Architectural design house plans are detailed blueprints that provide a visual representation of a house’s design and layout. They serve as a crucial guide for architects and builders, enabling them to effectively plan and construct a structure that meets the specific requirements and preferences of clients. For instance, in the design of a custom-built home, architectural designs house plans outline the placement of rooms, windows, doors, and other structural elements, ensuring that the final product accurately reflects the homeowner’s vision.
House plans play a vital role in the architectural design process, as they facilitate effective communication between architects, clients, and construction teams. By providing a comprehensive overview of the proposed structure, house plans enable all parties involved to gain a clear understanding of the project’s scope and requirements. This promotes efficient decision-making, reduces the risk of errors, and ultimately contributes to a successful building project.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the various aspects of architectural designs house plans, exploring their key components, industry standards, and the process of creating and using them in real-world construction projects.
Architectural designs house plans serve as the blueprint for a successful building project, providing a detailed visual representation of the structure’s design and layout. Here are 9 important points to consider:
- Define Scope and Requirements: Outline the project’s goals, space needs, and design preferences.
- Site Analysis: Study the building site’s topography, orientation, and environmental factors.
- Floor Plan Layout: Determine the placement and size of rooms, windows, and doors.
- Exterior Design: Choose the architectural style, materials, and finishes for the exterior.
- Structural Design: Specify the materials and methods used to construct the foundation, walls, and roof.
- Mechanical Systems: Plan for heating, ventilation, air conditioning, plumbing, and electrical systems.
- Building Codes and Regulations: Ensure compliance with local building codes and zoning requirements.
- Sustainability Features: Incorporate energy-efficient materials, appliances, and design elements.
- Cost Estimation: Determine the approximate construction costs based on the house plan.
By addressing these key points, architectural designs house plans provide a comprehensive roadmap for architects, builders, and homeowners to create a functional, aesthetically pleasing, and sustainable structure.
Define Scope and Requirements: Outline the project’s goals, space needs, and design preferences.
Defining the scope and requirements of an architectural design house plan is a crucial step that lays the foundation for a successful building project. It involves clearly outlining the project’s objectives, identifying the specific space needs, and establishing the desired design preferences. This process ensures that the house plan aligns with the client’s vision and meets their functional and aesthetic requirements.
Project Goals: The first step in defining the scope of a project is to establish its primary goals. This may include factors such as the intended use of the building (e.g., residential, commercial, institutional), the desired size and scale of the structure, and any specific functional requirements (e.g., accessibility features, energy efficiency).
Space Needs: Once the project goals are defined, the next step is to determine the specific space needs of the building. This involves identifying the number and types of rooms required, as well as their approximate sizes and configurations. It is important to consider both the current and future space requirements of the occupants to ensure the house plan accommodates their needs over time.
Design Preferences: The final aspect of defining the scope and requirements of a house plan is to establish the desired design preferences. This includes factors such as the architectural style of the building, the choice of materials and finishes, and any specific aesthetic elements that the client wishes to incorporate. By considering the client’s design preferences, the architect can create a house plan that reflects their personal taste and creates a visually appealing and comfortable living environment.
By clearly defining the scope and requirements of an architectural design house plan, architects and clients can establish a shared understanding of the project’s objectives and ensure that the final design meets the client’s specific needs and preferences.
Site Analysis: Study the building site’s topography, orientation, and environmental factors.
Site analysis is a critical step in the architectural design process that involves studying the building site’s topography, orientation, and environmental factors to inform the design of the house. By understanding the unique characteristics of the site, architects can create a house plan that is responsive to its surroundings and takes advantage of its natural features.
- Topography: The topography of the site refers to its physical features, such as its slope, elevation, and soil conditions. Understanding the topography is essential for determining the best location and orientation of the house, as well as for planning site drainage and landscaping.
- Orientation: The orientation of the site refers to its position relative to the sun and prevailing winds. By considering the orientation, architects can design a house that takes advantage of natural light and ventilation, reducing energy consumption and creating a more comfortable living environment.
- Environmental Factors: Environmental factors include the presence of trees, water bodies, and other natural features on the site. These factors can impact the design of the house in terms of its placement, landscaping, and the choice of materials and finishes.
- Zoning Regulations: In addition to natural site factors, architects must also consider local zoning regulations, which may restrict the size, height, and placement of buildings on the site. Understanding zoning regulations is essential for ensuring that the house plan complies with local laws and regulations.
By conducting a thorough site analysis, architects can gain a comprehensive understanding of the building site and make informed decisions about the design of the house. This results in a house plan that is well-suited to its surroundings, maximizes the potential of the site, and meets the specific needs and preferences of the client.
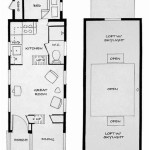
Floor Plan Layout: Determine the placement and size of rooms, windows, and doors.
The floor plan layout is a crucial aspect of architectural design house plans, as it determines the placement and size of rooms, windows, and doors within the structure. This layout has a significant impact on the functionality, flow, and overall aesthetic of the house.
Room Placement: The first step in creating a floor plan layout is to determine the placement of the different rooms within the house. This involves considering factors such as the number of occupants, the desired level of privacy, and the functional relationships between different spaces (e.g., the proximity of the kitchen to the dining room). By carefully planning the room placement, architects can create a layout that optimizes space utilization, promotes efficient movement, and fosters a comfortable and inviting living environment.
Room Size: Once the room placement has been determined, the next step is to determine the size of each room. This involves considering factors such as the intended use of the space, the number of occupants, and the desired level of comfort. The room size should be large enough to accommodate the necessary furniture and activities without feeling cramped or cluttered. Architects use space planning techniques to ensure that each room is appropriately sized and well-proportioned.
Window and Door Placement: The placement of windows and doors is another important aspect of the floor plan layout. Windows provide natural light and ventilation, while doors facilitate movement between different spaces. Architects carefully consider factors such as the orientation of the site, the desired views, and the privacy requirements when determining the placement of windows and doors. By optimizing the placement of these elements, they can create a layout that maximizes natural daylight, promotes cross-ventilation, and ensures a seamless flow of movement throughout the house.
Exterior Design: Choose the architectural style, materials, and finishes for the exterior.
The exterior design of a house is a crucial aspect of architectural design house plans, as it determines the overall look, feel, and curb appeal of the structure. Architects carefully consider the architectural style, materials, and finishes used on the exterior to create a cohesive and visually appealing design that reflects the client’s preferences and the surrounding environment.
Architectural Style
The architectural style of a house refers to its overall design aesthetic and historical influences. There are numerous architectural styles to choose from, each with its own unique characteristics and details. Some popular architectural styles include:- **Traditional:** Traditional styles, such as Colonial, Victorian, and Craftsman, are characterized by their timeless appeal and familiar design elements. They often feature symmetrical facades, pitched roofs, and decorative details.- **Modern:** Modern styles, such as Contemporary, Mid-Century Modern, and Bauhaus, emphasize clean lines, geometric shapes, and open floor plans. They often use materials such as glass, steel, and concrete.- **Transitional:** Transitional styles blend elements from both traditional and modern styles, creating a timeless and versatile look. They often feature classic architectural details combined with contemporary materials and finishes.
Materials
The materials used on the exterior of a house play a significant role in its durability, energy efficiency, and overall appearance. Common exterior materials include:- **Wood:** Wood is a classic and versatile material that can be used for siding, trim, and other exterior elements. It is available in a variety of species and finishes, allowing for a wide range of design options.- **Brick:** Brick is a durable and fire-resistant material that is often used for exterior walls. It is available in a variety of colors and textures, and can be laid in different patterns to create unique designs.- **Stone:** Stone is a natural material that adds a touch of elegance and sophistication to a house. It is available in a variety of types and finishes, and can be used for siding, veneer, or accents.
Finishes
The finishes used on the exterior of a house complete the overall design and add the final touches to its appearance. Common exterior finishes include:- **Paint:** Paint is a versatile and cost-effective way to add color and style to a house. It is available in a wide range of colors and finishes, and can be used to create a variety of effects.- **Staining:** Staining is a process that enhances the natural grain and color of wood. It is often used on siding, trim, and other wood elements to protect them from the elements and add a touch of warmth.- **Stucco:** Stucco is a durable and low-maintenance exterior finish that is often used in warm climates. It is available in a variety of colors and textures, and can be applied to create smooth or textured surfaces.By carefully considering the architectural style, materials, and finishes used on the exterior, architects can create house plans that are visually appealing, durable, and energy-efficient, and that meet the specific needs and preferences of their clients.
The exterior design of a house is not only about aesthetics but also about functionality. Architects consider factors such as the climate, local building codes, and the surrounding environment when making design decisions. For example, in areas with extreme weather conditions, they may choose materials that are resistant to wind, rain, and snow. In areas with strict building codes, they must ensure that the design complies with all applicable regulations.
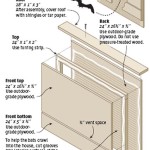
Structural Design: Specify the materials and methods used to construct the foundation, walls, and roof.
Foundation
The foundation of a house is the structural support that transfers the weight of the building to the ground. The type of foundation used depends on factors such as the soil conditions, the size and weight of the house, and local building codes. Common foundation types include:
- Slab-on-grade: A slab-on-grade foundation is a single, continuous piece of concrete that is poured directly on the ground. It is a cost-effective and simple foundation type that is suitable for stable soil conditions.
- Crawl space: A crawl space foundation is a shallow, excavated area beneath the house that allows access to plumbing, electrical, and other utilities. It is a good option for areas with wet or unstable soil conditions.
- Basement: A basement is a fully enclosed underground space that can be used for additional living space, storage, or other purposes. It is a more expensive foundation type, but it can add significant value to a home.
Walls
The walls of a house are the vertical structural elements that enclose the space and provide support for the roof. The materials and methods used to construct the walls depend on factors such as the architectural style of the house, the desired level of energy efficiency, and local building codes. Common wall construction methods include:
- Wood framing: Wood framing is a lightweight and cost-effective method of wall construction. It involves using wooden studs, joists, and sheathing to create the framework of the walls.
- Masonry: Masonry walls are constructed using bricks, stones, or concrete blocks. They are durable and fire-resistant, but they are also more expensive than wood framing.
- Steel framing: Steel framing is a strong and durable method of wall construction. It is often used in commercial buildings, but it can also be used in residential construction.
Roof
The roof of a house is the structural element that protects the building from the elements. The materials and methods used to construct the roof depend on factors such as the climate, the architectural style of the house, and local building codes. Common roof construction methods include:
- Shingles: Shingles are the most common type of roofing material. They are made from a variety of materials, including asphalt, wood, and metal.
- Metal: Metal roofing is durable and long-lasting. It is a good option for areas with extreme weather conditions.
- Tile: Tile roofing is a beautiful and durable option. It is often used in warm climates.
The structural design of a house is a complex and important aspect of architectural design house plans. By carefully considering the materials and methods used to construct the foundation, walls, and roof, architects can create houses that are safe, durable, and energy-efficient.
Mechanical Systems: Plan for heating, ventilation, air conditioning, plumbing, and electrical systems.
Mechanical systems are an essential part of any house, providing comfort, safety, and functionality. Architectural design house plans must carefully consider the design and installation of these systems to ensure that the house meets the needs of the occupants and complies with local building codes.
- Heating: The heating system is responsible for maintaining a comfortable temperature inside the house during cold weather. There are a variety of heating systems available, including forced-air furnaces, boilers, and heat pumps. The choice of heating system depends on factors such as the climate, the size of the house, and the energy efficiency of the building envelope.
- Ventilation: The ventilation system is responsible for providing fresh air to the house and removing stale air. Ventilation is essential for maintaining good indoor air quality and preventing the buildup of moisture and mold. There are two main types of ventilation systems: natural ventilation and mechanical ventilation. Natural ventilation relies on natural forces, such as wind and thermal buoyancy, to circulate air. Mechanical ventilation uses fans to circulate air.
- Air Conditioning: The air conditioning system is responsible for cooling the house during hot weather. Air conditioners work by removing heat from the air inside the house and transferring it to the outside air. There are a variety of air conditioning systems available, including central air conditioners, window units, and portable units. The choice of air conditioning system depends on factors such as the climate, the size of the house, and the energy efficiency of the building envelope.
- Plumbing: The plumbing system is responsible for supplying water to the house and removing wastewater. The plumbing system includes pipes, fixtures, and appliances. The design of the plumbing system must ensure that the house has an adequate supply of clean water and that wastewater is disposed of safely.
- Electrical: The electrical system is responsible for providing electricity to the house. The electrical system includes wiring, outlets, and fixtures. The design of the electrical system must ensure that the house has a safe and reliable supply of electricity.
The design of mechanical systems is a complex and important aspect of architectural design house plans. By carefully considering the factors discussed above, architects can create houses that are comfortable, safe, and energy-efficient.
Building Codes and Regulations: Ensure compliance with local building codes and zoning requirements.
Building codes and zoning regulations are essential aspects of architectural design house plans as they ensure that buildings are safe, habitable, and compliant with local laws. Architects must carefully consider these regulations when designing house plans to avoid costly delays or legal issues during the construction process.
- Building Codes: Building codes are a set of regulations that govern the design, construction, and alteration of buildings. These codes are developed by national and local authorities to ensure that buildings are structurally sound, energy-efficient, and accessible. Building codes cover a wide range of topics, including structural requirements, fire safety, plumbing, electrical systems, and energy efficiency.
- Zoning Regulations: Zoning regulations are a set of regulations that govern the use of land and the types of buildings that can be constructed in specific areas. These regulations are typically established by local governments to ensure orderly development and to protect the character of neighborhoods. Zoning regulations may restrict the height, size, and placement of buildings, as well as the types of activities that can be conducted on a property.
- Compliance Process: To ensure compliance with building codes and zoning regulations, architects must submit their house plans to the local building department for review and approval. The building department will review the plans to verify that they meet all applicable codes and regulations. If the plans are approved, the architect will receive a building permit, which authorizes the construction of the house.
- Consequences of Non-Compliance: Failure to comply with building codes and zoning regulations can have serious consequences. The building department may issue stop-work orders or fines, and in some cases, the building may be deemed unsafe and unfit for occupancy.
By carefully considering building codes and zoning regulations during the design process, architects can help ensure that their house plans are compliant and that the resulting buildings are safe, habitable, and in accordance with local laws.
Sustainability Features: Incorporate energy-efficient materials, appliances, and design elements.
Energy-Efficient Materials
Energy-efficient materials are designed to reduce the amount of energy required to heat, cool, and illuminate a house. These materials include:
- Insulation: Insulation is a material that slows the transfer of heat. It is installed in the walls, roof, and floor of a house to reduce heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer. Insulation can be made from a variety of materials, including fiberglass, cellulose, and spray foam.
- Windows and Doors: Windows and doors are another important source of heat loss and gain. Energy-efficient windows and doors are designed to minimize heat transfer by using double or triple glazing, low-emissivity coatings, and tight seals.
- Building Envelope: The building envelope is the exterior shell of a house. It includes the walls, roof, windows, and doors. A well-designed building envelope will minimize heat loss and gain and improve the energy efficiency of the house.
Energy-Efficient Appliances
Energy-efficient appliances use less energy to perform the same tasks as traditional appliances. Energy-efficient appliances are rated by the Energy Star program. The Energy Star rating system helps consumers identify appliances that are among the most energy-efficient in their class. Energy-efficient appliances can include:
- Refrigerators: Refrigerators are one of the most energy-consuming appliances in a home. Energy-efficient refrigerators use less energy to keep food cold.
- Dishwashers: Dishwashers use energy to heat water and wash dishes. Energy-efficient dishwashers use less energy to perform these tasks.
- Washing Machines: Washing machines use energy to wash and dry clothes. Energy-efficient washing machines use less energy to perform these tasks.
Energy-Efficient Design Elements
Energy-efficient design elements are features of a house that reduce energy consumption. These elements include:
- Passive Solar Design: Passive solar design uses the sun’s energy to heat and cool a house. Passive solar design elements include south-facing windows, thermal mass, and overhangs.
- Daylighting: Daylighting is the use of natural light to illuminate a house. Daylighting can reduce the need for artificial lighting, which can save energy.
- Landscaping: Landscaping can be used to shade a house from the sun in the summer and to provide wind protection in the winter. Landscaping can also be used to create microclimates that can reduce energy consumption.
By incorporating energy-efficient materials, appliances, and design elements into their house plans, architects can create houses that are more sustainable and energy-efficient. This can save homeowners money on their energy bills and reduce their environmental impact.
Cost Estimation: Determine the approximate construction costs based on the house plan.
Cost estimation is a crucial aspect of architectural design house plans as it provides clients with an approximate understanding of the financial implications of their project. By accurately estimating construction costs, architects can help clients make informed decisions about the design, materials, and finishes used in their homes.
The cost of building a house can vary significantly depending on a number of factors, including the size of the house, the complexity of the design, the materials used, and the location of the construction site. To determine the approximate construction costs, architects typically use a combination of methods, including:
- Square Footage Method: This method involves multiplying the square footage of the house by a cost per square foot. The cost per square foot varies depending on the factors mentioned above, but it typically ranges from $100 to $200 per square foot for a basic house.
- Unit Cost Method: This method involves breaking down the house into its individual components, such as the foundation, walls, roof, and finishes. The cost of each component is then estimated separately, and the total cost is calculated by adding up the individual costs.
- Historical Data: Architects may also refer to historical data on construction costs in their area to get a general idea of what the costs might be for a similar project.
Once the architect has estimated the construction costs, they will typically provide the client with a detailed breakdown of the costs, including the cost of materials, labor, and permits. This information can help the client make informed decisions about the project and ensure that it fits within their budget.
It is important to note that cost estimation is not an exact science, and there may be some variation in the actual construction costs. However, by using the methods described above, architects can provide clients with a reasonably accurate estimate of the costs involved in building their dream home.
In addition to the direct construction costs, there are also a number of other costs that clients need to consider when budgeting for a new home. These costs may include:
- Land Acquisition: The cost of the land on which the house will be built.
- Site Preparation: The cost of preparing the land for construction, including clearing the land, grading the site, and installing utilities.
- Permits and Fees: The cost of obtaining building permits and other necessary approvals.
- Contingency Fund: A contingency fund is a reserve of money that is set aside to cover unexpected costs that may arise during construction.
By considering all of these costs, clients can develop a realistic budget for their new home and avoid any financial surprises during the construction process.









Related Posts