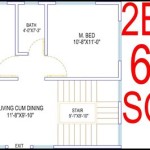
750 Square Foot House Plans: Maximize Space, Minimize Cost
The allure of homeownership is often tempered by the financial realities of the housing market. As property values continue to rise, particularly in urban areas, the prospect of purchasing a large, conventionally sized home becomes increasingly unattainable for many. This has led to a surge in interest for smaller, more affordable living spaces, with 750 square foot house plans emerging as a viable option. These plans are not merely about downsizing; they represent a strategic approach to efficient design, cost-effectiveness, and sustainable living.
A 750 square foot house, while compact, can provide a comfortable and functional living environment when meticulously planned. The focus shifts from maximizing square footage to optimizing the use of every inch of available space. This necessitates careful consideration of layout, storage solutions, and multi-functional furniture. Furthermore, it demands a mindful approach to construction materials and design features that minimize costs without compromising quality or aesthetic appeal.
The appeal of 750 square foot house plans extends beyond affordability. They also offer significant advantages in terms of reduced maintenance, lower energy consumption, and a diminished environmental footprint. A smaller home requires less cleaning, less heating and cooling, and utilizes fewer resources in its construction and operation. This makes it an attractive option for environmentally conscious individuals and those seeking a simpler, more minimalist lifestyle.
Designing a successful 750 square foot house requires a comprehensive understanding of spatial planning, material selection, and construction techniques. It is essential to consider the specific needs and preferences of the occupants, as well as the local building codes and environmental conditions. The following key points outline the critical aspects of maximizing space and minimizing costs in the design and construction of a small home.
Strategic Space Planning and Layout
The layout is paramount in a small home. Open floor plans are frequently employed to create a sense of spaciousness and improve natural light flow. Combining living, dining, and kitchen areas into a single, contiguous space eliminates the need for walls and hallways, which consume valuable square footage. Strategic zoning can then define these areas through the use of furniture placement, rugs, and subtle changes in flooring or ceiling height.
Vertical space should be fully exploited. High ceilings can create a more airy and open feel, and allow for the installation of loft areas for sleeping or storage. Building upwards, rather than outwards, can be a cost-effective way to increase usable space without expanding the foundation footprint.
Consider the movement of people within the space. Minimize hallways and traffic paths to prevent congestion and wasted space. Design the layout in a way that allows for easy flow and access to all areas of the home. The placement of doors and windows should be carefully considered to optimize natural light and ventilation, while also maintaining privacy.
Multi-functional spaces are crucial. A guest bedroom can double as a home office, or a dining table can serve as a work surface. Furniture should be carefully selected to serve multiple purposes. For example, a sofa bed can provide additional sleeping space, and a coffee table with built-in storage can offer a place to stow away items.
Built-in storage is another essential element. Custom-designed shelving units, cabinets, and drawers can maximize storage capacity while seamlessly integrating into the overall design. Consider incorporating storage into unexpected places, such as under stairs, along hallways, or behind furniture.
Cost-Effective Material Selection and Construction Techniques
Choosing the right materials is critical to minimizing construction costs. Opting for readily available, locally sourced materials can significantly reduce transportation expenses and lead times. Standardized sizes and dimensions can also streamline the construction process and minimize waste.
Consider alternative building materials that offer cost savings without sacrificing structural integrity or aesthetic appeal. For example, concrete floors can be a durable and affordable option, and can be stained or polished to create a visually appealing surface. Reclaimed wood or recycled materials can add character and reduce environmental impact.
Simple, straightforward designs are more cost-effective to build. Avoid complex roof lines, intricate detailing, and custom features that can increase labor costs and material expenses. A rectangular or square floor plan is generally the most efficient and economical option.
Prefabricated or modular construction can offer significant cost savings and faster construction times. These methods involve assembling pre-built components off-site and then transporting them to the building location for final assembly. This can reduce on-site labor costs and minimize waste.
Energy-efficient construction techniques can also lead to long-term cost savings. Proper insulation, energy-efficient windows and doors, and efficient heating and cooling systems can significantly reduce energy consumption and lower utility bills. Consider incorporating passive solar design principles to maximize natural heating and cooling.
Utilizing Light and Visual Tricks to Enhance Space
Natural light is a powerful tool for making a small space feel larger and more inviting. Maximize the use of windows and skylights to bring in as much daylight as possible. Consider the placement of windows to capture natural light throughout the day.
Strategic use of mirrors can create the illusion of more space. A large mirror on a wall can reflect light and make a room feel significantly larger. Placing mirrors opposite windows can amplify the effect of natural light.
Light paint colors can make a room feel brighter and more spacious. Avoid dark or heavy colors, which can make a small space feel closed in. Neutral tones, such as white, beige, and gray, are good choices.
Minimalist décor can help to create a sense of calm and order, which can make a small space feel more spacious. Avoid clutter and unnecessary items. Choose furniture and accessories that are functional and visually appealing.
Vertical lines can draw the eye upwards and create the illusion of height. Use vertical stripes on walls, tall bookshelves, or floor-to-ceiling curtains to create this effect. The use of continuous flooring throughout the space also eliminates visual breaks and creates a sense of continuity.
Incorporating these key principles into the design and construction process can transform a 750 square foot house plan into a comfortable, functional, and affordable living space. By prioritizing strategic space planning, cost-effective materials, and clever visual tricks, it is possible to create a home that feels both spacious and inviting, without breaking the bank.

750 Sq Ft House Plans Can Be Affordable Craft

750 Sq Ft House Plans Can Be Affordable Craft

750 Sq Ft House Plans Can Be Affordable Craft

750 Sq Ft House Plans Can Be Affordable Craft

2 Bedroom Guest House Plans 750 Sq Ft Square Design

2 Bedroom Guest House Plans 750 Sq Ft Square Design

Farmhouse Style House Plan 1 Beds Baths 750 Sq Ft 56 552 Houseplans Com

Modern Style House Plan 1 Beds Baths 750 Sq Ft 932 343 Houseplans Com

Farmhouse Style House Plan 1 Beds Baths 750 Sq Ft 56 552 Houseplans Com

Cottage Style House Plan 2 Beds 1 5 Baths 750 Sq Ft 915 13 Houseplans Com
Related Posts