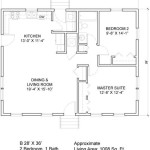
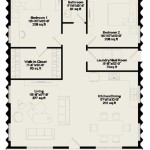
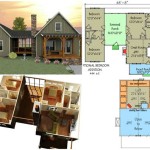
Affordable housing floor plans are architectural designs that prioritize cost-effectiveness without compromising functionality. These floor plans aim to provide adequate and comfortable living spaces while adhering to strict budgetary constraints. A typical example of an affordable housing floor plan is a two-bedroom, one-bathroom unit with an open kitchen and living area designed to maximize space utilization.
By incorporating innovative design techniques and selecting affordable materials, these floor plans enable individuals and families with limited financial means to access decent housing without sacrificing quality. From compact studio apartments to multi-family townhouses, affordable housing floor plans play a vital role in addressing the housing needs of our communities.
In the main body of this article, we will explore the various types of affordable housing floor plans, design principles, and emerging trends in this important area of architecture.
When designing affordable housing floor plans, it is crucial to consider the following key points:
- Maximize space utilization
- Prioritize natural lighting
- Incorporate energy-efficient features
- Provide accessible design elements
- Consider mixed-use spaces
- Optimize storage solutions
- Utilize sustainable materials
- Implement modular construction
- Explore innovative financing models
- Engage with community stakeholders
By adhering to these principles, architects and urban planners can create affordable housing floor plans that meet the needs of low-income individuals and families while promoting sustainable and inclusive communities.
Maximize space utilization
Maximizing space utilization is a crucial aspect of affordable housing floor plans. Every square foot of space must be carefully considered to ensure that the unit is both functional and comfortable. There are several key strategies that architects and designers can employ to achieve maximum space utilization:
1. **Open floor plans:** Open floor plans eliminate unnecessary walls and partitions, creating a more spacious and airy feel. This approach allows for multiple functions to be accommodated within a single room, such as a combined living and dining area or a kitchen that flows into the living space.
2. **Multi-purpose furniture:** Multi-purpose furniture pieces serve multiple functions, saving valuable space. For example, a sofa bed can provide both seating and sleeping accommodations, while a coffee table with built-in storage can serve as a storage unit as well as a table.
3. **Vertical storage:** Utilizing vertical space is essential in compact units. Wall-mounted shelves, cabinets, and drawers can provide ample storage without taking up floor space. Stackable bins and baskets can also be used to maximize vertical space in closets and pantries.
4. **Built-in features:** Built-in features, such as recessed shelves, desks, and beds, can create a more streamlined and space-saving design. These features are integrated into the structure of the unit, eliminating the need for separate furniture pieces and maximizing floor space.
By implementing these strategies, architects and designers can create affordable housing floor plans that make the most of every square foot, ensuring that residents have a comfortable and functional living space despite the space constraints.
Prioritize natural lighting
Incorporating natural lighting into affordable housing floor plans is essential for creating healthy and comfortable living spaces. Natural light has been shown to improve mood, boost productivity, and reduce energy costs. Here are some key strategies for prioritizing natural lighting in affordable housing design:
1. Maximize window placement: Windows should be strategically placed to allow for ample natural light to penetrate the unit. South-facing windows are ideal, as they receive the most sunlight throughout the day. Large windows and sliding glass doors can further enhance natural lighting.
2. Avoid obstructions: Obstructions such as walls, furniture, and curtains can block natural light. To maximize the amount of light entering the unit, avoid placing furniture in front of windows and use sheer curtains or blinds that allow light to filter through.
3. Utilize reflective surfaces: Reflective surfaces, such as white walls, light-colored flooring, and mirrors, can bounce natural light around the unit, making it feel more spacious and brighter. Glossy finishes on furniture and surfaces can also help to reflect light.
4. Consider skylights and solar tubes: Skylights and solar tubes are effective ways to bring natural light into units that have limited window access. Skylights are installed on the roof, while solar tubes are reflective tubes that channel sunlight from the roof into the interior of the unit.
By prioritizing natural lighting in affordable housing floor plans, architects and designers can create healthier, more comfortable, and more energy-efficient living spaces for residents.
Incorporate energy-efficient features
Incorporating energy-efficient features into affordable housing floor plans is crucial for reducing utility costs and creating more sustainable living spaces. Here are some key strategies for integrating energy efficiency into affordable housing design:
1. Insulation and air sealing: Proper insulation and air sealing prevent heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer, reducing the need for heating and cooling. Insulation materials can be installed in walls, ceilings, and floors, while air sealing measures include caulking and weatherstripping around windows, doors, and other openings.
2. Energy-efficient appliances and lighting: Energy-efficient appliances, such as refrigerators, dishwashers, and washing machines, consume less energy than traditional models. Similarly, LED lighting is more energy-efficient than incandescent or fluorescent lighting. By incorporating these energy-efficient appliances and lighting fixtures into affordable housing floor plans, utility costs can be significantly reduced.
3. Passive solar design: Passive solar design utilizes the sun’s energy to heat and cool a building naturally. This can be achieved through the use of south-facing windows, thermal mass materials, and overhangs. In the winter, the sun’s rays enter the unit through the south-facing windows and are absorbed by thermal mass materials, such as concrete or brick. This stored heat is then released slowly throughout the night, keeping the unit warm. In the summer, the overhangs shade the windows from the high sun, preventing the unit from overheating.
4. Renewable energy sources: Renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and geothermal heat pumps, can be integrated into affordable housing floor plans to further reduce energy consumption and costs. Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity, which can be used to power the unit’s appliances and lighting. Geothermal heat pumps use the earth’s constant temperature to heat and cool the unit, reducing the need for traditional heating and cooling systems.
By incorporating these energy-efficient features into affordable housing floor plans, architects and designers can create more sustainable and cost-effective living spaces for residents while reducing their environmental impact.
Provide accessible design elements
Incorporating accessible design elements into affordable housing floor plans is essential for creating inclusive living spaces that meet the needs of all residents, including those with disabilities. Here are some key strategies for providing accessible design elements in affordable housing:
1. Universal design principles: Universal design principles aim to create spaces that are accessible and usable by everyone, regardless of age, ability, or disability. These principles include providing clear pathways of travel, minimizing obstacles, and ensuring that all spaces and features are reachable and operable by people with diverse abilities.
2. Accessible entrances and doorways: Entrances and doorways should be wide enough to accommodate wheelchairs and other mobility devices. Thresholds should be level or have ramps to eliminate tripping hazards. Door handles should be easy to grasp and operate for people with limited hand mobility.
3. Accessible kitchens and bathrooms: Kitchens and bathrooms should be designed with accessible features such as roll-under sinks, adjustable countertops, grab bars, and accessible showers or bathtubs. These features allow people with disabilities to use these spaces independently and safely.
4. Accessible common areas: Common areas, such as hallways, laundry rooms, and community spaces, should also be accessible. Hallways should be wide enough for wheelchairs, and laundry rooms should have accessible machines and counters. Community spaces should provide accessible seating and meeting areas.
By providing accessible design elements in affordable housing floor plans, architects and designers can create inclusive living spaces that meet the needs of all residents and promote independence and dignity for people with disabilities.
Consider mixed-use spaces
Mixed-use spaces combine different functions within a single unit or building. This approach can be particularly beneficial in affordable housing floor plans, as it allows for more efficient use of space and can create more vibrant and inclusive communities.
- Residential and commercial spaces: Combining residential and commercial spaces within a single building can create a more vibrant and convenient living environment. For example, a ground-floor retail space could be combined with residential units on the upper floors. This approach can support local businesses and provide residents with easy access to goods and services.
- Live/work spaces: Live/work spaces are units that combine living and working areas within a single unit. This type of space is well-suited for entrepreneurs, artists, and other professionals who need dedicated workspaces within their homes. Live/work spaces can help to reduce commuting time and expenses, and can also provide greater flexibility and control over work-life balance.
- Community spaces: Incorporating community spaces into affordable housing floor plans can foster a sense of community and provide residents with opportunities for social interaction and engagement. These spaces can include shared kitchens, dining areas, laundry facilities, and outdoor gathering areas. Community spaces can also be used for educational programs, workshops, and other activities that benefit residents.
- Mixed-income housing: Mixed-income housing developments combine affordable units with market-rate units within a single building or community. This approach can help to create more diverse and inclusive communities, reduce stigma associated with affordable housing, and provide opportunities for residents to move into higher-income units as their incomes increase.
By considering mixed-use spaces in affordable housing floor plans, architects and designers can create more dynamic, sustainable, and inclusive living environments that meet the diverse needs of residents.
Optimize storage solutions
Optimizing storage solutions is crucial in affordable housing floor plans to ensure that residents have adequate space for their belongings without sacrificing comfort and functionality. Here are some key strategies for incorporating efficient storage solutions into affordable housing design:
1. Built-in storage: Built-in storage, such as closets, shelves, and drawers, can be integrated into the walls and other structural elements of the unit. This approach provides a seamless and space-saving way to store items, as it eliminates the need for separate furniture pieces. Built-in storage can be customized to fit the specific needs of the residents and the available space.
2. Vertical storage: Utilizing vertical space is essential in compact units. Wall-mounted shelves, cabinets, and drawers can provide ample storage without taking up floor space. Stackable bins and baskets can also be used to maximize vertical space in closets and pantries. Vertical storage solutions allow residents to store more items in a smaller footprint.
3. Multi-purpose furniture: Multi-purpose furniture pieces serve multiple functions, saving valuable space. For example, a sofa bed can provide both seating and sleeping accommodations, while a coffee table with built-in storage can serve as a storage unit as well as a table. Ottomans with hidden storage compartments can also be used to store blankets, pillows, and other items.
4. Under-utilized spaces: Under-utilized spaces, such as the area under beds and stairs, can be transformed into valuable storage areas. Drawers or rolling bins can be placed under beds to store seasonal items or bulky bedding. Shelves or cabinets can be installed under stairs to provide additional storage space for items that are not frequently used.
By optimizing storage solutions in affordable housing floor plans, architects and designers can create functional and comfortable living spaces that meet the needs of residents and maximize the use of available space.
Utilize sustainable materials
Incorporating sustainable materials into affordable housing floor plans is essential for creating healthy, durable, and environmentally friendly living spaces. Here are some key strategies for utilizing sustainable materials in affordable housing design:
1. Recycled and renewable materials: Recycled materials, such as reclaimed wood and recycled steel, can be used to reduce the environmental impact of construction and create unique and sustainable design features. Renewable materials, such as bamboo and cork, are rapidly renewable and offer durable and sustainable alternatives to traditional materials.
2. Low-VOC materials: Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are harmful chemicals that can be emitted from building materials, such as paints, adhesives, and flooring. Using low-VOC materials helps to improve indoor air quality and create healthier living environments for residents.
3. Energy-efficient materials: Energy-efficient materials, such as insulated concrete forms (ICFs) and high-performance windows, can reduce energy consumption and lower utility costs for residents. These materials help to regulate indoor temperatures, reducing the need for heating and cooling systems.
4. Durable and low-maintenance materials: Durable and low-maintenance materials, such as fiber cement siding and metal roofing, can extend the lifespan of affordable housing units and reduce maintenance costs. These materials are resistant to rot, moisture, and pests, ensuring that the units remain in good condition for years to come.
By utilizing sustainable materials in affordable housing floor plans, architects and designers can create healthy, durable, and environmentally friendly living spaces that promote the well-being of residents and reduce the environmental impact of construction and operation.
Implement modular construction
Modular construction is a method of building where individual building units, or modules, are constructed in a controlled factory environment and then transported to the building site for assembly. This approach offers several advantages for affordable housing floor plans:
1. Reduced construction time: Modular construction significantly reduces construction time compared to traditional methods. Modules are built in parallel in the factory, allowing for a more efficient and controlled construction process. This reduced construction time can lead to earlier occupancy for residents and faster project completion.
2. Improved quality control: Factory-controlled construction allows for better quality control and consistency. Modules are built to precise specifications in a controlled environment, reducing the risk of errors and defects. This results in higher-quality housing units that require less maintenance and repair.
3. Cost savings: Modular construction can lead to cost savings due to reduced labor costs, less material waste, and improved efficiency. Factory production allows for bulk purchasing of materials and optimization of the construction process, resulting in lower overall project costs.
4. Sustainable construction: Modular construction promotes sustainable building practices. Factory-controlled construction reduces waste and allows for the use of sustainable materials and construction methods. Additionally, modules can be designed to be energy-efficient and durable, contributing to lower operating costs for residents.
Overall, modular construction offers a range of benefits for affordable housing floor plans, including reduced construction time, improved quality control, cost savings, and sustainable construction practices. This approach can help to create high-quality, affordable housing units that meet the needs of residents and communities.
Explore innovative financing models
Innovative financing models can play a crucial role in making affordable housing floor plans more accessible to low-income individuals and families. Here are some key innovative financing models to consider:
- Rent-to-own programs: Rent-to-own programs allow low-income tenants to rent a home with the option to purchase it in the future. A portion of the monthly rent payment goes towards a down payment, gradually building equity in the home. This model provides a path to homeownership for individuals who may not have the financial means to purchase a home outright.
- Shared equity models: Shared equity models involve a partnership between a low-income homebuyer and a non-profit organization or government agency. The non-profit or government agency provides a portion of the down payment and retains a share of the equity in the home. As the homebuyer’s income increases, they can gradually buy out the non-profit’s or government agency’s share of equity.
- Community land trusts: Community land trusts (CLTs) are non-profit organizations that acquire land and develop affordable housing on that land. CLTs retain ownership of the land, while individual families purchase the homes built on that land. This model ensures that the homes remain affordable in perpetuity, as the CLT controls the resale price of the homes.
- Lease-purchase options: Lease-purchase options allow low-income individuals and families to lease a home with the option to purchase it at a later date. During the lease period, a portion of the monthly rent payment is applied towards a down payment. This model provides flexibility for individuals who may not be ready to commit to homeownership immediately but want to build equity over time.
These innovative financing models offer creative solutions to address the financial barriers to affordable housing. By exploring these models, architects, developers, and policymakers can create more accessible and sustainable housing options for low-income communities.
Engage with community stakeholders
Engaging with community stakeholders is essential for creating affordable housing floor plans that are responsive to the needs of the community. This involves actively seeking input from residents, community organizations, and local businesses to ensure that the plans align with the community’s vision and priorities.
Community engagement can take various forms, such as public meetings, focus groups, and surveys. These forums provide opportunities for stakeholders to share their perspectives on housing needs, preferences, and concerns. Architects and planners can gather valuable insights into the community’s housing challenges, such as overcrowding, lack of accessibility, or affordability constraints.
By involving community stakeholders in the planning process, architects and planners can ensure that affordable housing floor plans are tailored to the specific needs of the community. This participatory approach fosters a sense of ownership and empowers residents to shape their living environments. Furthermore, community engagement can help identify potential barriers to affordability and develop strategies to overcome them.
Ongoing engagement with community stakeholders is crucial throughout the planning and implementation process. This ensures that the project remains responsive to the evolving needs of the community and that any adjustments or modifications are made in a collaborative manner. Regular communication and updates keep stakeholders informed and provide opportunities for feedback, ensuring that the final affordable housing floor plans reflect the community’s aspirations and priorities.
Engaging with community stakeholders is not only a matter of fulfilling a requirement but also a valuable opportunity to build trust, foster collaboration, and create a sense of shared ownership in affordable housing developments. By actively involving the community in the planning process, architects and planners can create housing solutions that are truly responsive to the needs and aspirations of the people they serve.

.jpg?1407288286)
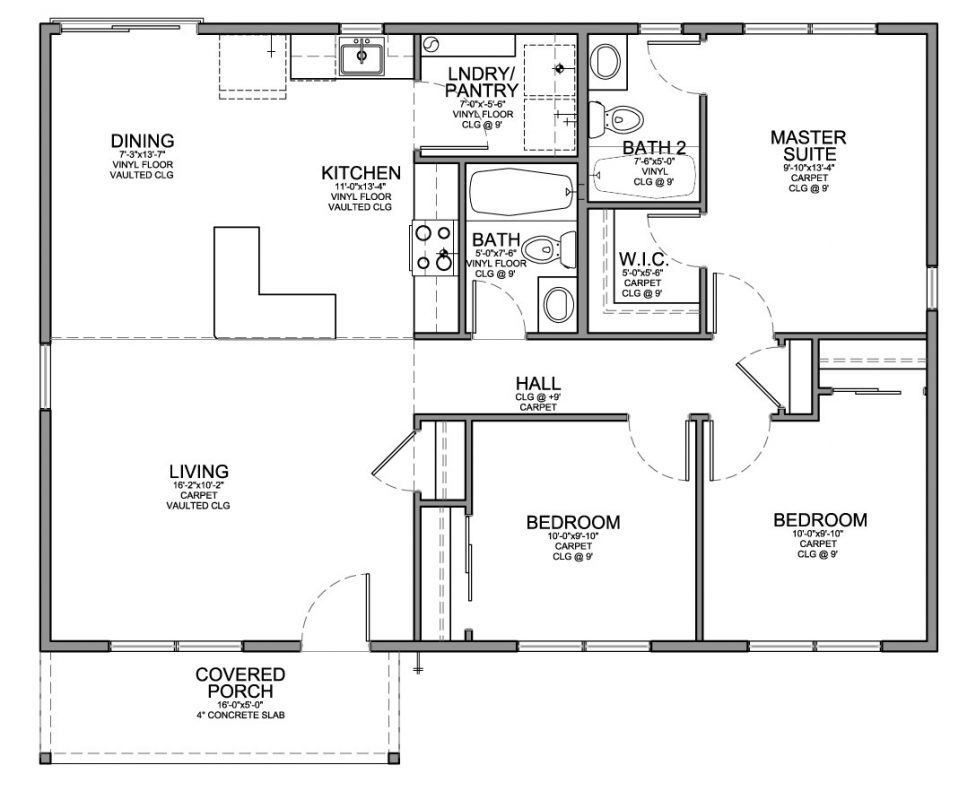







Related Posts