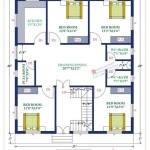
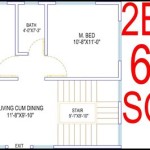
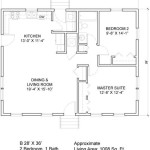
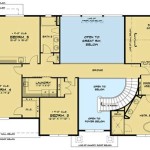
In the realm of architecture, basic house plans serve as foundational blueprints that outline the skeletal structure and layout of a residential building. These plans provide a comprehensive overview of the house’s dimensions, room arrangements, and functional spaces. For instance, a simple house plan might include details on the placement of the kitchen, living room, bedrooms, and bathrooms, as well as the location of doors, windows, and stairs.
Basic house plans are essential tools for architects, engineers, and builders alike, as they guide the construction process and ensure that the house meets the specific needs and requirements of its occupants. They play a crucial role in determining the overall livability, functionality, and aesthetic appeal of the home.
In this article, we will explore the key elements and considerations involved in basic house plans, providing valuable insights for homeowners and professionals engaged in the design and construction of residential dwellings.
Basic house plans encompass a range of important elements and considerations that shape the design and functionality of a residential dwelling.
- Room layout
- Space allocation
- Structural integrity
- Material selection
- Energy efficiency
- Accessibility features
- Aesthetics and style
- Building codes
- Sustainability
- Cost implications
Understanding these key points is essential for creating house plans that meet the specific needs and requirements of homeowners while ensuring a safe, comfortable, and aesthetically pleasing living space.
Room layout
Room layout refers to the arrangement and placement of rooms within a house plan. It is a crucial aspect that determines the functionality, flow, and overall livability of the home.
- Space allocation:
Room layout involves carefully allocating space to different rooms based on their intended use and size requirements. This includes determining the dimensions, shape, and placement of each room to ensure efficient use of space and comfortable living conditions.
- Traffic flow:
A well-planned room layout considers the flow of movement throughout the house. It aims to create a smooth and logical transition between rooms, avoiding bottlenecks or awkward pathways. Proper traffic flow enhances the overall usability and convenience of the home.
- Natural lighting:
Room layout should take advantage of natural lighting to create bright and inviting spaces. Positioning rooms with windows or skylights in strategic locations allows for maximum sunlight penetration, reducing the need for artificial lighting and creating a more energy-efficient home.
- Privacy and noise control:
Room layout should consider the privacy and noise levels of different spaces. Bedrooms and bathrooms, for example, should be placed in quieter areas away from high-traffic zones like the living room or kitchen. Proper placement of walls, doors, and windows can help minimize noise transmission and create private and peaceful environments.
Optimizing room layout is a complex task that requires careful planning and consideration of various factors. By following these principles, homeowners and architects can create house plans that maximize space utilization, enhance traffic flow, and provide a comfortable and functional living environment.
Space allocation
Space allocation in basic house plans refers to the careful distribution of available space among different rooms and functional areas to ensure efficient and comfortable living. It involves determining the size, shape, and placement of each room based on its intended use and the overall flow of the house.
Proper space allocation considers the following key factors:
- Number of occupants: The number of people living in the house influences the amount of space required for bedrooms, bathrooms, and common areas.
- Lifestyle and needs: The lifestyle and daily routines of the occupants should be taken into account to determine the size and layout of rooms dedicated to specific activities, such as cooking, dining, entertaining, or working from home.
- Storage requirements: Adequate storage space is essential for keeping the house organized and clutter-free. Space allocation should include designated areas for closets, cabinets, pantries, and other storage solutions.
Space allocation also involves considering the relationship and proximity of different rooms. For example, the kitchen should be conveniently located near the dining area, and bedrooms should be placed away from high-traffic zones like the living room or entryway to ensure privacy and quiet.
Optimizing space allocation is crucial for creating a house plan that meets the specific needs and requirements of the homeowners. By carefully considering the factors discussed above, architects and homeowners can design homes that maximize space utilization, enhance functionality, and provide a comfortable and livable environment.
Structural integrity
Structural integrity refers to the ability of a house to withstand various loads and forces without compromising its stability or safety. It is a critical aspect of basic house plans as it ensures the long-term durability and reliability of the structure.
- Foundation:
The foundation is the base of the house and plays a crucial role in its structural integrity. It must be strong enough to support the weight of the entire structure, including walls, roof, and occupants. Factors such as soil conditions, climate, and seismic activity must be considered when designing the foundation.
- Framing:
The framing consists of the skeletal structure of the house, including walls, floors, and roof. It provides the framework for the house and must be designed to withstand both vertical loads (gravity) and lateral loads (wind and earthquakes). The choice of framing materials, such as wood, steel, or concrete, depends on the size and complexity of the house.
- Load-bearing walls:
Load-bearing walls are structural walls that support the weight of the house above them. They must be properly designed and constructed to ensure the stability of the structure. Non-load-bearing walls, on the other hand, do not carry any significant weight and can be moved or altered without compromising the structural integrity of the house.
- Roof system:
The roof system protects the house from the elements and must be designed to withstand wind, rain, snow, and other environmental factors. It consists of the roof structure, roofing materials, and gutters and downspouts. Proper drainage is essential to prevent water damage and ensure the longevity of the roof.
Ensuring structural integrity is paramount in basic house plans. By carefully considering the factors discussed above, architects and engineers can design homes that are safe, durable, and capable of withstanding the various loads and forces they may encounter throughout their lifespan.
Material selection
Material selection is a crucial aspect of basic house plans as it determines the durability, energy efficiency, and aesthetic appeal of the structure. The choice of materials affects various elements of the house, including the foundation, framing, exterior cladding, roofing, and interior finishes.
Foundation:
The foundation is typically made of concrete, which provides strength and stability to the entire structure. Concrete is resistant to moisture, fire, and insects, making it a durable and reliable choice. In some cases, alternative materials such as treated wood or steel may be used for the foundation, depending on the soil conditions and climate.
Framing:
The framing of the house can be constructed using various materials, including wood, steel, or concrete. Wood is a traditional and cost-effective option that is easy to work with and provides good insulation. Steel framing is stronger and more durable than wood, but it is also more expensive. Concrete framing is the most durable and fire-resistant option, but it is also the most expensive and labor-intensive.
Exterior cladding:
Exterior cladding materials protect the house from the elements and contribute to its overall aesthetic appeal. Common cladding materials include vinyl, fiber cement, brick, and wood. Vinyl is a low-maintenance and affordable option that is available in a wide range of colors and styles. Fiber cement is a durable and fire-resistant material that resembles wood or stucco. Brick is a classic and timeless option that provides excellent durability and insulation. Wood cladding offers a natural and rustic look, but it requires regular maintenance and is susceptible to moisture damage.
Material selection for basic house plans is a complex process that involves careful consideration of factors such as cost, durability, energy efficiency, and aesthetic preferences. By carefully weighing the pros and cons of different materials, homeowners and architects can make informed decisions that will ensure the long-term performance and appeal of their homes.
Energy efficiency
Energy efficiency is a crucial aspect of basic house plans as it directly impacts the environmental footprint and operating costs of the home. By incorporating energy-efficient features into the design, homeowners can reduce their energy consumption, lower their utility bills, and contribute to a more sustainable built environment.
- Insulation:
Insulation is a key factor in reducing heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer. Proper insulation in the walls, roof, and floor can significantly improve the energy efficiency of the home. Common insulation materials include fiberglass, cellulose, and spray foam.
- Windows and doors:
Windows and doors are another important source of heat loss and gain. Energy-efficient windows and doors are designed to minimize air leakage and heat transfer. Look for windows with double or triple glazing, low-e coatings, and ENERGY STAR certification.
- HVAC systems:
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems account for a significant portion of energy consumption in homes. Energy-efficient HVAC systems, such as heat pumps and geothermal systems, can reduce energy usage and improve indoor comfort.
- Lighting:
Lighting is another area where energy savings can be made. Energy-efficient lighting fixtures, such as LED and CFL bulbs, use less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs and last longer.
Incorporating energy-efficient features into basic house plans is essential for creating homes that are sustainable, comfortable, and cost-effective to operate. By considering the factors discussed above, architects and homeowners can design homes that minimize energy consumption and create a more environmentally friendly living environment.
Accessibility features
Accessibility features in basic house plans are essential for creating homes that are safe, comfortable, and accessible for people of all abilities, including those with disabilities or impairments. By incorporating these features into the design, architects and homeowners can ensure that everyone can live independently and with dignity in their own homes.
- Ramped entrances:
Ramps provide an alternative to stairs, making it easier for people with mobility impairments to enter and exit the home. Ramps should be designed with a gentle slope and non-slip surfaces for safety.
- Wide doorways:
Wide doorways allow for easier access for wheelchairs and other mobility aids. Standard doorways are typically 32 inches wide, but accessible doorways should be at least 36 inches wide.
- Zero-threshold showers:
Zero-threshold showers eliminate the step or curb at the entrance to the shower, making it easier for people with mobility impairments to enter and exit. These showers also provide a more seamless and accessible bathing experience.
- Grab bars:
Grab bars provide support and stability in bathrooms and other areas where falls are a risk. They can be installed near toilets, showers, and bathtubs to assist people with balance issues or limited mobility.
Incorporating accessibility features into basic house plans is not only a legal requirement in many jurisdictions but also a moral imperative. By creating accessible homes, we can ensure that everyone has the opportunity to live independently and with dignity, regardless of their abilities.
Aesthetics and style
Aesthetics and style play a significant role in basic house plans, as they influence the overall appearance and character of the home. Homeowners have a wide range of options to choose from, depending on their personal preferences and the architectural style of their neighborhood.
- Architectural style:
The architectural style of a house refers to its overall design and form. Common architectural styles include traditional, contemporary, modern, and Craftsman. Each style has its own distinct characteristics, such as rooflines, window shapes, and exterior finishes.
- Exterior finishes:
Exterior finishes, such as siding, roofing, and trim, contribute to the overall aesthetic appeal of the home. Homeowners can choose from a variety of materials, colors, and textures to create a unique and personalized look.
- Landscaping:
Landscaping is an essential element of a home’s exterior design. Well-designed landscaping can enhance the curb appeal of the home and create a harmonious relationship between the house and its surroundings.
- Interior finishes:
Interior finishes, such as paint colors, flooring, and fixtures, play a crucial role in creating the desired ambiance and style within the home. Homeowners can choose from a wide range of options to reflect their personal taste and create a comfortable and inviting living space.
By carefully considering aesthetics and style in basic house plans, homeowners can create homes that are not only functional and comfortable but also visually appealing and reflective of their own unique personality and style.
Building codes
Building codes are a set of regulations that govern the design, construction, and alteration of buildings to ensure their safety, structural integrity, and habitability. They are established by local, state, and national authorities to protect the public from unsafe or unhealthy building practices.
- Structural safety:
Building codes set minimum standards for structural safety to ensure that buildings can withstand various loads and forces, such as gravity, wind, earthquakes, and snow. These codes specify requirements for the design and construction of foundations, framing, walls, and roofs to ensure the stability and integrity of the structure.
- Fire safety:
Building codes include provisions to minimize the risk of fire and its spread within buildings. These provisions include requirements for fire-resistant materials, fire-rated assemblies, and fire suppression systems. The goal is to protect occupants from injury or death in the event of a fire and to prevent the spread of fire to neighboring buildings.
- Health and sanitation:
Building codes also address health and sanitation issues to ensure that buildings are habitable and promote the well-being of occupants. These provisions include requirements for adequate ventilation, natural lighting, plumbing systems, and waste disposal systems. The aim is to create healthy and comfortable indoor environments that minimize the risk of illness or disease.
- Energy efficiency:
In response to growing concerns about energy consumption and climate change, many building codes now include provisions to improve the energy efficiency of buildings. These provisions may include requirements for insulation, energy-efficient appliances and lighting, and renewable energy systems. The goal is to reduce the environmental impact of buildings and lower energy costs for occupants.
Adhering to building codes is essential for ensuring the safety, functionality, and habitability of basic house plans. By incorporating these regulations into the design process, architects and builders can create homes that meet the minimum standards set by local authorities and provide a safe and healthy living environment for occupants.
Sustainability
Sustainability in basic house plans refers to the design and construction of homes that minimize their environmental impact and promote the well-being of occupants. By incorporating sustainable features into the design process, architects and homeowners can create homes that are energy-efficient, resource-conserving, and healthy to live in.
- Energy efficiency:
Energy efficiency is a key aspect of sustainable house plans. By incorporating energy-efficient features, such as insulation, energy-efficient appliances and lighting, and renewable energy systems, homes can consume less energy and reduce their carbon footprint. This not only benefits the environment but also lowers energy costs for occupants.
- Water conservation:
Water conservation is another important aspect of sustainable house plans. By incorporating water-saving fixtures and appliances, such as low-flow toilets, faucets, and showerheads, homes can reduce their water consumption and minimize their impact on water resources. Rainwater harvesting systems can also be incorporated to collect and reuse rainwater for irrigation or other non-potable uses.
- Material selection:
The choice of building materials has a significant impact on the sustainability of a house. Sustainable materials, such as recycled or renewable materials, can reduce the environmental impact of the construction process. Sustainable materials are often more durable and have lower maintenance costs, which can benefit homeowners in the long run.
- Indoor air quality:
Indoor air quality is an important factor for the health and well-being of occupants. Sustainable house plans incorporate features to improve indoor air quality, such as natural ventilation, low-VOC (volatile organic compound) materials, and air purification systems. These features can reduce the risk of respiratory problems and other health issues associated with poor indoor air quality.
Incorporating sustainability into basic house plans is essential for creating homes that are not only environmentally friendly but also healthy and comfortable to live in. By considering the factors discussed above, architects and homeowners can design homes that minimize their environmental impact and promote the well-being of occupants for generations to come.
Cost implications
Cost implications play a significant role in the design and construction of basic house plans. Various factors related to the plan can impact the overall cost of the project, including the size and complexity of the house, the choice of materials and finishes, and the local construction costs.
Size and complexity: Larger houses with more rooms, intricate designs, and complex rooflines are generally more expensive to build than smaller, simpler homes. The cost of materials and labor increases with the size and complexity of the house, making it important for homeowners to carefully consider their needs and budget when determining the size and layout of their home.
Materials and finishes: The choice of materials and finishes used in the construction of a house can significantly impact the overall cost. Higher-quality materials, such as hardwood floors, granite countertops, and custom cabinetry, are more expensive than standard or budget-friendly options. Homeowners should research the cost of different materials and finishes and make informed decisions based on their budget and preferences.
Local construction costs: Construction costs vary depending on the location of the project. Factors such as labor rates, material availability, and local building codes can influence the cost of construction. Homeowners should consult with local contractors and builders to get an accurate estimate of the construction costs in their area.
Understanding the cost implications related to basic house plans is essential for homeowners to make informed decisions during the design and construction process. By carefully considering the factors discussed above, homeowners can develop a realistic budget and choose a house plan that meets their needs and financial constraints.










Related Posts