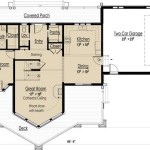
Homestead Style House Plans are meticulously designed blueprints that serve as comprehensive guidelines for constructing a homestead-style dwelling. These plans incorporate essential features that cater to the specific needs of homesteaders, individuals who live off the land and strive for self-sufficiency. They are a blend of functionality, efficiency, and sustainability, maximizing the home’s potential as a hub for food production, shelter, and other homesteading activities.
Homesteaders often seek out plans that optimize space utilization, allowing for the integration of living quarters, workshops, storage areas, and agricultural spaces within a single structure. By incorporating a thoughtful layout and intelligent design, these plans enhance the efficiency of daily tasks and foster a harmonious balance between work and life.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the key elements of Homestead Style House Plans, exploring their unique characteristics, benefits, and practical applications. We will also provide insights into the planning process, ensuring that your homestead-style home aligns with your specific needs and aspirations.
Homestead Style House Plans encompass a range of important considerations:
- Functional design
- Energy efficiency
- Sustainable materials
- Adaptability to climate
- Multipurpose spaces
- Resilient construction
- Water conservation
- Food production integration
- Community-oriented design
These elements collectively contribute to creating homesteads that are self-sufficient, sustainable, and enriching.
Functional design
Functional design is a cornerstone of Homestead Style House Plans. Every aspect of the home’s layout and features is meticulously considered to maximize efficiency, practicality, and comfort. The goal is to create a living space that seamlessly integrates with the homesteading lifestyle, supporting daily tasks and activities.
One key element of functional design is the incorporation of multipurpose spaces. These flexible areas can serve multiple purposes, adapting to the changing needs of the homesteaders. For example, a mudroom can double as a laundry room, providing a convenient and efficient space for managing outdoor gear and clothing. Similarly, a kitchen can be designed to seamlessly connect with a pantry or root cellar, ensuring easy access to food storage.
Another important aspect is the thoughtful placement of windows and doors. Natural light and ventilation are essential for creating a healthy and comfortable living environment. Well-positioned windows can harness passive solar energy, reducing heating costs in colder climates. Cross-ventilation promotes air circulation, improving indoor air quality and reducing the need for artificial cooling.
Finally, functional design also considers the flow of movement within the home. The layout should allow for easy and efficient transitions between different areas, minimizing wasted steps and maximizing convenience. This is especially important for homesteaders who may be carrying heavy loads or equipment throughout the day.
By incorporating these principles of functional design, Homestead Style House Plans create homes that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also highly practical and supportive of the homesteading lifestyle.
Energy efficiency
Energy efficiency is a crucial consideration in Homestead Style House Plans. Homesteaders often strive to reduce their reliance on external energy sources and live more sustainably. By incorporating energy-efficient features into the design of their homes, they can significantly lower their energy consumption and utility bills.
- Insulation and air sealing
Proper insulation and air sealing are essential for minimizing heat loss and air infiltration. This helps to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature year-round, reducing the need for heating and cooling systems. Homestead Style House Plans typically incorporate high-performance insulation materials in walls, ceilings, and floors, as well as measures to seal gaps around windows, doors, and other openings.
- Passive solar design
Passive solar design takes advantage of the sun’s energy to heat and light the home naturally. Homes are oriented to maximize solar exposure, and windows are strategically placed to capture sunlight. Thermal mass, such as concrete or stone, is often incorporated into the design to absorb and store solar heat, releasing it gradually throughout the day.
- Energy-efficient appliances and systems
Homestead Style House Plans prioritize the use of energy-efficient appliances and systems. This includes high-efficiency refrigerators, dishwashers, washing machines, and lighting fixtures. Energy-efficient heating and cooling systems, such as heat pumps and geothermal systems, can also significantly reduce energy consumption.
- Renewable energy sources
Many Homestead Style House Plans incorporate renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines, to generate electricity and reduce reliance on the grid. These systems can provide clean, sustainable energy for the home, further reducing energy costs and environmental impact.
By implementing these energy-efficient measures, Homestead Style House Plans create homes that are not only comfortable and sustainable but also cost-effective to operate. This allows homesteaders to live more independently and reduce their overall energy footprint.
In addition to the points listed above, Homestead Style House Plans often consider other factors that contribute to energy efficiency, such as the use of natural building materials, proper ventilation, and efficient water management systems. By taking a holistic approach to energy efficiency, these plans help homesteaders create truly sustainable and resilient homes.
Sustainable materials
Sustainable materials play a vital role in Homestead Style House Plans. Homesteaders are often committed to living in harmony with the environment and minimizing their ecological impact. By incorporating sustainable materials into their homes, they can create healthier, more durable, and more environmentally friendly living spaces.
- Recycled and reclaimed materials
Homestead Style House Plans often incorporate recycled and reclaimed materials, such as salvaged lumber, bricks, and roofing materials. These materials not only reduce waste and conserve natural resources, but they can also add character and charm to the home. Recycled and reclaimed materials can be used in a variety of applications, including flooring, countertops, and cabinetry.
- Natural and renewable materials
Natural and renewable materials, such as wood, bamboo, and cork, are popular choices for Homestead Style House Plans. These materials are biodegradable and have a lower environmental impact than synthetic materials. They can be used in a variety of applications, including framing, siding, and flooring. Natural materials also contribute to a healthier indoor environment, as they do not emit harmful chemicals or toxins.
- Low-VOC materials
Homestead Style House Plans prioritize the use of low-VOC (volatile organic compound) materials. VOCs are chemicals that can be harmful to human health and the environment. They are found in many building materials, including paints, finishes, and adhesives. By choosing low-VOC materials, homesteaders can reduce their exposure to these harmful chemicals and create a healthier indoor environment.
- Locally sourced materials
Homestead Style House Plans often incorporate locally sourced materials to reduce transportation costs and support the local economy. Using materials that are produced or harvested nearby can also reduce the environmental impact associated with transportation and distribution. Local materials can include lumber, stone, and other natural resources.
By incorporating sustainable materials into their homes, homesteaders can create living spaces that are not only beautiful and comfortable but also environmentally responsible. Sustainable materials contribute to a healthier indoor environment, reduce the ecological impact of the home, and support a more sustainable lifestyle.
Adaptability to climate
Homestead Style House Plans are designed to be adaptable to a variety of climates, ensuring that homesteaders can create comfortable and sustainable living spaces regardless of their location.
Passive solar design is a key element of climate adaptability. By carefully orienting the home to take advantage of the sun’s energy, homesteaders can reduce their reliance on heating and cooling systems. In colder climates, south-facing windows and thermal mass can help to absorb and store solar heat, releasing it gradually throughout the day. In warmer climates, overhangs and shading devices can be used to minimize solar heat gain and keep the home cool.
Proper insulation and air sealing are also essential for climate adaptability. In colder climates, adequate insulation helps to prevent heat loss and maintain a comfortable indoor temperature. In warmer climates, insulation can help to reduce heat gain and keep the home cool. Air sealing measures, such as weatherstripping and caulking, help to prevent drafts and air infiltration, further improving energy efficiency.
Climate-appropriate building materials are another important consideration. In areas with extreme temperatures, durable materials that can withstand heat, cold, and moisture are essential. For example, in hot and humid climates, moisture-resistant materials and finishes can help to prevent mold and mildew growth. In cold climates, materials with high thermal resistance can help to minimize heat loss and keep the home warm.
By incorporating these climate-adaptive features into their Homestead Style House Plans, homesteaders can create homes that are comfortable, energy-efficient, and resilient to the challenges of their local climate.
Multipurpose spaces
Homestead Style House Plans often incorporate multipurpose spaces to maximize space utilization and accommodate the diverse needs of homesteaders. These flexible areas can serve multiple functions, adapting to changing needs and activities throughout the day.
One common example of a multipurpose space is a mudroom. This entryway serves as a transition zone between the outdoors and the home’s interior. It provides a convenient space for storing outdoor gear, such as boots, coats, and tools. The mudroom can also double as a laundry room, with space for a washer, dryer, and utility sink. By combining these functions, homesteaders can streamline their daily routines and minimize clutter.
Another example of a multipurpose space is a great room. This open-concept area combines the functions of a living room, dining room, and kitchen. The great room provides a spacious and inviting gathering space for family and friends. It can also serve as a homeschooling area, a home office, or a workshop. The flexibility of the great room allows homesteaders to adapt the space to their specific needs and activities.
Homestead Style House Plans may also incorporate multipurpose outbuildings. These detached structures can serve a variety of functions, such as a garage, workshop, storage shed, or guest house. By locating these functions in an outbuilding, homesteaders can free up space in their main house and create dedicated areas for specific activities. Outbuildings can also be designed to be energy-efficient and sustainable, further supporting the homesteading lifestyle.
Multipurpose spaces are an essential element of Homestead Style House Plans. By incorporating these flexible areas into their homes, homesteaders can create functional and adaptable living spaces that support their unique needs and aspirations.
Resilient construction
Homestead Style House Plans prioritize resilient construction methods to ensure that the home can withstand the elements and provide a safe and secure shelter for homesteaders. Resilient construction involves using durable materials, sound building practices, and design features that enhance the home’s ability to resist damage from natural disasters and other threats.
- Strong foundation and framing
The foundation and framing of a homestead should be designed to withstand the specific threats and hazards present in the local climate. In areas prone to earthquakes, for example, the foundation should be reinforced with concrete piers and the framing should be engineered to resist seismic forces. In areas prone to hurricanes and high winds, the framing should be reinforced with hurricane straps and the roof should be designed to resist wind uplift.
- Durable exterior materials
The exterior materials used in a homestead should be resistant to moisture, pests, and fire. Siding materials such as fiber cement, metal, or stucco can provide excellent protection from the elements. Roofing materials such as metal or tile can withstand high winds and resist fire. Windows and doors should be impact-resistant to protect against storms and other hazards.
- Redundant systems
Homestead Style House Plans often incorporate redundant systems to ensure that essential functions can be maintained even if one system fails. For example, a homestead may have a backup generator to provide electricity in the event of a power outage. A rainwater harvesting system can provide a backup water supply in the event of a drought or contamination of the main water source. Redundant systems provide peace of mind and help homesteaders to maintain their self-sufficiency even in challenging circumstances.
- Fire-resistant design
Homesteads are often located in rural areas where access to fire services may be limited. Therefore, it is essential to incorporate fire-resistant design features into the home. This includes using fire-resistant building materials, installing smoke detectors and fire alarms, and creating defensible space around the home to reduce the risk of wildfire.
By incorporating resilient construction methods into their Homestead Style House Plans, homesteaders can create homes that are safe, durable, and able to withstand the challenges of their environment.
Water conservation
Water conservation is a critical consideration in Homestead Style House Plans, especially in areas where water resources are scarce. By incorporating water-efficient fixtures, systems, and design features, homesteaders can reduce their water consumption, protect local water sources, and ensure a sustainable water supply for their homestead.
- Rainwater harvesting
Rainwater harvesting is a sustainable and cost-effective way to collect and store rainwater for non-potable uses, such as irrigation, washing, and cleaning. Homestead Style House Plans often incorporate rainwater harvesting systems, which typically involve a roof catchment area, a storage tank, and a distribution system. Rainwater harvesting can significantly reduce reliance on municipal water supplies and help homesteaders to become more self-sufficient.
- Low-flow fixtures
Low-flow fixtures, such as toilets, faucets, and showerheads, use significantly less water than conventional fixtures without sacrificing performance. By installing low-flow fixtures throughout the home, homesteaders can reduce their water consumption without compromising their comfort or hygiene.
- Water-efficient landscaping
Water-efficient landscaping is an important aspect of Homestead Style House Plans. By choosing drought-tolerant plants and implementing water-saving irrigation techniques, homesteaders can reduce their outdoor water consumption. Xeriscaping, a type of landscaping that uses minimal water, is a popular choice for homesteaders in arid climates.
- Greywater systems
Greywater systems collect and reuse wastewater from sinks, showers, and bathtubs for irrigation and other non-potable uses. By implementing a greywater system, homesteaders can further reduce their reliance on municipal water supplies and conserve valuable water resources.
Incorporating these water conservation measures into Homestead Style House Plans helps homesteaders to live more sustainably and reduce their environmental impact. By using water wisely, homesteaders can protect local water sources, ensure a reliable water supply for their families, and contribute to a more water-secure future.
Food production integration
Homestead Style House Plans prioritize the integration of food production spaces and features to support homesteaders in growing their own food and achieving greater self-sufficiency. By incorporating these elements into the home’s design, homesteaders can create a seamless connection between their living quarters and their food sources.
One key aspect of food production integration is the inclusion of dedicated growing spaces within or adjacent to the home. This can include indoor grow rooms, greenhouses, or raised garden beds. Indoor grow rooms provide a controlled environment for growing plants year-round, regardless of the outdoor climate. Greenhouses extend the growing season and protect plants from pests and harsh weather conditions. Raised garden beds offer improved drainage and soil quality, making them ideal for growing vegetables, herbs, and fruits.
Another important consideration is the integration of food storage and preservation facilities. Homestead Style House Plans often incorporate pantries, root cellars, or other storage areas specifically designed to maintain the freshness and quality of homegrown produce. Pantries provide a cool, dry space for storing non-perishable foods, such as canned goods, grains, and legumes. Root cellars are underground storage spaces that maintain a consistent temperature and humidity, making them ideal for storing root vegetables, fruits, and other produce over long periods.
In addition to dedicated growing and storage spaces, Homestead Style House Plans may also include features that support food processing and preparation. This can include kitchens equipped with ample counter space, storage, and appliances for canning, preserving, and cooking. Outdoor kitchens or cooking areas allow homesteaders to process and prepare their harvests al fresco. By integrating these features into their home’s design, homesteaders can create a truly self-sufficient living environment where food production is seamlessly woven into their daily lives.
Community-oriented design
Homestead Style House Plans often incorporate community-oriented design elements to foster a sense of connection and collaboration among homesteaders. These features encourage social interaction, resource sharing, and mutual support, strengthening the bonds within the homesteading community.
One key aspect of community-oriented design is the inclusion of shared spaces and amenities. This can include communal kitchens, dining areas, meeting rooms, or outdoor gathering spaces. These shared spaces provide opportunities for homesteaders to connect with each other, share meals, host workshops, and engage in social activities. By creating a central hub for community interaction, Homestead Style House Plans promote a sense of belonging and foster a supportive network among residents.
Another important consideration is the integration of guest accommodations into the home’s design. Guest rooms or separate cabins allow homesteaders to host visitors, share their knowledge and skills, and build relationships with like-minded individuals. Welcoming guests into the homestead not only strengthens the local community but also provides opportunities for cultural exchange and collaboration.
Homestead Style House Plans also prioritize the creation of shared resources and infrastructure. This can include community gardens, tool libraries, or renewable energy systems. By pooling their resources, homesteaders can reduce individual costs, increase efficiency, and foster a sense of collective ownership and responsibility. Shared resources promote cooperation, reduce waste, and contribute to the overall sustainability of the homesteading community.
In addition to these physical elements, community-oriented design in Homestead Style House Plans also encompasses the promotion of social and cultural activities. This can include organizing regular potlucks, workshops, educational programs, or community events. By fostering a sense of shared purpose and values, homesteaders can create a vibrant and supportive community that extends beyond the individual homestead.










Related Posts