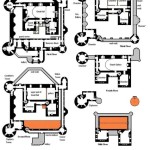
House Plan Design 2 Storey refers to the architectural blueprint that outlines the layout, dimensions, and structural elements of a two-storey residential building. It encompasses the planning and organization of spaces within the house, including bedrooms, bathrooms, kitchen, living areas, and any other relevant rooms and features.
The design process involves meticulous consideration of various factors such as the site’s topography, building codes, and the client’s specific requirements and preferences. Architects and designers collaborate to create a functional and aesthetically pleasing two-storey home that meets the needs and aspirations of its occupants.
In the following sections, we will delve into the key considerations, elements, and benefits of House Plan Design 2 Storey, providing practical advice and inspiration for designing an optimal living space that maximizes functionality, comfort, and visual appeal.
Designing a two-storey house plan requires careful consideration of various elements to ensure functionality, comfort, and aesthetic appeal. Here are ten important points to keep in mind:
- Site orientation and topography
- Building codes and regulations
- Functional room layout
- Efficient use of space
- Natural lighting and ventilation
- Staircase design and placement
- Structural integrity and safety
- Exterior aesthetics
- Sustainability and energy efficiency
- Budget and construction costs
By addressing these key points, architects and homeowners can create two-storey house plans that meet their specific needs and aspirations, ensuring a comfortable, functional, and visually appealing living space.
Site orientation and topography
Site orientation and topography play a crucial role in house plan design, particularly for two-storey homes. The way a house is positioned on a site can impact factors such as natural lighting, ventilation, energy efficiency, and views.
- Sun exposure: Consider the path of the sun throughout the day and how it will affect the house. Position the house to maximize natural light in living areas and to minimize heat gain in bedrooms during summer months.
- Wind patterns: Pay attention to prevailing wind patterns and design the house to take advantage of natural ventilation. Place windows and doors to capture breezes and create cross-ventilation, reducing the need for air conditioning.
- Topography: The slope and elevation of the site can influence the design of the house. A house built on a sloping site may require additional foundation work and retaining walls, but it can also offer opportunities for walk-out basements or multi-level decks.
- Views: If the site offers scenic views, orient the house to take advantage of them. Place windows and balconies strategically to maximize the views from key rooms.
By carefully considering site orientation and topography, architects and homeowners can create two-storey house plans that are not only functional and comfortable but also energy-efficient and visually appealing.
Building codes and regulations
Building codes and regulations are essential guidelines that govern the design and construction of buildings, including two-storey houses. These codes are established to ensure the safety, structural integrity, and habitability of buildings. Architects and homeowners must adhere to these codes to obtain building permits and ensure that their house plans comply with local and national standards.
- Zoning laws: Zoning laws regulate the use of land and buildings in specific areas. They determine the types of buildings that can be built in a particular zone, the maximum height and size of buildings, and the setbacks from property lines. Architects must carefully review zoning laws before designing a house plan to ensure that it complies with the regulations for the site.
- Building codes: Building codes specify the minimum standards for the design and construction of buildings. These codes cover a wide range of topics, including structural requirements, fire safety, plumbing, electrical systems, and energy efficiency. Architects must ensure that their house plans meet or exceed the minimum requirements of the applicable building codes.
- Fire codes: Fire codes are designed to minimize the risk of fire and protect occupants in the event of a fire. These codes specify requirements for fire-resistant materials, fire alarms, sprinkler systems, and evacuation routes. Architects must carefully consider fire codes when designing a house plan to ensure that the house is safe for its occupants.
- Accessibility codes: Accessibility codes ensure that buildings are accessible to people with disabilities. These codes specify requirements for ramps, elevators, wider doorways, and accessible bathrooms. Architects must consider accessibility codes when designing a house plan to ensure that the house is accessible to all occupants.
By adhering to building codes and regulations, architects and homeowners can ensure that their two-storey house plans are safe, structurally sound, and compliant with local and national standards. This helps to protect the health and safety of occupants and ensures that the house is habitable andlegal requirements.
Functional room layout
Functional room layout is crucial in house plan design, especially for two-storey homes. It involves carefully arranging and organizing the rooms within the house to ensure efficient use of space, smooth flow of traffic, and easy access to all areas of the house. A well-designed floor plan enhances the functionality and comfort of the home for its occupants.
- Public and private spaces: Divide the house into public and private spaces. Public spaces, such as the living room, dining room, and kitchen, are typically located on the first floor and are designed for entertaining guests and family gatherings. Private spaces, such as bedrooms and bathrooms, are usually located on the second floor to provide privacy and tranquility.
- Flow of traffic: Consider the flow of traffic when designing the layout of the house. Avoid creating bottlenecks or awkward transitions between rooms. Ensure that there is a clear and logical path from the entrance to the different areas of the house.
- Adjacency and separation of rooms: Group rooms that are frequently used together, such as the kitchen and dining room, or the master bedroom and bathroom. Separate rooms that require privacy, such as bedrooms, from noisy areas, such as the living room or kitchen.
- Natural light and ventilation: Position rooms to take advantage of natural light and ventilation. Place windows in strategic locations to maximize daylighting and minimize the need for artificial lighting. Consider cross-ventilation to promote air flow and reduce the need for air conditioning.
By carefully considering these factors, architects and homeowners can create two-storey house plans with functional room layouts that meet the needs and lifestyles of their occupants. A well-designed floor plan not only enhances the comfort and convenience of the home but also contributes to its overall aesthetic appeal.
Efficient use of space
Efficient use of space is a crucial consideration in house plan design, particularly for two-storey homes. With careful planning, architects can maximize the functionality and livability of a two-storey house while minimizing wasted space. Here are some key strategies for efficient use of space:
- Open floor plans: Open floor plans create a more spacious and airy feel by eliminating unnecessary walls and partitions. By combining living areas, such as the living room, dining room, and kitchen, into one large space, architects can make a small house feel larger and more open.
- Multi-purpose rooms: Multi-purpose rooms serve multiple functions, maximizing the use of space. For example, a guest room can also be used as a home office or a playroom. A breakfast nook can double as a homework station or a craft area.
- Built-in storage: Built-in storage solutions, such as closets, shelves, and drawers, can be seamlessly integrated into the walls and under stairs, maximizing storage space without taking up valuable floor space. Custom-built storage can be tailored to specific needs, ensuring that every nook and cranny is utilized.
- Vertical space utilization: Two-storey homes offer the opportunity to maximize vertical space utilization. Lofts and mezzanines can be incorporated to create additional living space or storage areas. High ceilings can be used to create dramatic double-height spaces, adding a sense of grandeur and spaciousness.
By implementing these strategies, architects and homeowners can create two-storey house plans that make the most of every square foot, resulting in homes that are both functional and comfortable.
Natural lighting and ventilation
Natural lighting and ventilation are essential elements of a comfortable and healthy home. In house plan design, architects carefully consider the placement of windows, doors, and other openings to maximize natural light and promote air flow. This not only reduces the need for artificial lighting and air conditioning, but also creates a more pleasant and healthier living environment.
To maximize natural lighting, architects position windows and skylights strategically to capture sunlight throughout the day. South-facing windows allow the most sunlight into a home. Windows should be placed in all rooms, even small ones, to ensure that every space has access to natural light. Skylights can be used to bring light into interior spaces that do not have windows, such as bathrooms and hallways.
Ventilation is equally important as natural lighting. Proper ventilation helps to remove stale air, reduce humidity, and improve indoor air quality. Cross-ventilation is a passive ventilation strategy that involves placing windows and doors on opposite sides of a room to create a natural airflow. This helps to circulate fresh air throughout the house and reduce the need for mechanical ventilation.
In addition to windows and doors, architects may also incorporate other design elements to improve natural lighting and ventilation. Atriums and courtyards can be used to bring light into the center of a house. Clerestory windows are high windows that allow light to enter a room without compromising privacy. Solar chimneys and wind towers can be used to create natural ventilation by harnessing the power of the sun and wind.
By carefully considering natural lighting and ventilation in house plan design, architects can create homes that are not only beautiful and functional, but also healthy and sustainable.
Staircase design and placement
Staircase design and placement are crucial considerations in house plan design, particularly for two-storey homes. Staircases serve as the primary vertical connection between floors and can significantly impact the functionality, safety, and overall aesthetic of a home.
When designing a staircase, architects must carefully consider factors such as the location, size, shape, and materials. The location of the staircase should provide easy access to both floors without disrupting the flow of traffic. The size and shape of the staircase should be proportional to the size of the house and should allow for comfortable and safe passage. Common staircase shapes include straight stairs, L-shaped stairs, and U-shaped stairs.
The choice of materials for the staircase is also important. Wood is a popular choice for its warmth and beauty, but it can be expensive and requires regular maintenance. Metal stairs are durable and modern, but they can be noisy and cold to the touch. Concrete stairs are strong and fire-resistant, but they can be bulky and difficult to modify. Architects must carefully weigh the pros and cons of each material to select the best option for the specific house design.
In addition to functionality and safety, architects also consider the aesthetic appeal of the staircase. Staircases can be designed as focal points or as subtle elements that blend into the background. Ornate staircases with elaborate railings and newel posts can add a touch of grandeur to a home, while simple, minimalist staircases can create a more modern and understated look.
Overall, staircase design and placement play a vital role in the functionality, safety, and aesthetic of a two-storey house. By carefully considering all the factors involved, architects can create staircases that are both beautiful and practical, enhancing the overall livability and enjoyment of the home.
Structural integrity and safety
Structural integrity and safety are paramount considerations in house plan design, particularly for two-storey homes. The structural system of a house must be able to withstand various loads and forces, including gravity, wind, and seismic activity, to ensure the safety and stability of the building. Architects must carefully design and engineer the structural system to meet or exceed building codes and ensure the long-term integrity of the house.
The foundation of a two-storey house is critical for its structural stability. The foundation must be designed to distribute the weight of the house evenly and prevent settling or shifting. Common foundation types include concrete slabs, crawl spaces, and basements. The choice of foundation depends on factors such as soil conditions, climate, and the overall design of the house.
The framing system of a two-storey house typically consists of a combination of load-bearing walls, beams, and columns. Load-bearing walls are structural walls that support the weight of the house and transfer it to the foundation. Beams and columns are used to support floors and roofs and to distribute loads more efficiently. The framing system must be designed to withstand both vertical and lateral forces.
In addition to the primary structural system, architects may also incorporate additional safety features into the house design. These features may include hurricane straps, shear walls, and earthquake bracing. Hurricane straps are metal connectors that are used to reinforce the connection between the roof and the walls, preventing the roof from being torn off in high winds. Shear walls are structural panels that are designed to resist lateral forces, such as those caused by earthquakes or high winds. Earthquake bracing is a system of beams and braces that is used to strengthen the house against seismic activity.
By carefully considering structural integrity and safety in house plan design, architects can create homes that are not only beautiful and functional, but also safe and durable. Structural integrity ensures that the house can withstand various loads and forces, while safety features provide additional protection against natural disasters and other hazards.
Exterior aesthetics
Exterior aesthetics play a vital role in the overall appeal and character of a two-storey house. The exterior design should complement the architectural style of the house and enhance its functionality. Architects consider various elements to create a visually pleasing and cohesive exterior, including the choice of materials, colors, textures, and architectural features.
The choice of exterior materials is crucial for both aesthetic and practical reasons. Common materials include brick, stone, wood, stucco, and vinyl siding. Each material has its own unique characteristics and advantages. Brick and stone are durable and fire-resistant, but they can be expensive. Wood is a versatile material that can be painted or stained to match any color scheme, but it requires regular maintenance. Stucco is a low-maintenance material that can be molded into various shapes and textures, but it can be susceptible to cracking. Vinyl siding is a cost-effective and low-maintenance option, but it may not be as durable as other materials.
Color is another important element of exterior aesthetics. The color of the house should complement the architectural style and the surrounding environment. Neutral colors, such as white, gray, and beige, are popular choices because they are versatile and timeless. However, bolder colors can be used to create a more dramatic or unique look. Architects may also use contrasting colors to highlight certain features of the house, such as the trim, shutters, or entryway.
Textures and architectural features can add depth and interest to the exterior of a two-storey house. Textures can be created through the use of different materials, such as rough-hewn stone or smooth stucco. Architectural features, such as columns, moldings, and decorative trim, can add a touch of elegance or whimsy to the house. By carefully combining materials, colors, textures, and architectural features, architects can create exterior designs that are both beautiful and functional.
Exterior aesthetics are not only about visual appeal but also about functionality. The exterior design should consider factors such as energy efficiency, weather resistance, and maintenance requirements. By carefully selecting materials and features, architects can create exteriors that are not only beautiful but also durable and sustainable.
Sustainability and energy efficiency
Sustainability and energy efficiency are increasingly important considerations in house plan design, particularly for two-storey homes. By incorporating sustainable and energy-efficient features into the design, architects can create homes that are not only comfortable and functional but also environmentally friendly and cost-effective to operate.
- Energy-efficient building envelope: The building envelope refers to the exterior shell of the house, including the walls, roof, windows, and doors. A well-insulated and airtight building envelope helps to reduce heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer, resulting in lower energy consumption for heating and cooling.
- Passive solar design: Passive solar design involves orienting the house to take advantage of natural sunlight for heating and lighting. South-facing windows allow the most sunlight into the home, which can help to reduce the need for artificial lighting and heating during the winter months.
- Energy-efficient appliances and systems: Energy-efficient appliances, such as Energy Star-rated refrigerators and dishwashers, can help to reduce energy consumption. Energy-efficient heating and cooling systems, such as heat pumps and geothermal systems, can also significantly reduce energy costs.
- Renewable energy sources: Renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines, can be incorporated into the house design to generate electricity and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
By carefully considering sustainability and energy efficiency in house plan design, architects can create homes that are not only comfortable and functional but also environmentally friendly and cost-effective to operate. These features can contribute to a healthier indoor environment, reduced carbon footprint, and lower energy bills, making two-storey homes more sustainable and desirable.
Budget and construction costs
Budget and construction costs are crucial considerations in house plan design, particularly for two-storey homes. The cost of building a two-storey house can vary significantly depending on a number of factors, including the size and complexity of the house, the choice of materials, and the local construction costs. It is important for homeowners to carefully consider their budget and construction costs before finalizing their house plan design.
One of the key factors thatconstruction costs is the size of the house. Larger houses typically require more materials and labor to build, which can increase the overall cost. The complexity of the house design can also impact construction costs. Houses with complex rooflines, multiple stories, and custom features can be more expensive to build than simpler houses with a more straightforward design.
The choice of materials is another important factor that can affect construction costs. Some materials, such as brick and stone, are more expensive than others, such as vinyl siding. It is important to carefully consider the cost of materials when selecting finishes for the exterior and interior of the house. In addition, the cost of labor can vary depending on the location and availability of skilled workers.
It is important for homeowners to work closely with their architect and contractor to develop a realistic budget for their two-storey house. The architect can help to design a house that meets the homeowner’s needs and budget, and the contractor can provide an accurate estimate of the construction costs. By carefully considering budget and construction costs, homeowners can avoid costly surprises and ensure that their dream home is within their financial reach.
In addition to the initial construction costs, homeowners also need to consider the ongoing costs of owning and maintaining a two-storey house. These costs can include property taxes, insurance, utilities, and repairs. It is important to factor these ongoing costs into the overall budget when planning for a new home.










Related Posts