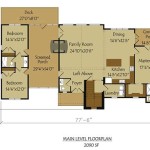
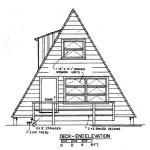
Architectural design for house plans involves the creation of detailed blueprints and specifications that outline the structural elements, spatial layout, and aesthetic features of a residential building. This encompasses the planning, design, and development of the architectural drawings that serve as the foundation for constructing a house.
An architectural design for a house plan can range from basic sketches to highly detailed and comprehensive documents. These plans provide a visual representation of the intended structure, ensuring that all aspects of the building are carefully considered and coordinated. They include floor plans, elevations, sections, and other drawings that allow for accurate construction.
Transition Paragraph:
In the following sections, we will delve into the key considerations, principles, and elements involved in architectural design for house plans. We will explore the various factors that influence the design process, from the client’s needs and budget to the site conditions and building regulations.
Architectural design for house plans involves meticulous planning and execution. Here are nine important points to consider:
- Client needs and preferences
- Site conditions and orientation
- Building codes and regulations
- Sustainable design principles
- Space planning and functionality
- Aesthetics and curb appeal
- Structural integrity and safety
- Construction materials and methods
- Cost considerations and budget
By carefully addressing these factors, architects can create house plans that are not only visually appealing but also functional, safe, and tailored to the specific requirements of the client and site.
Client needs and preferences
Understanding and incorporating the client’s needs and preferences is paramount in architectural design for house plans. The architect works closely with the client to gather detailed information about their lifestyle, family structure, and aspirations for their home. This involves exploring their daily routines, entertaining habits, hobbies, and any specific requirements they may have.
The client’s budget is also a crucial consideration. The architect must balance the client’s desired features and finishes with the financial constraints of the project. Open and honest communication is essential to ensure that the final design aligns with the client’s financial capabilities.
The client’s personal taste and aesthetic preferences play a significant role in shaping the design. The architect presents various design concepts and options, taking into account the client’s preferred architectural styles, color schemes, and material choices. By understanding the client’s vision, the architect can create a house plan that reflects their unique personality and aspirations.
In addition to these primary considerations, the architect also discusses with the client their preferences for specific features and amenities. This may include the number of bedrooms and bathrooms, the layout of the kitchen and living areas, the presence of outdoor spaces such as patios or decks, and any special requirements for accessibility or energy efficiency.
By carefully considering the client’s needs and preferences, the architect can create a house plan that is not only functional and practical but also tailored to their unique lifestyle and aspirations.
Site conditions and orientation
The site conditions and orientation play a crucial role in architectural design for house plans. The architect must carefully consider the physical characteristics of the site, including its size, shape, topography, and vegetation, as well as its orientation relative to the sun and prevailing winds.
The size and shape of the site will determine the overall footprint and layout of the house. The architect must ensure that the house fits comfortably on the site, with adequate space for outdoor areas, driveways, and landscaping. The topography of the site can also impact the design, as it may require special considerations for drainage, retaining walls, or grading.
The orientation of the house relative to the sun and prevailing winds can have a significant impact on its energy efficiency and comfort. The architect should design the house to take advantage of natural light and ventilation, while minimizing heat gain and wind exposure. This can be achieved through the placement of windows, doors, and overhangs, as well as the use of passive solar design principles.
Other site conditions that may need to be considered include soil conditions, the presence of easements or setbacks, and any existing structures or vegetation that may need to be preserved. By carefully considering the site conditions and orientation, the architect can create a house plan that is not only aesthetically pleasing but also functional and responsive to its environment.
Paragraph after details:
In addition to the physical characteristics of the site, the architect must also consider the surrounding context and neighborhood when designing a house plan. This includes the architectural styles of neighboring houses, the presence of any historical or cultural landmarks, and the overall character of the community. The architect should strive to create a design that is compatible with the existing context while also adding something unique and distinctive to the neighborhood.
Building codes and regulations
Building codes and regulations are an essential part of architectural design for house plans. These codes and regulations are established to ensure the safety, structural integrity, and energy efficiency of buildings.
- Zoning codes
Zoning codes regulate the use of land and the placement of buildings within a specific area. These codes determine the allowable building height, setbacks, and lot coverage, among other factors. Zoning codes are intended to promote orderly development and maintain the character of neighborhoods.
- Building codes
Building codes establish minimum standards for the construction of buildings. These codes address structural safety, fire safety, plumbing, electrical systems, and other aspects of building design and construction. Building codes are intended to protect the health and safety of building occupants.
- Energy codes
Energy codes set standards for the energy efficiency of buildings. These codes address factors such as insulation, window glazing, and HVAC systems. Energy codes are intended to reduce energy consumption and promote sustainability.
- Accessibility codes
Accessibility codes ensure that buildings are accessible to people with disabilities. These codes address features such as ramps, elevators, and accessible restrooms. Accessibility codes are intended to provide equal access to buildings for everyone.
Architects must be familiar with the building codes and regulations that apply to their projects. These codes and regulations can vary from one jurisdiction to another, so it is important for architects to stay up-to-date on the latest requirements. By complying with building codes and regulations, architects can ensure that their designs are safe, functional, and sustainable.
Sustainable design principles
Sustainable design principles aim to minimize the environmental impact of buildings while promoting the health and well-being of occupants. These principles are becoming increasingly important in architectural design for house plans, as homeowners become more aware of the need to reduce their carbon footprint and live in a more sustainable manner.
- Energy efficiency
Energy-efficient house plans incorporate features that reduce energy consumption and operating costs. This can be achieved through the use of high-performance insulation, energy-efficient windows and appliances, and renewable energy sources such as solar panels. By reducing energy consumption, homeowners can save money on their utility bills and contribute to a cleaner environment.
- Water conservation
Water conservation is an important aspect of sustainable design. House plans can incorporate water-saving fixtures and appliances, such as low-flow toilets and faucets, and rainwater harvesting systems. By reducing water consumption, homeowners can help to conserve this precious resource and reduce their water bills.
- Material selection
The selection of building materials can have a significant impact on the sustainability of a house plan. Architects can specify materials that are recycled, renewable, or sustainably harvested. They can also use materials that have low embodied energy, which is the energy required to extract, process, and transport the materials to the construction site.
- Indoor environmental quality
Indoor environmental quality refers to the health and comfort of the occupants of a building. Sustainable house plans incorporate features that promote good indoor air quality, such as natural ventilation, low-VOC (volatile organic compound) materials, and moisture control. By creating a healthy indoor environment, homeowners can improve their health and well-being.
By incorporating sustainable design principles into house plans, architects can create homes that are not only beautiful and functional, but also environmentally responsible and healthy for the occupants.
Space planning and functionality
Space planning and functionality are essential considerations in architectural design for house plans. The goal is to create a home that not only meets the aesthetic desires of the client but also provides a comfortable, efficient, and healthy living environment.
- Flow and circulation
The flow and circulation of a house plan should be carefully considered to ensure that the spaces are connected in a logical and efficient manner. The architect should create a layout that allows for easy movement between rooms and avoids any awkward or cramped spaces. This is especially important in high-traffic areas such as the kitchen, entryway, and hallways.
- Room sizes and proportions
The size and proportions of each room should be carefully considered to ensure that they are appropriate for their intended use. The architect should take into account the number of occupants, the type of activities that will take place in the room, and the need for furniture and storage. Rooms should be large enough to be comfortable and functional, but not so large that they feel empty or overwhelming.
- Natural light and ventilation
Natural light and ventilation are essential for a healthy and comfortable living environment. The architect should design the house plan to take advantage of natural light and ventilation, while also providing privacy and security. This can be achieved through the placement of windows, doors, and skylights, as well as the use of passive solar design principles.
- Storage and organization
Adequate storage and organization is essential for a well-functioning home. The architect should incorporate a variety of storage solutions into the house plan, such as closets, cabinets, drawers, and shelves. Storage should be located in convenient locations throughout the house, and it should be designed to meet the specific needs of the occupants.
By carefully considering space planning and functionality, architects can create house plans that are not only beautiful and stylish, but also comfortable, efficient, and healthy for the occupants.
Aesthetics and curb appeal
Aesthetics and curb appeal are important considerations in architectural design for house plans. The goal is to create a home that is not only functional and comfortable, but also visually appealing and inviting. The exterior of the house should be designed to make a positive first impression and to complement the surrounding neighborhood.
- Architectural style
The architectural style of a house is one of the most important factors that determines its curb appeal. The architect should select an architectural style that is appropriate for the client’s taste, the surrounding neighborhood, and the overall character of the house. Popular architectural styles include traditional, contemporary, modern, and farmhouse.
- Exterior materials
The exterior materials used on a house can have a significant impact on its curb appeal. The architect should select materials that are durable, low-maintenance, and aesthetically pleasing. Popular exterior materials include brick, stone, siding, and stucco.
- Color scheme
The color scheme of a house is another important factor that affects its curb appeal. The architect should select a color scheme that is both attractive and appropriate for the architectural style of the house. Popular color schemes include neutral colors, earth tones, and bold accent colors.
- Landscaping
Landscaping can play a major role in enhancing the curb appeal of a house. The architect should work closely with a landscape designer to create a landscape plan that complements the architectural style of the house and provides year-round interest. Landscaping can include trees, shrubs, flowers, and other plantings, as well as hardscaping elements such as patios, walkways, and retaining walls.
By carefully considering aesthetics and curb appeal, architects can create house plans that not only meet the functional needs of the client, but also create a beautiful and inviting home that is a pleasure to live in.
Structural integrity and safety
Structural integrity and safety are paramount in architectural design for house plans. The architect must ensure that the house is designed to withstand the various loads and forces that it will be subjected to, including gravity, wind, snow, and earthquakes. This involves careful consideration of the structural system, the materials used, and the overall design of the house.
The structural system is the framework of the house that provides support and stability. It typically consists of a combination of load-bearing walls, beams, columns, and trusses. The architect must select the appropriate structural system for the size and shape of the house, as well as the local building codes and regulations.
The materials used in the construction of the house also play a role in its structural integrity. The architect must specify materials that are strong, durable, and able to withstand the expected loads. Common materials used in house construction include wood, concrete, steel, and masonry.
The overall design of the house can also impact its structural integrity. For example, a house with a complex roofline or large expanses of glass may require additional structural support. The architect must carefully consider the overall design of the house and ensure that it is structurally sound.
By carefully considering structural integrity and safety, architects can create house plans that are not only beautiful and functional, but also safe and durable.
Construction materials and methods
The choice of construction materials and methods has a significant impact on the overall design, cost, and performance of a house. Architects must carefully consider the available options and select materials and methods that are appropriate for the specific project.
Wood framing is the most common construction method for houses in the United States. Wood is a strong and versatile material that is relatively easy to work with. Wood-framed houses are typically built using a combination of load-bearing walls, beams, and trusses. Wood framing is a relatively inexpensive construction method, and it allows for a great deal of flexibility in design.
Concrete construction is another popular option for houses. Concrete is a strong and durable material that can be used to create a variety of structural elements, including walls, floors, and roofs. Concrete houses are typically more expensive to build than wood-framed houses, but they offer greater durability and fire resistance.
Steel framing is a less common construction method for houses, but it offers several advantages. Steel is a very strong and durable material, and it can be used to create long-span structures with minimal support. Steel-framed houses are typically more expensive to build than wood-framed houses, but they offer greater strength and durability.
Masonry construction is another option for houses. Masonry refers to the use of bricks, stones, or other masonry units to create structural elements. Masonry houses are typically more expensive to build than wood-framed houses, but they offer greater durability and fire resistance.
In addition to the structural materials, architects must also select the materials that will be used for the exterior and interior finishes of the house. These materials include roofing, siding, windows, doors, flooring, and cabinetry. The choice of materials will impact the overall appearance, durability, and maintenance requirements of the house.
Cost considerations and budget
Cost considerations and budget play a crucial role in architectural design for house plans. Architects must carefully consider the costs associated with the design and construction of the house and work within the client’s budget. This involves estimating the costs of materials, labor, permits, and other expenses, and making design decisions that balance cost and quality.
Material costs
The cost of materials is a major factor in the overall cost of a house. Architects must select materials that are appropriate for the design and budget of the house. Less expensive materials, such as vinyl siding and asphalt shingles, can help to reduce costs, while more expensive materials, such as natural stone and cedar shake roofing, can add to the cost of the house.
Labor costs
Labor costs are another significant factor in the cost of a house. The cost of labor will vary depending on the location, the type of construction, and the complexity of the design. Architects must work with contractors to get accurate estimates of labor costs and to ensure that the budget is realistic.
Permit costs
Permits are required for the construction of any new house. The cost of permits will vary depending on the location and the size of the house. Architects must factor the cost of permits into the overall budget for the house.
Once the architect has estimated the costs of materials, labor, and permits, they can work with the client to develop a budget for the house. The budget should include a contingency fund for unexpected expenses. By carefully considering cost considerations and budget, architects can help their clients to build beautiful and functional homes that meet their needs and financial constraints.









Related Posts