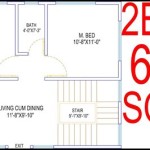
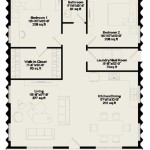
Multifamily house plans are architectural blueprints specifically designed for residential buildings intended to accommodate multiple families. These plans provide a comprehensive layout for the construction of units within a single building or complex, each with its own independent living spaces.
Multifamily house plans are commonly used for various residential developments, including apartment complexes, townhouses, duplexes, and triplexes. They enable the efficient use of space and resources while offering a cost-effective solution for providing housing in urban areas or dense residential neighborhoods.
Transition Paragraph:
In this article, we will explore the key considerations and essential elements of multifamily house plans, providing insights into the design principles, unit configurations, and building systems that contribute to their functionality and quality.
When designing multifamily house plans, several important points should be considered:
- Unit mix and size
- Building layout and configuration
- Common areas and amenities
- Energy efficiency and sustainability
- Structural integrity and safety
- Code compliance and accessibility
- Construction costs and budget
- Long-term maintenance and management
By carefully addressing these considerations, architects and developers can create multifamily house plans that meet the needs of residents, optimize space and resources, and ensure the long-term viability of the development.
Unit mix and size
Unit mix and size are crucial factors in multifamily house plans. The variety and dimensions of the units within a development determine its overall appeal and marketability to potential tenants or buyers.
- Number of bedrooms and bathrooms: The number of bedrooms and bathrooms in each unit is a primary consideration. A mix of unit sizes, from studios to multi-bedroom units, can cater to the diverse needs of different households and individuals.
- Square footage: The overall square footage of each unit determines its spaciousness and livability. Factors such as local market demand, construction costs, and building code requirements influence the optimal unit size.
- Layout and functionality: The layout of each unit should maximize space utilization and functionality. Efficient use of space, adequate storage, and natural light are essential for creating comfortable and livable units.
- Accessibility and adaptability: Multifamily house plans should consider accessibility features for individuals with disabilities and the potential for future adaptations to meet changing needs.
A well-balanced unit mix and appropriate unit sizes contribute to the overall success and marketability of a multifamily development. By carefully considering these factors, architects and developers can create housing options that meet the diverse needs of residents and optimize the value of the property.
Building layout and configuration
The building layout and configuration of multifamily house plans have a significant impact on the overall functionality, aesthetics, and livability of the development.
- Building footprint and setbacks: The building’s footprint and setbacks determine its placement on the site and its relationship to neighboring structures. Careful consideration should be given to factors such as sunlight exposure, privacy, and access to outdoor spaces.
- Number of stories: The number of stories in a multifamily building affects the overall height and density of the development. Low-rise buildings with fewer stories offer a more intimate and neighborhood-friendly scale, while high-rise buildings can maximize density and provide panoramic views.
- Unit arrangement: The arrangement of units within the building influences factors such as privacy, natural light, and cross-ventilation. Common configurations include side-by-side units, stacked units, and courtyard designs.
- Common areas and amenities: Multifamily house plans often incorporate common areas and amenities to enhance the living experience for residents. These may include lobbies, elevators, laundry facilities, fitness centers, and outdoor recreation areas.
A well-conceived building layout and configuration contribute to the overall livability, desirability, and value of a multifamily development. By carefully considering these factors, architects and developers can create buildings that meet the needs of residents and maximize the potential of the site.
Common areas and amenities
Multifamily house plans often incorporate common areas and amenities to enhance the living experience for residents. These shared spaces and facilities provide opportunities for socialization, recreation, and convenience, contributing to the overall desirability and value of the development.
- Lobby and reception area: The lobby is a welcoming and functional space that serves as the main entrance to the building. It may include a reception desk, seating areas, and amenities such as a concierge or package delivery services.
- Elevators and stairs: Multi-story buildings require elevators to provide convenient access to upper floors. Well-maintained and efficient elevators ensure accessibility and enhance the overall functionality of the building.
- Laundry facilities: Shared laundry facilities are a common amenity in multifamily developments, offering residents convenient and cost-effective access to laundry equipment.
- Fitness centers: On-site fitness centers provide residents with convenient and affordable access to workout equipment and fitness classes, promoting healthy and active lifestyles.
In addition to these core amenities, multifamily house plans may also include a range of other common areas and amenities, such as:
- Courtyards and outdoor spaces: Outdoor spaces provide residents with areas for relaxation, recreation, and socialization. Courtyards, balconies, and rooftop terraces can enhance the livability and desirability of multifamily developments.
- Community rooms and clubhouses: These shared spaces can be used for social gatherings, events, or meetings, fostering a sense of community among residents.
- Business centers: Business centers offer residents access to computers, printers, and other office equipment, providing convenience and support for those who work from home or need a dedicated workspace.
- Guest suites: Guest suites provide temporary accommodations for visitors or family members of residents, offering added convenience and flexibility.
By incorporating a well-rounded selection of common areas and amenities, multifamily house plans create a more enjoyable and fulfilling living experience for residents, contributing to the overall success and desirability of the development.
Energy efficiency and sustainability
Energy efficiency and sustainability are increasingly important considerations in multifamily house plans. By incorporating sustainable design principles and energy-efficient features, developers and architects can create buildings that minimize environmental impact, reduce operating costs, and enhance the overall well-being of residents.
- Energy-efficient appliances and systems: Multifamily house plans can specify energy-efficient appliances, lighting systems, and HVAC systems. These measures reduce energy consumption and lower utility costs for residents, contributing to long-term savings and environmental sustainability.
- Renewable energy sources: Incorporating renewable energy sources, such as solar panels or geothermal systems, can significantly reduce the building’s reliance on fossil fuels. This not only lowers greenhouse gas emissions but also provides a hedge against rising energy costs.
- Sustainable building materials: Using sustainable building materials, such as recycled or locally sourced materials, can reduce the environmental impact of construction. These materials often have lower embodied energy and contribute to a healthier indoor environment.
- Water conservation measures: Water conservation measures, such as low-flow fixtures and rainwater harvesting systems, can reduce water usage and promote sustainable water management. These measures can be particularly important in regions with water scarcity or drought conditions.
By embracing energy efficiency and sustainability in multifamily house plans, developers and architects can create buildings that are not only environmentally responsible but also financially savvy and attractive to environmentally conscious tenants and buyers.
Structural integrity and safety
Foundation and load-bearing elements
The foundation of a multifamily house plan is the structural basis upon which the entire building rests. It must be designed to safely support the weight of the building, including all its occupants, fixtures, and potential additional loads such as snow or wind. Common foundation types for multifamily buildings include concrete slabs, spread footings, and pile foundations. Load-bearing elements, such as columns, beams, and shear walls, are carefully positioned throughout the structure to transfer loads from the upper floors and roof to the foundation.
Lateral force resistance
Multifamily house plans must be designed to resist lateral forces, such as those caused by wind or earthquakes. Lateral force resistance is achieved through a combination of structural elements, including shear walls, moment frames, and braced frames. Shear walls are vertical elements that resist lateral forces by transferring them to the foundation, while moment frames and braced frames are horizontal elements that resist lateral forces by bending or deforming.
Fire safety
Fire safety is paramount in multifamily house plans. Building codes and fire safety regulations mandate the use of fire-resistant materials and construction methods to minimize the spread of fire. Fire-rated walls and doors compartmentalize the building into smaller sections, preventing the rapid spread of fire and smoke. Fire sprinklers, smoke detectors, and fire alarm systems provide early detection and suppression of fires.
Life safety and accessibility
Multifamily house plans must incorporate life safety features to ensure the safety of occupants in the event of an emergency. These features include clearly marked and well-lit exit paths, emergency lighting, and fire escapes. Accessibility features, such as ramps, elevators, and accessible units, are also essential for ensuring that all residents have safe and equitable access to the building.
Code compliance and accessibility
Multifamily house plans must adhere to building codes and accessibility regulations to ensure the health, safety, and well-being of occupants. These codes and regulations provide minimum standards for structural integrity, fire safety, and accessibility, among other aspects.
- Building codes: Building codes establish minimum requirements for the design, construction, and maintenance of buildings. These codes are developed by national, state, and local authorities to ensure that buildings are safe, habitable, and energy-efficient. Compliance with building codes is essential for obtaining building permits and ensuring the safety of occupants.
- Fire codes: Fire codes regulate the construction and use of buildings to minimize the risk of fire and protect occupants in the event of a fire. Fire codes specify requirements for fire-rated materials, fire suppression systems, and emergency egress. Compliance with fire codes is crucial for ensuring the safety of occupants and preventing the spread of fire.
- Accessibility codes: Accessibility codes ensure that buildings are accessible to individuals with disabilities. These codes specify requirements for ramps, elevators, accessible units, and other features that facilitate access and mobility for all occupants. Compliance with accessibility codes is essential for creating inclusive and equitable living environments.
- Energy codes: Energy codes establish minimum standards for energy efficiency in buildings. These codes regulate the use of energy-efficient appliances, lighting systems, and building envelopes. Compliance with energy codes reduces energy consumption, lowers utility costs, and promotes sustainability.
By adhering to code compliance and accessibility regulations, multifamily house plans ensure the safety, well-being, and inclusivity of the building for all occupants.
Construction costs and budget
Construction costs and budget are critical considerations in multifamily house plans. Careful planning and budgeting are essential to ensure the financial viability and success of the development.
- Land acquisition: The cost of acquiring land for the development is a major expense. Factors such as location, size, and topography influence the land cost.
- Construction materials and labor: The cost of materials and labor accounts for a significant portion of the construction budget. Material selection, labor availability, and market conditions can impact these costs.
- Design complexity: The complexity of the design, including architectural features, structural requirements, and amenities, can affect construction costs. Simpler designs with fewer custom elements are generally more cost-effective.
- Permits and fees: Building permits, inspections, and other fees associated with the construction process can add to the overall cost.
It is important to conduct thorough research and analysis to accurately estimate construction costs and develop a realistic budget. Contingency funds should be included to cover unexpected expenses or market fluctuations.
Long-term maintenance and management
Long-term maintenance and management are crucial aspects of multifamily house plans to ensure the durability, functionality, and value of the development. A well-planned maintenance and management program helps to preserve the building’s structural integrity, systems, and common areas, and contributes to the overall satisfaction and well-being of residents.
Preventive maintenance: Regular inspections and maintenance tasks are essential to prevent minor issues from escalating into major problems. Preventive maintenance includes tasks such as inspecting and cleaning HVAC systems, plumbing fixtures, and electrical components. By addressing potential issues early on, maintenance teams can extend the lifespan of building systems and reduce the risk of costly repairs.
Repair and replacement: As buildings age, repairs and replacements become necessary to maintain their functionality and safety. These may include repairs to the roof, exterior cladding, or common areas. Regular inspections help to identify potential issues early on, allowing for timely repairs and replacements before they become more extensive and expensive.
Capital improvements: Over time, buildings may require major upgrades or renovations to maintain their desirability and functionality. Capital improvements can include upgrades to building systems, such as energy-efficient appliances or security systems, or renovations to common areas to enhance resident amenities. Proper planning and budgeting for capital improvements ensure that the building remains competitive in the market and meets the evolving needs of residents.










Related Posts