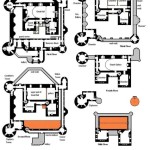
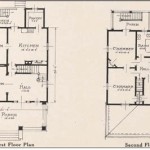
House Floor Plan Design: A Blueprint for Your Dream Home
House floor plan design refers to the architectural layout of a residential building, outlining the arrangement and dimensions of rooms, hallways, and other spaces within the structure. It serves as a blueprint for the construction and organization of a home, determining the flow of traffic, natural lighting, and functionality of living areas.
Whether designing a new home or renovating an existing one, a well-planned floor plan is crucial for creating a comfortable, efficient, and aesthetically pleasing living space. By carefully considering factors such as room placement, circulation patterns, and the desired lifestyle of the occupants, architects and designers can craft floor plans that enhance the quality of life and meet the specific needs of individuals and families.
House floor plan design encompasses a range of important considerations, including:
- Room placement: Optimizing the location and adjacency of rooms for functionality and privacy.
- Circulation patterns: Ensuring smooth and efficient flow of traffic throughout the home.
- Natural lighting: Maximizing access to natural light for a brighter and healthier living environment.
- Space planning: Allocating appropriate square footage to each room based on its intended use and occupants.
- Storage solutions: Incorporating adequate storage options to keep the home organized and clutter-free.
- Structural integrity: Ensuring the floor plan adheres to building codes and structural requirements.
- Accessibility: Considering the needs of individuals with disabilities and designing for universal accessibility.
- Aesthetic appeal: Creating a floor plan that reflects the desired architectural style and personal preferences.
- Energy efficiency: Incorporating energy-saving features such as passive solar design and efficient window placement.
- Future expansion: Planning for potential future additions or renovations to the home.
By carefully addressing these aspects, architects and homeowners can create well-planned floor plans that enhance the functionality, comfort, and overall enjoyment of their living spaces.
Room placement: Optimizing the location and adjacency of rooms for functionality and privacy.
Room placement is a crucial aspect of house floor plan design as it directly impacts the functionality, privacy, and overall livability of the home. By carefully considering the location and adjacency of rooms, architects and homeowners can create a harmonious living environment that meets the specific needs of the occupants.
- Public and private zones: Separating public areas, such as the living room and kitchen, from private areas, such as bedrooms and bathrooms, ensures privacy and creates a sense of sanctuary within the home.
- Activity-based placement: Grouping rooms based on their function, such as placing all bedrooms together or situating the kitchen adjacent to the dining room, enhances convenience and efficiency.
- Circulation and flow: Optimizing the flow of traffic throughout the home is essential for daily living. Creating clear pathways and evitando bottlenecks between rooms improves accessibility and reduces congestion.
- Privacy considerations: Designing the floor plan to minimize noise and visual intrusion between rooms is important for privacy. For example, placing bedrooms away from noisy areas like the kitchen or garage, and providing visual barriers between bathrooms and other rooms, can help create a more private and peaceful living environment.
By thoughtfully considering these factors, architects and homeowners can create floor plans that maximize functionality, privacy, and the overall comfort and enjoyment of the home’s occupants.
Circulation patterns: Ensuring smooth and efficient flow of traffic throughout the home.
Creating smooth and efficient circulation patterns is essential for a well-functioning and comfortable home. By carefully planning the layout of rooms, hallways, and other spaces, architects and designers can ensure that occupants can move around the home safely, easily, and without congestion.
- Defined pathways: Clearly defined pathways throughout the home help to direct traffic and prevent bottlenecks. Wide hallways and open floor plans allow for easy movement, especially in high-traffic areas like the kitchen and living room.
- Natural flow: Designing the floor plan to follow a natural flow of movement enhances convenience and reduces the need for backtracking. For example, placing the kitchen adjacent to the dining room and living room creates a seamless transition between these commonly used spaces.
- Separate circulation paths: In larger homes, creating separate circulation paths for different activities can help to reduce congestion and improve privacy. For instance, a dedicated hallway for bedrooms can separate private areas from public areas.
- Minimize dead-end spaces: Dead-end spaces, such as long narrow hallways or isolated rooms, can disrupt the flow of traffic and create a sense of disorientation. Aim to design the floor plan with minimal dead-end spaces and ensure that all rooms are easily accessible.
By incorporating these principles into house floor plan design, architects and homeowners can create homes that are both functional and enjoyable to live in, where occupants can move around with ease and efficiency.
Natural lighting: Maximizing access to natural light for a brighter and healthier living environment.
Natural lighting plays a crucial role in creating a healthy and comfortable living environment. By carefully designing the floor plan to maximize access to natural light, architects and homeowners can create homes that are filled with sunlight, reducing the need for artificial lighting and providing numerous benefits for occupants.
- Improved mood and well-being: Exposure to natural light has been linked to improved mood, increased energy levels, and reduced stress. Designing homes with large windows and skylights allows occupants to connect with the outdoors and experience the positive effects of natural light.
- Reduced energy consumption: Natural light can significantly reduce the need for artificial lighting, especially during the daytime. By incorporating ample windows and skylights into the floor plan, homeowners can save energy and lower their utility bills.
- Enhanced visual comfort: Natural light provides superior visual comfort compared to artificial light. It reduces glare and harsh shadows, creating a more comfortable and inviting living environment.
- Health benefits: Natural light has been shown to have numerous health benefits, including regulating circadian rhythms, improving sleep quality, and boosting vitamin D production.
To maximize natural lighting in house floor plan design, architects and homeowners should consider the following strategies:
- Window placement: Placing windows strategically throughout the home ensures that all rooms receive adequate natural light. South-facing windows allow for maximum sunlight exposure, while windows on multiple walls can provide cross-ventilation and reduce heat gain.
- Skylights and solar tubes: Installing skylights or solar tubes in areas with limited access to natural light, such as interior rooms or hallways, can bring additional sunlight into the home.
- Light-colored interiors: Using light-colored paint, flooring, and furnishings helps to reflect and distribute natural light more effectively, creating a brighter and more spacious feel.
- Avoidance of obstructions: Minimizing obstructions, such as large furniture or heavy curtains, in front of windows allows for maximum natural light penetration.
By incorporating these strategies into house floor plan design, architects and homeowners can create homes that are filled with natural light, providing a healthier, more comfortable, and more energy-efficient living environment.
Space planning: Allocating appropriate square footage to each room based on its intended use and occupants.
Space planning is a crucial aspect of house floor plan design as it determines the size and proportions of each room, ensuring that they meet the functional needs and lifestyle of the occupants. By carefully allocating appropriate square footage to each room, architects and homeowners can create a home that is both comfortable and efficient.
- Room size and function: The size of a room should be commensurate with its intended use and the number of occupants. For example, a master bedroom typically requires more space than a guest bedroom, and a family room should be large enough to accommodate seating for multiple people.
- Furniture layout: Consider the furniture that will be used in each room and ensure that there is adequate space for movement and circulation. Avoid overcrowding rooms with too much furniture or bulky pieces.
- Storage needs: Determine the storage requirements for each room and incorporate adequate storage solutions, such as closets, cabinets, and shelves. This helps to keep the home organized and clutter-free.
- Future needs: Consider potential future needs and design the floor plan with flexibility in mind. For example, a room that can be easily converted into an additional bedroom or home office can be a valuable asset.
By carefully considering these factors, architects and homeowners can create floor plans that optimize space utilization, ensuring that each room is functional, comfortable, and meets the specific needs of the occupants.
Storage solutions: Incorporating adequate storage options to keep the home organized and clutter-free.
Adequate storage solutions are essential for maintaining a well-organized and clutter-free home. By incorporating thoughtful storage options into the house floor plan, architects and homeowners can create spaces that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
- Closets: Closets are a fundamental storage solution for bedrooms, providing space for clothes, shoes, and other personal belongings. Walk-in closets offer ample storage capacity and can be customized with shelves, drawers, and hanging rods to maximize space utilization.
- Cabinets: Cabinets are versatile storage solutions that can be used in various rooms throughout the home. Kitchen cabinets provide storage for cookware, dishes, and food supplies, while bathroom cabinets can store toiletries, linens, and cleaning supplies. Built-in cabinets can be incorporated into walls or under stairs, providing additional storage space without sacrificing floor area.
- Shelving: Shelves are a flexible and efficient way to store books, display collectibles, or organize items in any room. Open shelves provide easy access to frequently used items, while closed shelves with doors can conceal clutter and maintain a more polished look.
- Multi-purpose furniture: Multi-purpose furniture pieces, such as ottomans with built-in storage or beds with drawers, offer dual functionality while saving space. These pieces can be used to store blankets, pillows, toys, or other items that need to be kept out of sight but within easy reach.
By carefully considering the storage needs of the occupants and incorporating a variety of storage solutions into the floor plan, architects and homeowners can create homes that are both organized and inviting.
Structural integrity: Ensuring the floor plan adheres to building codes and structural requirements.
Structural integrity is paramount in house floor plan design as it ensures the safety and stability of the building. By adhering to building codes and structural requirements, architects and engineers can create floor plans that meet the necessary safety standards and withstand the forces that act upon the structure.
Building codes are established regulations that govern the design and construction of buildings to ensure public safety and well-being. These codes specify minimum requirements for structural elements, such as the foundation, walls, roof, and framing, to withstand various loads and forces, including gravity, wind, and seismic activity. By complying with building codes, architects and engineers can ensure that the floor plan meets the required safety standards and is suitable for the intended location and use.
In addition to building codes, structural requirements are also essential considerations in floor plan design. These requirements are based on engineering principles and calculations that determine the necessary strength and stability of the structure. Factors such as the size and shape of the building, the materials used, and the anticipated loads and forces acting on the structure are carefully analyzed to determine the appropriate structural system and member sizes.
By carefully considering structural integrity in house floor plan design, architects and engineers can create safe and durable homes that can withstand the test of time and provide peace of mind to the occupants. This involves a thorough understanding of building codes, structural engineering principles, and the proper selection and integration of structural elements into the floor plan.
Accessibility: Considering the needs of individuals with disabilities and designing for universal accessibility.
Accessibility in house floor plan design involves creating spaces that are inclusive and usable for individuals with disabilities, ensuring that they can navigate and enjoy the home safely and independently. Universal accessibility aims to remove barriers and provide equal access to all, regardless of their abilities or limitations.
To achieve accessibility in floor plan design, several key considerations must be addressed:
- Wide doorways and hallways: Wider doorways and hallways allow for easy movement of wheelchairs and other mobility aids. Standard doorways should be at least 32 inches wide, while hallways should be at least 36 inches wide to accommodate turns and passing.
- Accessible bathrooms: Accessible bathrooms include features such as roll-in showers with grab bars, raised toilets with grab bars, and accessible sinks with knee clearance. These features enable individuals with mobility impairments to use the bathroom safely and independently.
- Ramps and elevators: Ramps provide an accessible means of navigating changes in level, while elevators connect different floors of a home. Ramps should have a gentle slope and non-slip surfaces, and elevators should be large enough to accommodate wheelchairs.
- Visual and auditory cues: Visual cues, such as contrasting colors and textures, can assist individuals with visual impairments in navigating the home. Auditory cues, such as audible signals for doorbells and alarms, can assist individuals with hearing impairments.
By incorporating these accessibility features into house floor plan design, architects and homeowners can create homes that are welcoming and inclusive for all, empowering individuals with disabilities to live independently and with dignity.
Aesthetic appeal: Creating a floor plan that reflects the desired architectural style and personal preferences.
The aesthetic appeal of a house floor plan plays a significant role in creating a home that is both visually pleasing and reflective of the occupants’ tastes and lifestyle. By considering the desired architectural style and personal preferences in the design process, architects and homeowners can craft floor plans that are both functional and aesthetically captivating.
- Architectural style: The architectural style of a home influences the overall look and feel of the floor plan. From traditional styles like Victorian and Colonial to modern styles like Contemporary and Minimalist, the choice of architectural style sets the tone for the home’s aesthetic. Factors such as rooflines, window shapes, and exterior finishes should be considered to create a cohesive design.
- Interior design preferences: Personal preferences play a significant role in shaping the aesthetic appeal of a floor plan. The arrangement of rooms, the selection of finishes, and the choice of fixtures and furnishings all contribute to the overall ambiance of the home. Architects and homeowners should consider the occupants’ lifestyle, color preferences, and desired level of formality to create a floor plan that aligns with their personal tastes.
- Flow and symmetry: The flow and symmetry of a floor plan can greatly enhance its aesthetic appeal. Smooth transitions between rooms, well-proportioned spaces, and a sense of balance can create a harmonious and inviting living environment. Architects often use design principles such as the golden ratio and the rule of thirds to achieve visual harmony in floor plans.
- Natural elements: Incorporating natural elements into the floor plan can add warmth and organic beauty to the home. Large windows that frame scenic views, skylights that bring in natural light, and outdoor living spaces that seamlessly connect with the interior can create a stronger connection to the surrounding environment and enhance the overall aesthetic appeal.
By carefully considering these factors, architects and homeowners can design floor plans that not only meet functional requirements but also create visually stunning and emotionally resonant living spaces.
Energy efficiency: Incorporating energy-saving features such as passive solar design and efficient window placement.
Incorporating energy-saving features into house floor plan design is crucial for creating sustainable and environmentally friendly homes. By implementing strategies such as passive solar design and efficient window placement, architects and homeowners can reduce energy consumption, lower utility bills, and minimize the home’s carbon footprint.
- Passive solar design: Passive solar design utilizes the sun’s natural energy to heat and cool a home, reducing the reliance on artificial heating and cooling systems. Floor plans that incorporate passive solar design typically feature large south-facing windows that allow sunlight to penetrate deep into the home during the winter months, absorbing heat. Thermal mass, such as concrete or brick, can be used to store this heat and release it gradually throughout the night, maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature. In the summer months, overhangs and strategically placed trees can shade windows and reduce heat gain.
- Efficient window placement: The placement and size of windows have a significant impact on a home’s energy efficiency. Windows should be placed to maximize natural daylighting and minimize heat loss. South-facing windows allow for maximum solar heat gain in the winter, while north-facing windows provide natural light without excessive heat gain. Double- or triple-glazed windows with low-e coatings can help reduce heat loss and improve insulation. Proper window shading, such as curtains or blinds, can further control heat gain and loss.
- Building orientation: The orientation of the house on the building site can greatly influence its energy efficiency. In the Northern Hemisphere, homes that are oriented with their long axis facing south receive the most sunlight. This orientation allows for optimal passive solar heating and daylighting. In the Southern Hemisphere, the reverse is true, with homes oriented with their long axis facing north.
- Thermal insulation: Adequate insulation in walls, ceilings, and floors is essential for reducing heat loss and improving energy efficiency. Insulation materials such as fiberglass, cellulose, or spray foam can help trap heat inside the home during the winter and prevent heat from entering during the summer. Proper insulation can significantly reduce the load on heating and cooling systems, leading to lower energy consumption.
By carefully considering these energy-saving features in house floor plan design, architects and homeowners can create homes that are not only comfortable and functional but also environmentally responsible and cost-effective to operate.
Future expansion: Planning for potential future additions or renovations to the home.
When designing a house floor plan, it is wise to consider potential future additions or renovations. This foresight can save significant time, effort, and expense in the long run. By incorporating flexibility and adaptability into the initial design, homeowners can ensure that their home can grow and evolve to meet their changing needs.
One key aspect of planning for future expansion is to create a flexible structural system. This means using materials and construction methods that can easily accommodate additions or alterations. For example, steel framing or modular construction techniques can provide greater flexibility than traditional wood framing. Additionally, designing the floor plan with a clear hierarchy of spaces can make it easier to add or remove rooms in the future.
Another important consideration is to provide adequate space for future expansion. This may involve leaving extra land around the house for potential additions, or designing the floor plan with unused or unfinished spaces that can be converted into additional rooms later on. For example, an unfinished basement or attic can provide valuable space for future expansion.
Finally, it is important to think about the potential impact of future additions or renovations on the home’s overall aesthetics and functionality. By considering the architectural style, exterior materials, and interior finishes, homeowners can ensure that any future additions or renovations will seamlessly blend with the existing structure. This will help to maintain the home’s overall value and curb appeal.
By carefully considering future expansion in house floor plan design, homeowners can create homes that are adaptable, flexible, and ready to grow with their changing needs. This foresight can save significant time, effort, and expense in the long run, and ensure that the home remains a comfortable and enjoyable living space for years to come.









Related Posts