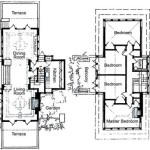
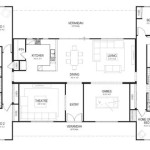
Architect House Plans are detailed blueprints that provide instructions for the construction of a house. These plans encompass every aspect of the building’s design, from the foundation and framing to the electrical and plumbing systems. For instance, an architect house plan for a spacious three-bedroom home may include specifications for a two-car garage, a large kitchen with an island, and a covered patio in the backyard.
Creating architect house plans requires meticulous attention to detail and an in-depth understanding of building codes and construction techniques. Architects meticulously consider factors such as functionality, aesthetics, and energy efficiency to ensure that the final structure meets the specific requirements and desires of the client. These plans serve as a roadmap for contractors, guiding them through every stage of the construction process.
In the following sections of this article, we will delve deeper into the essential elements of architect house plans, exploring their components, benefits, and the role they play in the successful execution of residential construction projects.
Architect house plans encompass a multitude of important elements that contribute to the successful construction of a house. Here are eight crucial points to consider:
- Detailed Blueprints
- Structural Integrity
- Electrical and Plumbing Systems
- Functionality and Layout
- Aesthetics and Design
- Energy Efficiency
- Compliance with Codes
- Contractor’s Guide
These elements work in conjunction to ensure that the house meets the specific requirements and desires of the client, while adhering to building codes and construction standards.
Detailed Blueprints
Detailed blueprints form the cornerstone of architect house plans. They provide precise visual representations of every aspect of the building’s design, from the overall layout to the smallest details.
- Floor Plans:
Floor plans depict the layout of each level of the house, including the placement of rooms, walls, windows, and doors. They specify the dimensions and relationships between different spaces, ensuring a functional and efficient flow.
- Elevations:
Elevations are two-dimensional drawings that show the exterior walls of the house from different sides. They illustrate the height, shape, and architectural features of the building, providing a clear understanding of its overall appearance.
- Sections:
Sections are vertical slices through the house that reveal the interior and layout. They show the relationship between different levels, the placement of stairs, and the heights of ceilings and walls.
- Details:
Detailed drawings provide specific instructions for the construction of particular elements, such as stairs, fireplaces, and built-in cabinetry. These drawings ensure that each component is crafted with precision and meets the architect’s design intent.
Together, these detailed blueprints provide a comprehensive visual guide for the construction team, minimizing the potential for errors and ensuring that the final structure accurately reflects the architect’s vision.
Structural Integrity
Structural integrity refers to the ability of a building to withstand external forces and maintain its stability. In architect house plans, structural integrity is paramount, as it ensures the safety and durability of the structure.
- Foundation:
The foundation is the base of the house and plays a crucial role in its structural integrity. Architect house plans specify the type of foundation required, such as a slab, crawlspace, or basement, based on factors like soil conditions and the weight of the building.
- Framing:
The framing, consisting of walls, floors, and roof, provides the skeleton of the house. Architect house plans detail the materials and dimensions of the framing members, ensuring they can withstand the weight of the structure and resist lateral forces like wind and earthquakes.
- Load-bearing Walls:
Load-bearing walls are structural walls that support the weight of the building above. Architect house plans clearly indicate which walls are load-bearing and must not be altered or removed, as doing so could compromise the structural integrity of the house.
- Connections:
Proper connections between framing members are essential for structural integrity. Architect house plans specify the types of connections to be used, such as nails, screws, bolts, or welded joints, ensuring that the structure is securely held together.
By addressing structural integrity in architect house plans, architects ensure that the building can withstand the rigors of daily use, environmental factors, and unforeseen events, providing a safe and stable living environment for the occupants.
Electrical and Plumbing Systems
Electrical and plumbing systems are crucial components of architect house plans as they ensure the functionality, comfort, and safety of the building’s occupants.
- Electrical Wiring:
Electrical wiring plans specify the location and type of electrical outlets, switches, lighting fixtures, and circuits throughout the house. These plans ensure that the electrical system can safely and efficiently power all appliances, devices, and lighting.
- Lighting Design:
Lighting design plans indicate the placement and type of lighting fixtures in each room, considering factors such as natural light availability, task requirements, and aesthetic preferences. Proper lighting design enhances the functionality and ambiance of the living space.
- Plumbing Layout:
Plumbing layout plans outline the location and size of pipes, fixtures, and appliances in the kitchen, bathrooms, and laundry areas. These plans ensure that the plumbing system can efficiently supply water and drain waste throughout the house.
- Water Heating and Distribution:
Architect house plans specify the type of water heater to be used and its location. They also include details on the distribution of hot and cold water throughout the house, ensuring an adequate supply for all plumbing fixtures.
By carefully planning and detailing electrical and plumbing systems in architect house plans, architects ensure that the building meets the occupants’ needs for functionality, comfort, and safety, while adhering to building codes and industry standards.
Functionality and Layout
Functionality and layout are crucial aspects of architect house plans, as they directly impact the usability, comfort, and overall livability of the building. Architects meticulously consider these factors to create spaces that meet the specific needs and preferences of the occupants.
- Space Planning:
Space planning involves the efficient allocation of space within the house. Architect house plans consider the size and shape of each room, the flow of traffic between spaces, and the placement of furniture and fixtures to maximize functionality and comfort.
- Room Relationships:
The relationship between different rooms is a key factor in creating a functional layout. Architect house plans carefully consider the proximity and accessibility of rooms based on their intended use. For example, the kitchen may be located near the dining room for convenience, while the bedrooms may be situated in a separate wing for privacy.
- Circulation and Flow:
Circulation refers to the movement of people and objects within the house. Architect house plans strive to create a smooth and efficient flow of traffic by minimizing obstacles and providing clear pathways between spaces. This ensures that the occupants can move around the house comfortably and safely.
- Natural Light and Ventilation:
Natural light and ventilation are essential for the well-being of the occupants. Architect house plans incorporate windows and other openings to allow for ample natural light to enter the house. They also consider cross-ventilation to promote air circulation and create a healthy and comfortable living environment.
By carefully considering functionality and layout in architect house plans, architects create spaces that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also highly functional, comfortable, and conducive to a better quality of life for the occupants.
Aesthetics and Design
Aesthetics and design play a significant role in architect house plans as they shape the overall appearance and character of the building. Architects carefully consider various design elements to create visually appealing and harmonious structures that reflect the occupants’ preferences and aspirations.
- Architectural Style:
The architectural style of a house refers to its overall design and aesthetic. Architect house plans may incorporate elements from various architectural styles, such as traditional, modern, contemporary, or regional styles. The choice of style is influenced by the surrounding environment, the client’s preferences, and the architect’s vision.
- Exterior Design:
The exterior design of a house encompasses its facade, materials, and overall form. Architect house plans consider the visual impact of the house from different angles, ensuring a cohesive and visually appealing appearance. The choice of materials, such as brick, stone, wood, or stucco, and the use of design elements like windows, doors, and porches contribute to the overall aesthetic of the exterior.
- Interior Design:
Interior design focuses on the aesthetic and functional aspects of the interior spaces of the house. Architect house plans may include suggestions for interior finishes, such as flooring, wall coverings, and millwork, as well as the placement of fixtures and furniture. The goal is to create a harmonious and inviting living environment that reflects the occupants’ lifestyle and tastes.
- Landscape Design:
Landscape design considers the relationship between the house and its surrounding outdoor environment. Architect house plans may include suggestions for landscaping, such as the placement of trees, shrubs, and gardens. The aim is to create a seamless transition between the interior and exterior spaces, enhancing the overall aesthetic appeal of the property.
By carefully considering aesthetics and design in architect house plans, architects create buildings that are not only functional and comfortable but also visually stunning and expressive of the occupants’ unique style and aspirations.
Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is a crucial consideration in architect house plans as it directly impacts the environmental footprint and operating costs of the building. Architects employ various strategies to design energy-efficient houses that minimize energy consumption and promote sustainable living.
One key strategy is optimizing the building envelope, which includes the walls, roof, and windows. Architect house plans specify the use of energy-efficient materials, such as insulated walls and double-glazed windows, to reduce heat transfer and minimize energy loss. Proper insulation helps maintain a comfortable indoor temperature, reducing the need for heating and cooling systems.
Another important aspect is the orientation of the house on the building site. Architect house plans consider the sun’s path and prevailing winds to maximize natural light and ventilation. Proper orientation can reduce the need for artificial lighting and minimize heat gain during summer months, leading to lower energy consumption.
Furthermore, architect house plans incorporate energy-efficient systems and appliances. These may include high-efficiency HVAC systems, LED lighting, and ENERGY STAR-rated appliances. By specifying energy-efficient equipment, architects can help reduce the overall energy consumption of the house, resulting in lower utility bills and a smaller carbon footprint.
By incorporating energy-efficient strategies into architect house plans, architects create buildings that are not only comfortable and functional but also environmentally responsible and cost-effective to operate, contributing to a more sustainable future.
Compliance with Codes
Compliance with building codes and regulations is paramount in architect house plans to ensure the safety, structural integrity, and habitability of the building. Building codes establish minimum standards for various aspects of construction, including structural design, fire safety, and accessibility.
- Zoning Regulations:
Zoning regulations specify the permitted uses of land and the dimensional requirements for buildings within a particular area. Architect house plans must adhere to zoning regulations to ensure the house complies with local land use ordinances and neighborhood character.
- Building Codes:
Building codes govern the structural design, fire safety, and accessibility features of buildings. Architect house plans must meet or exceed the requirements of applicable building codes to ensure the safety and well-being of the occupants. This includes specifying proper structural systems, fire-resistant materials, and accessible entrances and pathways.
- Energy Codes:
Energy codes establish minimum standards for energy efficiency in buildings. Architect house plans must comply with energy codes to minimize energy consumption and promote sustainable practices. This involves specifying energy-efficient building materials, insulation, and systems, such as high-efficiency HVAC and lighting.
- Accessibility Codes:
Accessibility codes ensure that buildings are accessible to individuals with disabilities. Architect house plans must incorporate accessible features, such as ramps, wide doorways, and accessible bathrooms, to comply with accessibility codes and provide an inclusive environment for all.
By adhering to building codes and regulations, architect house plans help ensure that the constructed building is safe, functional, energy-efficient, and accessible, meeting the necessary standards for habitability and contributing to a livable and sustainable built environment.
Contractor’s Guide
Architect house plans serve as a comprehensive guide for contractors throughout the construction process. These plans provide detailed instructions and specifications that ensure the accurate and efficient execution of the project.
Each sheet of the house plans typically includes a title block that specifies the project name, address, and contact information. The plans are organized into different sections, such as floor plans, elevations, and details, each serving a specific purpose in guiding the construction.
Floor plans provide a bird’s-eye view of each level of the house, indicating the placement of walls, doors, windows, and other structural elements. Contractors use these plans to lay out the foundation, frame the walls, and install the necessary utilities.
Elevations show the exterior walls of the house from different sides, providing a clear understanding of the building’s height, shape, and architectural features. These drawings guide contractors in constructing the exterior walls, installing windows and doors, and adding siding or other exterior finishes.
Overall, architect house plans are indispensable tools for contractors, as they provide a roadmap for every stage of the construction process. By following these plans meticulously, contractors can ensure that the final structure aligns precisely with the architect’s design intent and meets the highest standards of quality and safety.









Related Posts