans should specify the size, spacing, and connection details for the framing members, such as studs, joists, and rafters. The type of framing used will depend on the size and design of the tiny house.
Electrical and plumbing systems
Electrical and plumbing systems are essential for the functionality and comfort of a tiny house. Building plans should include detailed specifications for these systems, ensuring they are designed and installed safely and efficiently.
- Electrical system: The electrical system provides power to the house and includes components such as wiring, outlets, switches, and a main electrical panel. The plans should specify the type and size of wiring to be used, the location of electrical outlets and switches, and the amperage and voltage requirements for the house. They should also include details on any special electrical features, such as solar panels or backup generators.
- Plumbing system: The plumbing system manages the water supply and drainage for the house and includes components such as pipes, fixtures, and a water heater. The plans should specify the type and size of pipes to be used, the location of plumbing fixtures, and the capacity and type of water heater required. They should also include details on any special plumbing features, such as rainwater harvesting systems or composting toilets.
By carefully considering the electrical and plumbing systems in the building plans, you can ensure that your tiny house has a safe, reliable, and efficient infrastructure.
Window and door placement
Window and door placement is a crucial aspect of tiny house design, affecting both functionality and aesthetics. Building plans should carefully consider the location, size, and type of windows and doors to optimize natural light, ventilation, and space utilization.
Natural light: Windows are the primary source of natural light in a tiny house. The plans should specify the size and placement of windows to maximize natural light and create a bright and inviting interior. Consider the orientation of the house to take advantage of sunlight during different times of the day.
Ventilation: Windows and doors also play a vital role in ventilation. Cross-ventilation, achieved by placing windows on opposite walls, allows air to flow through the house, reducing moisture and improving air quality. The plans should include windows and doors that can be opened to promote airflow.
Space utilization: The placement of windows and doors can impact the layout and space utilization within the tiny house. Sliding doors or bifold doors can save space compared to traditional hinged doors. Windows placed high on walls can allow for furniture or storage below.
Material specifications
Material specifications in building plans for a tiny house define the types and quality of materials to be used in its construction. Choosing the right materials is crucial for durability, energy efficiency, and the overall aesthetics of the house.
- Foundation:
The foundation is the base of the house and must be able to support its weight and withstand the forces of the ground. Common materials used for tiny house foundations include concrete, steel piers, and helical piles. The plans should specify the type of foundation, its dimensions, and the materials to be used.
- Framing:
The framing is the skeleton of the house and provides structural support. Common materials used for tiny house framing include wood, steel, and aluminum. The plans should specify the type of framing, the size and spacing of the framing members, and the materials to be used.
- Walls:
The walls enclose the house and protect it from the elements. Common materials used for tiny house walls include wood, metal, and insulated panels. The plans should specify the type of wall construction, the materials to be used, and the thickness of the walls.
- Roof:
The roof protects the house from the elements and provides structural support. Common materials used for tiny house roofs include metal, shingles, and TPO roofing. The plans should specify the type of roof, the materials to be used, and the pitch of the roof.
By carefully specifying the material specifications in the building plans, you can ensure that your tiny house is constructed using high-quality materials that meet your specific needs and requirements.
Foundation and framing details
Foundation
The foundation of a tiny house is crucial for its structural integrity and durability. The type of foundation chosen depends on factors such as the soil conditions, climate, and size of the house. Common foundation options for tiny houses include:
- Concrete slab: A concrete slab is a solid, poured-in-place foundation that provides a stable base for the house. It is suitable for a variety of soil conditions and is relatively easy to construct.
- Pier foundation: A pier foundation consists of concrete piers that support the house above the ground. This type of foundation is often used in areas with uneven or sloping terrain, as it allows for the house to be leveled.
- Helical piles: Helical piles are steel piles that are screwed into the ground. They are a good option for soft or unstable soil conditions, as they can provide a secure foundation without the need for excavation.
Framing
The framing of a tiny house provides structural support and defines the shape of the house. Common framing materials include wood, steel, and aluminum. Wood framing is the most popular choice for tiny houses, as it is relatively inexpensive and easy to work with. Steel framing is more durable and fire-resistant, but it is also more expensive. Aluminum framing is lightweight and corrosion-resistant, making it a good option for tiny houses that will be moved frequently.
The type of framing used will depend on the size and design of the tiny house. Common framing techniques include:
- Platform framing: Platform framing is a common method used in tiny house construction. In this technique, the floor, walls, and roof are built separately and then assembled on the foundation.
- Stick framing: Stick framing is a traditional framing method where the walls are built directly on the foundation and the roof is then framed on top of the walls.
- Panelized framing: Panelized framing involves building the walls and roof in panels off-site and then assembling them on the foundation. This method is often used for tiny houses that are built in a factory setting.
By carefully considering the foundation and framing details in the building plans, you can ensure that your tiny house is structurally sound and able to withstand the elements.
Roofing and siding options
The choice of roofing and siding materials for a tiny house is an important consideration that affects both the aesthetics and functionality of the house. Roofing materials protect the house from the elements, while siding materials protect the walls and provide insulation.
- Metal roofing:
Metal roofing is a popular choice for tiny houses due to its durability, longevity, and fire resistance. It is available in a variety of colors and styles, and can be installed over an existing roof or on new construction. Metal roofing is relatively expensive compared to other options, but it can last for 50 years or more with proper maintenance.
- Asphalt shingles:
Asphalt shingles are a more affordable option than metal roofing, and they are available in a wide range of colors and styles. However, asphalt shingles are not as durable as metal roofing, and they may need to be replaced after 15-20 years. Asphalt shingles are also more susceptible to damage from wind and hail.
- TPO roofing:
TPO roofing is a type of single-ply roofing membrane that is made from thermoplastic polyolefin. It is a lightweight and durable material that is resistant to UV rays and chemicals. TPO roofing is also relatively inexpensive, making it a good option for budget-conscious tiny house builders.
- Wood siding:
Wood siding is a classic choice for tiny houses, and it can give the house a warm and inviting look. However, wood siding requires regular maintenance to protect it from the elements, and it is susceptible to rot and insects. Wood siding is also more expensive than other siding options.
- Vinyl siding:
Vinyl siding is a low-maintenance option that is available in a variety of colors and styles. It is also fade-resistant and moisture-resistant. However, vinyl siding is not as durable as wood siding, and it can be damaged by hail or strong winds.
- Fiber cement siding:
Fiber cement siding is a durable and fire-resistant option that is made from a mixture of cement, sand, and cellulose fibers. It is available in a variety of textures and colors, and it can be painted or stained to match the style of the house. Fiber cement siding is more expensive than vinyl siding, but it is also more durable and requires less maintenance.
Interior layout options
Open floor plans
Open floor plans are a popular choice for tiny houses as they make the space feel larger and more inviting. In an open floor plan, the kitchen, living room, and dining room are all combined into one large space. This allows for a more flexible use of space and makes it easier to move around the house.
Sleeping lofts
Sleeping lofts are a great way to create more space in a tiny house. A sleeping loft is a raised platform that is used for sleeping. It can be accessed by a ladder or stairs. Sleeping lofts are often used in tiny houses with high ceilings, as they allow for a full-size bed without taking up too much floor space.
Multi-purpose spaces
Multi-purpose spaces are another great way to save space in a tiny house. A multi-purpose space is a room that can be used for multiple purposes. For example, a living room can also be used as a dining room or a bedroom. Multi-purpose spaces are a great way to make the most of the space you have.
Storage solutions
Storage is always a challenge in a tiny house, so it is important to plan for it carefully. There are a number of different storage solutions that can be used in a tiny house, such as built-in shelves, under-bed storage, and vertical storage. By carefully planning your storage, you can make sure that you have a place for everything.
The interior layout of your tiny house will depend on your specific needs and preferences. By carefully considering your options, you can create a tiny house that is both functional and stylish.
Code compliance
Building codes are regulations that govern the construction of buildings. These codes are in place to ensure that buildings are safe and habitable. Tiny houses must comply with the same building codes as traditional houses. This means that the plans for your tiny house must be reviewed and approved by the local building department before you can begin construction.
- Structural integrity:
The building code requires that tiny houses be structurally sound and able to withstand the forces of nature, such as wind, snow, and earthquakes. The plans for your tiny house must include details on the foundation, framing, and roof to show that the house will be able to withstand these forces.
- Fire safety:
The building code requires that tiny houses be fire-resistant. This means that the materials used in the construction of the house must be non-flammable or fire-resistant. The plans for your tiny house must include details on the materials that will be used and how they will be installed to ensure fire safety.
- Electrical safety:
The building code requires that tiny houses have safe electrical systems. This means that the electrical wiring and fixtures must be installed in a way that prevents electrical fires and shocks. The plans for your tiny house must include details on the electrical system to show that it will be safe.
- Plumbing safety:
The building code requires that tiny houses have safe plumbing systems. This means that the plumbing fixtures and pipes must be installed in a way that prevents leaks and contamination. The plans for your tiny house must include details on the plumbing system to show that it will be safe.
By ensuring that your tiny house complies with the building code, you can be sure that it is safe and habitable. You can also avoid any problems with the local building department when you are ready to build your tiny house.
Permit requirements
Once you have obtained building plans for your tiny house, you will need to apply for a building permit from your local building department. The building permit process ensures that your tiny house will be built in accordance with the building code and that it is safe and habitable.
- Submittal of plans:
The first step in the building permit process is to submit your building plans to the local building department. The building department will review your plans to ensure that they comply with the building code. They will also check to make sure that your tiny house is properly designed and that it will be able to withstand the forces of nature.
- Plan review:
Once your plans have been submitted, the building department will review them to ensure that they meet the requirements of the building code. The building department may also require you to make changes to your plans before they can be approved. The plan review process can take several weeks or even months, so it is important to start the process early.
- Issuance of permit:
Once your plans have been approved, the building department will issue you a building permit. The building permit will allow you to begin construction on your tiny house. The building permit will also include a set of conditions that you must follow during construction.
- Inspections:
During construction, the building department will conduct inspections to ensure that your tiny house is being built in accordance with the building code and the conditions of your building permit. The building department will typically conduct inspections at the following stages of construction: foundation, framing, electrical, plumbing, and final.
Once your tiny house is complete, you will need to obtain a certificate of occupancy from the building department. The certificate of occupancy certifies that your tiny house is safe and habitable and that it complies with the building code.



![The Top 8 Tiny House Floor Plans [2020 Choosing Guide] Tiny Living Life](https://i2.wp.com/inylivinglife.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/pad-tiny.jpg)






Related Posts