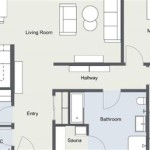
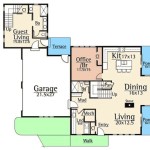
Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU) House Plans are blueprints and designs specifically tailored for the construction of accessory dwelling units, commonly known as granny flats, in-law suites, or second units. These plans provide a structured framework for architects, builders, and homeowners to create functional and aesthetically pleasing living spaces that complement the primary residence on a property.
ADUs serve a range of practical purposes. They can provide affordable housing for family members or guests, generate rental income, or create dedicated work or studio spaces. By offering additional living units on the same property, ADUs can enhance the value and versatility of a home while promoting aging-in-place and multi-generational living.
With the growing popularity of ADUs, a comprehensive selection of house plans is available to suit different preferences and requirements. These plans cover a wide range of styles, sizes, and configurations, from compact studio apartments to spacious two-bedroom units. In the following sections, we will delve into the key considerations and benefits associated with ADU house plans, providing guidance on selecting the right plan for your specific needs.
When selecting Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU) house plans, several important points should be considered to ensure the unit meets your needs and complies with local regulations:
- Zoning Compliance
- Unit Size and Layout
- Building Codes
- Energy Efficiency
- Accessibility Features
- Connectivity to Utilities
- Privacy and Security
- Resale Value
By carefully considering these factors, you can choose an ADU house plan that aligns with your goals and creates a functional, comfortable, and legally compliant living space.
Zoning Compliance
Zoning compliance is paramount when selecting ADU house plans. Local zoning ordinances establish regulations regarding the size, placement, and use of ADUs on a property. Failure to adhere to these regulations can result in permit delays, fines, or even the inability to construct an ADU.
- Setbacks and Lot Coverage: Zoning codes often specify minimum setbacks from property lines and maximum lot coverage percentages. These regulations ensure that ADUs do not encroach on neighboring properties or create excessive density.
- Unit Size and Height: Zoning ordinances may limit the square footage and height of ADUs. These restrictions aim to maintain the character and scale of the neighborhood while preventing overcrowding.
- Permitted Uses: Zoning codes typically specify the allowable uses for ADUs. Common permitted uses include residential units, home offices, and studios. It is essential to verify that the intended use of your ADU complies with local zoning regulations.
- Parking Requirements: Many municipalities require additional parking spaces for properties with ADUs. These requirements vary depending on the size and use of the ADU. It is important to factor in the cost of additional parking when budgeting for your project.
By carefully researching and adhering to zoning compliance regulations, you can avoid costly delays and ensure that your ADU project proceeds smoothly.
Unit Size and Layout
The size and layout of an Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU) are crucial considerations that impact its functionality, livability, and overall cost. A well-designed ADU should provide adequate space for its intended purpose while adhering to zoning regulations and maximizing efficiency.
ADU Size Considerations
ADU size is typically determined by local zoning ordinances, which often specify maximum square footage limits. These limits vary depending on the size of the property and the overall density of the neighborhood. It is important to carefully review zoning regulations to ensure that the planned ADU size complies with local requirements.
When determining the appropriate size for an ADU, consider the number of occupants, their lifestyle, and the intended use of the unit. A small studio apartment may be sufficient for a single person or a couple, while a larger unit with multiple bedrooms and bathrooms may be necessary for a family or guests.
ADU Layout Options
ADU layouts can vary significantly depending on the available space and the desired functionality. Some common layout options include:
- Studio Layout: A studio layout combines the living, sleeping, and cooking areas into a single open space. This layout is ideal for small ADUs or for individuals who prefer a minimalist lifestyle.
- One-Bedroom Layout: A one-bedroom layout provides a separate bedroom, in addition to a combined living and kitchen area. This layout offers more privacy and space than a studio layout, making it suitable for couples or small families.
- Two-Bedroom Layout: A two-bedroom layout includes two separate bedrooms, along with a living area and kitchen. This layout is ideal for families or individuals who require more space and privacy.
When selecting an ADU layout, consider the following factors: the number of occupants, their privacy needs, the desired level of separation between living and sleeping areas, and the available space.
Building Codes
Building codes are essential regulations that ensure the safety, structural integrity, and energy efficiency of buildings. When it comes to Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs), adherence to building codes is crucial to guarantee the well-being of occupants and the longevity of the structure.
- Structural Safety: Building codes establish minimum standards for structural elements such as foundations, framing, and roofing. These standards are designed to withstand various loads, including dead loads (the weight of the structure itself), live loads (occupants and their belongings), and environmental loads (wind, snow, and earthquakes). By complying with structural safety codes, ADUs can resist these loads and provide a safe and stable living environment.
- Fire Safety: Building codes also include strict fire safety provisions. These provisions dictate the use of fire-resistant materials, the installation of smoke detectors and sprinkler systems, and the provision of adequate means of egress. By adhering to fire safety codes, ADUs can minimize the risk of fires and protect occupants in the event of a fire.
- Energy Efficiency: Energy efficiency codes are becoming increasingly important as we strive to reduce our environmental impact and lower energy costs. Building codes often include requirements for insulation, energy-efficient appliances, and lighting systems. By meeting these requirements, ADUs can consume less energy, resulting in lower utility bills and a smaller carbon footprint.
- Accessibility: Building codes also address accessibility features for individuals with disabilities. These features include ramps, wider doorways, and accessible bathrooms. By incorporating accessibility features into ADU designs, we can create inclusive living spaces that meet the needs of all occupants.
Compliance with building codes is not only a legal requirement but also a fundamental aspect of responsible construction. By adhering to these codes, homeowners can ensure the safety, comfort, and sustainability of their ADUs.
Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is a crucial consideration in Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU) house plans, as it directly impacts the environmental impact and operating costs of the unit. By incorporating energy-efficient features and practices, homeowners can reduce their energy consumption, lower utility bills, and contribute to a more sustainable future.
One key aspect of energy efficiency in ADUs is the building envelope, which includes the walls, roof, and windows. Proper insulation and air sealing can significantly reduce heat loss and gain, maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature while minimizing energy usage. High-performance windows and doors with low U-factors and high R-values further enhance the thermal performance of the building envelope.
Energy-efficient appliances and lighting systems are also essential components of an ADU house plan. Look for appliances with the ENERGY STAR label, which indicates that they meet strict energy efficiency standards set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). LED lighting is another excellent choice, as it consumes significantly less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs and lasts longer.
In addition to these measures, consider incorporating renewable energy sources into your ADU design. Solar panels can generate electricity from sunlight, reducing reliance on the grid and potentially eliminating energy bills altogether. Solar water heaters can also significantly reduce the energy required for water heating.
By prioritizing energy efficiency in ADU house plans, homeowners can create sustainable living spaces that minimize their environmental footprint and provide long-term cost savings.
Accessibility Features
Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU) house plans should consider accessibility features to ensure that the unit is inclusive and comfortable for all occupants, including those with disabilities or mobility impairments.
- Wide Doorways and Hallways:
Wider doorways and hallways allow for easy movement of wheelchairs, walkers, and other mobility aids. Standard doorways should be at least 32 inches wide, while hallways should be at least 42 inches wide.
- Roll-In Showers:
Roll-in showers are designed with a zero-threshold entry and a sloped floor that drains water away from the wheelchair. Grab bars and a built-in seat provide additional support and safety for users.
- Lever Handles:
Door handles and faucet handles should be lever-operated instead of knobs. Lever handles are easier to grip and maneuver for individuals with limited hand mobility.
- Accessible Kitchen Features:
Kitchens should be designed with accessible features such as lower countertops, pull-out shelves, and adjustable-height cabinets. These features make it easier for individuals in wheelchairs or with limited reach to prepare meals and access items.
By incorporating accessibility features into ADU house plans, homeowners can create living spaces that are welcoming and functional for all occupants, regardless of their abilities.
Connectivity to Utilities
Ensuring proper connectivity to utilities is essential for the functionality and comfort of an Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU). Careful planning and coordination with utility providers are crucial to avoid costly surprises and ensure a seamless connection.
The first step is to determine the availability and capacity of utilities at the property where the ADU will be located. Contact local utility companies to inquire about the availability of water, electricity, gas, and sewer services. They can provide information on the connection process, fees, and any necessary upgrades.
Water and sewer connections are essential for basic sanitation and hygiene. The ADU should be connected to the main water supply and sewer system, or an alternative system such as a septic tank and well may be required. Adequate water pressure and flow rates must be ensured to meet the needs of the occupants.
Electricity is crucial for lighting, appliances, and heating/cooling systems. The ADU’s electrical system should be connected to the main electrical panel or a separate meter may be installed. The electrical capacity should be sufficient to handle the anticipated electrical load of the ADU.
Privacy and Security
Privacy and security are essential considerations in Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU) house plans to ensure the well-being and peace of mind of occupants.
- Separate Entrances and Exits:
Providing separate entrances and exits for the ADU allows occupants to maintain their privacy and independence. This is especially important if the ADU is attached to the main house or is located on the same property.
- Fencing and Landscaping:
Fencing and landscaping can create physical barriers that enhance privacy and security. Fences can define the boundaries of the ADU, while landscaping with trees and shrubs can provide visual screening and reduce noise.
- Window Placement and Coverings:
Careful placement of windows can ensure privacy while still allowing natural light into the ADU. Curtains, blinds, or other window coverings can provide additional privacy and control over light levels.
- Security Systems:
Installing security systems such as alarms, motion sensor lights, and surveillance cameras can deter potential intruders and provide peace of mind for occupants. These systems can be integrated with smart home technology for remote monitoring and control.
By incorporating privacy and security features into ADU house plans, homeowners can create safe and comfortable living spaces that respect the privacy of occupants and protect their well-being.
Resale Value
Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs) can significantly impact the resale value of a property. By adding an additional living unit to the property, homeowners can increase its overall value and appeal to a broader range of potential buyers.
- Increased Square Footage:
ADUs add additional square footage to the property, which is a major factor in determining its value. The additional living space can be used for various purposes, such as rental income, accommodating extended family members, or creating a home office.
- Rental Income Potential:
ADUs can generate rental income, providing homeowners with an additional source of revenue. Rental income can offset the cost of owning the property and increase its overall return on investment.
- Multi-Generational Living:
ADUs offer flexibility for multi-generational living arrangements. They can provide space for elderly parents or adult children to live independently while remaining close to family.
- Increased Buyer Pool:
ADUs expand the potential buyer pool for a property. They can appeal to families looking for additional space, investors seeking rental income, or individuals seeking multi-generational living options.
By carefully planning and designing an ADU, homeowners can enhance the resale value of their property while creating a functional and comfortable living space.









Related Posts