Plans To Build A Tiny House: Comprehensive Guidelines
The burgeoning popularity of tiny house living stems from a variety of factors, including a desire for financial freedom, reduced environmental impact, and a minimalist lifestyle. Embarking on the journey of building a tiny house requires meticulous planning, a solid understanding of construction principles, and adherence to local regulations. This article provides comprehensive guidelines for developing effective plans and successfully building a tiny house.
Before even considering the aesthetic aspects of a tiny house, a thorough assessment of personal needs and lifestyle is paramount. This involves considering factors such as the number of occupants, anticipated activities within the space, storage requirements, and any accessibility needs. A detailed inventory of possessions can help determine the necessary storage volume and minimize unnecessary clutter. Considering the intended location, whether it will be stationary or mobile, significantly impacts the design and construction process.
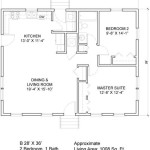
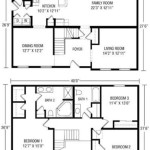
The design phase is crucial, encompassing the selection of appropriate dimensions, floor plan layout, material choices, and utility systems. Several online resources and software programs are available to assist in creating detailed plans, including 3D models and construction documentation. Careful consideration should be given to maximizing space efficiency through multi-functional furniture, vertical storage solutions, and strategic placement of windows for natural light. Selecting durable and sustainable building materials not only enhances the longevity of the tiny house but also minimizes its environmental footprint.
Key Point 1: Site Selection and Legal Considerations
The selection of a suitable site is a critical first step. If the intention is for the tiny house to be stationary, zoning regulations, building codes, and homeowner association rules must be carefully examined. Many municipalities have specific requirements regarding minimum dwelling sizes, setback distances, and utility connections. For mobile tiny houses, researching and adhering to relevant transportation regulations, including size and weight restrictions, is essential. Furthermore, understanding legal aspects related to parking or residing in a mobile tiny house on various properties is crucial to avoid potential legal issues.
Comprehensive due diligence concerning local zoning laws is indispensable. These laws often dictate the permissible uses of land and the types of structures allowed. Some areas may not permit tiny houses outright, while others may have specific requirements that must be met. It is advisable to consult with local planning officials and building inspectors to clarify any ambiguities and ensure compliance. Failure to comply with zoning regulations can result in fines, legal action, or even the forced removal of the tiny house.
Building codes are sets of regulations that establish minimum standards for the construction and safety of buildings. These codes cover various aspects of construction, including structural integrity, fire safety, electrical systems, plumbing, and ventilation. Tiny houses are often subject to the same building codes as conventional houses, although some jurisdictions may have specific provisions for smaller dwellings. Obtaining the necessary permits is a critical step in the building process. Permits ensure that the construction meets the required standards and provide legal authorization for the project. Applying for permits typically involves submitting detailed building plans and specifications to the local building department. Inspections are conducted at various stages of construction to verify compliance with the building codes.
Homeowner associations (HOAs) are private organizations that govern the rules and regulations within a specific community. If the tiny house is to be located within an HOA-governed area, it is essential to review the HOA's covenants, conditions, and restrictions (CC&Rs). These documents may contain restrictions on the size, design, or placement of homes within the community. Some HOAs may prohibit tiny houses altogether, while others may have specific architectural guidelines that must be followed. Obtaining approval from the HOA before starting construction is crucial to avoid potential conflicts.
For mobile tiny houses, transportation regulations play a significant role. Each state or province typically has regulations governing the size, weight, and lighting requirements for trailers and recreational vehicles. Exceeding these limits can result in fines or the requirement to obtain special permits. Additionally, the chosen towing vehicle must be appropriately sized and equipped to handle the weight of the tiny house. Regular maintenance of the trailer and towing vehicle is essential for safe transportation.
Key Point 2: Foundation and Structural Integrity
The foundation provides the critical base for the tiny house, bearing the weight of the structure and transferring it to the ground. The type of foundation chosen will depend on several factors, including site conditions, soil type, and whether the tiny house is intended to be stationary or mobile. Common foundation options include slab-on-grade foundations, pier and beam foundations, and trailer foundations. Each option has its advantages and disadvantages in terms of cost, complexity, and suitability for different site conditions.
Slab-on-grade foundations involve pouring a concrete slab directly onto the ground. This type of foundation is relatively inexpensive and easy to construct, but it can be susceptible to moisture issues if not properly insulated and waterproofed. Slab-on-grade foundations are best suited for stable, well-drained sites. Pier and beam foundations consist of concrete piers or posts that support a framework of beams. This type of foundation allows for better ventilation and drainage under the tiny house, which can help prevent moisture problems. Pier and beam foundations are suitable for sites with sloping terrain or poor soil conditions.
Trailer foundations are commonly used for mobile tiny houses. These foundations consist of a steel or aluminum frame with wheels and axles. Trailer foundations allow the tiny house to be easily towed from one location to another. However, trailer foundations can be less stable and require regular maintenance to ensure structural integrity. The structural integrity of the tiny house is paramount, ensuring that the building can withstand the forces of nature, including wind, snow, and earthquakes. Proper framing techniques and the use of high-quality building materials are essential. Walls, floors, and roofs should be designed to distribute loads evenly and prevent excessive stress on any one component.
Wall framing typically involves constructing a framework of wooden studs or metal studs. The spacing of the studs should be determined based on the structural loads and the type of sheathing used. Walls should be properly insulated to provide thermal comfort and energy efficiency. Floor framing typically consists of joists that are spaced according to the floor load requirements. Subflooring is then installed over the joists to create a solid surface. Roof framing can be either a sloped or flat design. Sloped roofs are more common in tiny houses as they provide better drainage and can accommodate attic space. The roof framing should be designed to withstand wind and snow loads.
Selecting appropriate building materials is crucial for ensuring the structural integrity and longevity of the tiny house. Wood is a common choice for framing due to its strength, availability, and ease of use. However, it is essential to use pressure-treated lumber for components that are in contact with the ground or exposed to moisture. Steel framing is another option that offers high strength and resistance to fire and pests. However, steel framing can be more expensive and require specialized tools and skills to install.
Key Point 3: Utility Systems and Energy Efficiency
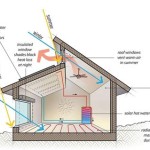
The integration of efficient utility systems is essential for making the tiny house comfortable and sustainable. This includes plumbing, electrical, heating, cooling, and ventilation systems. Careful planning and design are needed to optimize the use of space and minimize energy consumption. Water conservation measures, such as low-flow fixtures and rainwater harvesting systems, can significantly reduce water usage. Efficient appliances and lighting fixtures can minimize electricity consumption. These steps are essential for reducing utility bills and environmental impact.
Plumbing systems in tiny houses typically consist of a water supply system, a drainage system, and a wastewater treatment system. The water supply system provides potable water for drinking, cooking, and bathing. The drainage system removes wastewater from sinks, showers, and toilets. The wastewater treatment system processes the wastewater before it is discharged into a septic system or sewer system. Water-saving fixtures, such as low-flow showerheads, toilets, and faucets, can significantly reduce water consumption. Tankless water heaters provide hot water on demand and eliminate the need for a storage tank, saving space and energy. Rainwater harvesting systems can collect rainwater from the roof and store it for non-potable uses, such as irrigation and toilet flushing.
Electrical systems in tiny houses typically consist of a power source, a distribution panel, wiring, and outlets. The power source can be either grid electricity or off-grid sources, such as solar panels, wind turbines, or generators. The distribution panel distributes electricity to different circuits throughout the tiny house. Wiring carries electricity from the distribution panel to outlets, switches, and appliances. Energy-efficient appliances, such as LED lighting, Energy Star refrigerators, and induction cooktops, can significantly reduce electricity consumption. Solar panels can generate electricity from sunlight, reducing reliance on grid electricity. Batteries can store excess solar energy for use during periods of low sunlight.
Heating, cooling, and ventilation systems are essential for maintaining a comfortable indoor environment in the tiny house. Heating systems provide warmth during cold weather. Cooling systems provide cooling during hot weather. Ventilation systems remove stale air and bring in fresh air. Efficient heating and cooling systems, such as mini-split heat pumps, can provide both heating and cooling with high energy efficiency. Properly insulating the tiny house can reduce heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer, reducing the need for heating and cooling. A well-designed ventilation system can remove moisture and pollutants from the air, improving indoor air quality.
Energy efficiency is a key consideration in tiny house design and construction. Maximizing insulation, minimizing air leaks, and using energy-efficient appliances and lighting can significantly reduce energy consumption. Passive solar design principles can be used to take advantage of natural sunlight for heating and daylighting. Orienting the tiny house to maximize solar gain in the winter and minimize solar gain in the summer can reduce heating and cooling loads. Planting trees and shrubs around the tiny house can provide shade and reduce the urban heat island effect. These measures help to create a comfortable and sustainable living environment.

Tiny Houses The Comprehensive Guide To Living In A House With Examples And Ideas Of Designs Hardcover
Tiny Homes Build Your Home Live Off Grid In House Today Become A Minamilist And Travel Micro Shelter With Floor Plans By Jim Gears 2024 Trade

Tiny House Decisions The

Tiny House Design Construction Guide Your To Building A Mortgage Free 9780997288704

Designing And Building Your Tiny Farmhouse A Comprehensive Guide

The Planning Stage Of Building A Tiny House

The Tiny Project Modern House Plans

How To Choose The Right Tiny Home For You A Comprehensive Guide Central

Designing And Building Your Tiny Farmhouse A Comprehensive Guide

Tips For Building The Most Cost Effective Tiny House
Related Posts